2. How to create a BT - fkie/fkie_behavior_trees GitHub Wiki
A tree is the formal representation of how the tasks are going to be executed. This page describes how to create a tree file using XML format.
Note: This library is based on BehaviorTree.CPP, and some concepts presented here are deeply explained in its documentation behaviortree.dev.
BTs are modeled using standard XML files, a simple example is presented as follows:
<root main_tree_to_execute = "MainTree" >
<BehaviorTree ID="MainTree">
<Sequence name="root_sequence">
<SaySomething name="action_hello_1" message="Hello"/>
<SaySomething name="action_hello_2" message="Hello Again!"/>
</Sequence>
</BehaviorTree>
</root>As we can notice, there is a root tag containing the property main_tree_to_execute, which defines the entry point of the tree, in this case MainTree.
The BehaviorTree tag creates a new tree, that might contain both control and execution nodes.
Inside, two actions, action_hello_1 and action_hello_2 from type SaySomething, are defined with their specific message property.
Finally, a control node root_sequence of type Sequence is created for executing actions action_hello_1 and action_hello_2 sequentially.
Note that, it is also possible to create several sub-trees using tag BehaviorTree, and join them using tag Subtrees.
More information about XML format in behavior trees: BT XML format
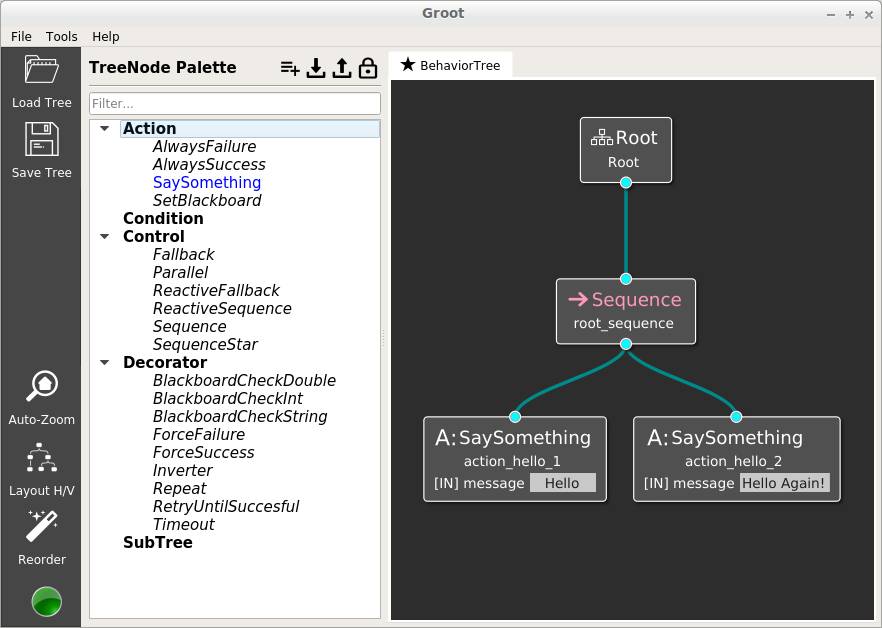
Even if XML-format is human-readable, sometimes the tree is just too complex. In this case, a graphical visualization might be required.
Groot is a nice tool for visualization and monitoring of Behavior Trees.
It uses ZeroMQ protocol to receive information about the tree structure and the current execution state. The previous example can be visualized in Groot:
Groot is not yet available as Ubuntu 18.04 package, and thus, manual compilation is required.