Phishing - firelily20/WRT231 GitHub Wiki
What is phishing?
According to phishing.org, “Phishing is a cybercrime in which a target or targets are contacted by email, telephone or text message by someone posing as a legitimate institution to lure individuals into providing sensitive data such as personally identifiable information, banking and credit card details, and passwords. The information is then used to access important accounts and can result in identity theft and financial loss.”
How to identify phishing.
Phishing often comes in the form of emails, text messages, and even phone calls. The messages are often structured to look like they are from a company or agency. These emails or texts could be faked to look like they are from a social media site, a credit card company, a bank, an online store, a government agency, and many more.
The email or text message will often contain some information to trick you into thinking it’s real. This could be something like a suspicious login attempt, a payment information issue, a fake invoice, and many more. Oftentimes these scammers want you to click on a link to login, or input some personal information that they can use for their benefit. These scammers are often out to get your login credentials, banking or credit card information, or social security number.
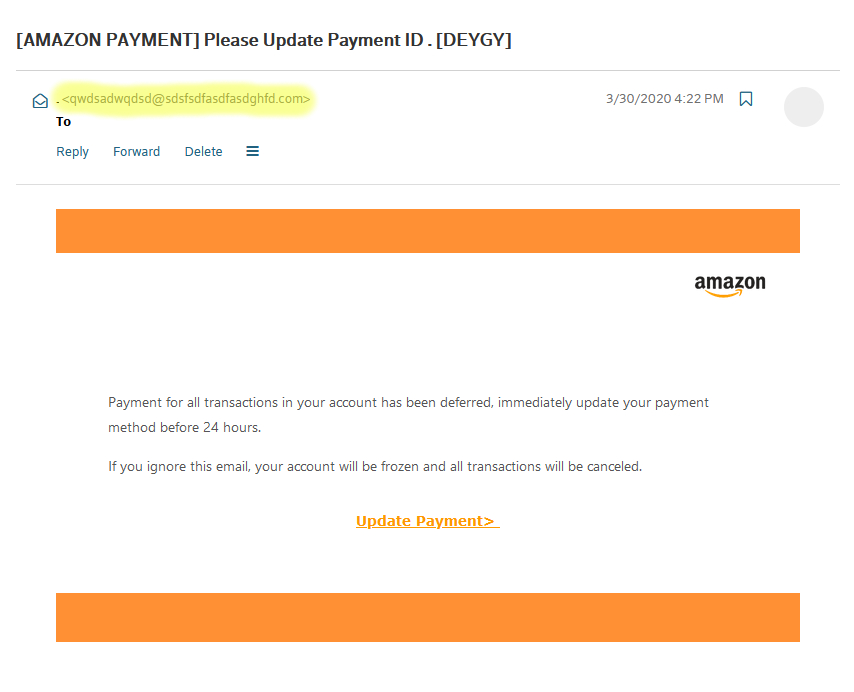
Below is an example of a real phishing email sent to a victim.
How do I identify this as a phishing email?
In this particular phishing attack, the scammer is posing as amazon.com. They are telling the victim that they need to update their payment information immediately. It is also not uncommon that these emails contain a sense of urgency. This email says the payment method needs to be updated in the next 24 hours or the account will be frozen. This is done to get the person to quickly react without thinking about the legitimacy of the email.
If you have never used Amazon, or don’t have an account under the email then it is very likely that this is a phishing email. The email that received these attacks has never been registered by myself to amazon.com yet I still get them. More things to look at are grammar, a generic greeting, or illegitimate looking links. A dead giveaway here is the sender email, which has been highlighted in the screenshot. An email from amazon.com would have a sender address ending in @amazon.com. This phishing email certainly isn’t using an actual amazon.com email address. Also, the email is very short and vague, which doesn’t mean it's a phishing email but is something to keep in mind.
Here is another example of a real phishing email
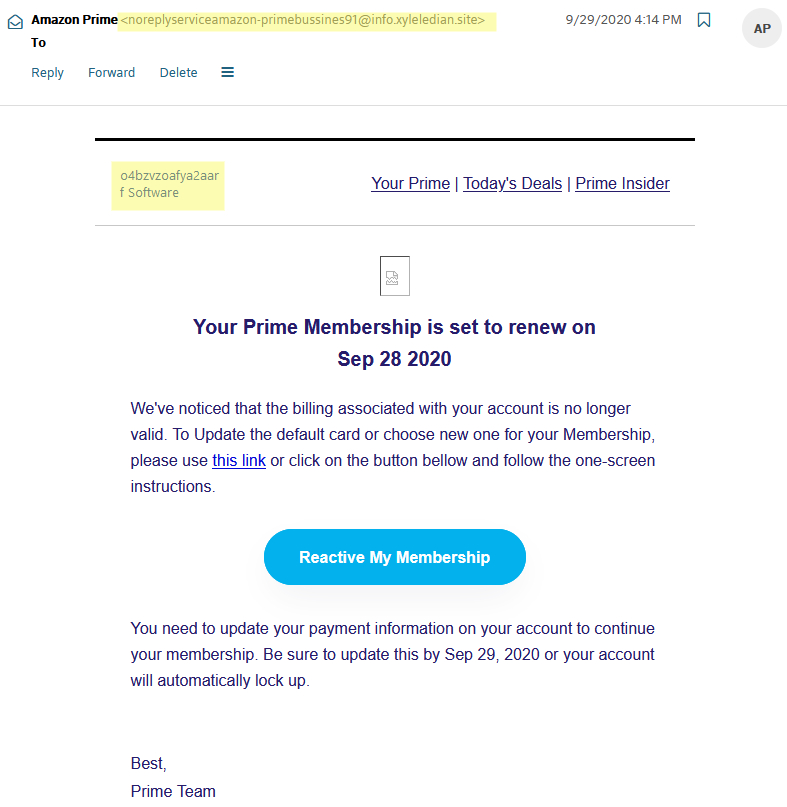
Phishing emails don't always look the same. Some are more real-looking than others. The second screenshot here is a much more legitimate-looking phishing email than the first but is still not real. In this screenshot, the sender's name is set as "Amazon Prime" which makes it seem more real but upon looking at the sender's email it doesn't end in @amazon.com. Another giveaway here is the highlighted text in the top left where it says "o4bzvzoafya2aarf Software". Something like this would never be found in an actual email from Amazon. Again just like the last one they are looking to take the victim's payment information and are using a date to make it seem urgent.
Looking for clues like the ones listed above can often give away a phishing email. If you do come across an email that seems legit and contains almost no red flags but you are still unsure about, then contacting the sending company is never a bad idea. For example, if you received an email from "amazon" about a billing problem and the email looks real but you are uncomfortable clicking any links, then contacting Amazon directly is a good idea. By contacting customer support you can verify if the issue in the email is in fact real or fake ensuring that your information is not stolen.
What can I do to stop it from affecting me?
First, think before you click. Think about if you have an account or any interaction with the sender of the email. If not, then the email is likely not real. Another thing you can do to avoid phishing emails is to install anti-phishing browser extensions. These are very useful, easy to install, and free. Some popular ones include Phishdetector, Netcraft, Cloudphish, and kryptonite. These extensions check the sites you are on against known phishing sites to keep you safe. Another good habit is keeping your web browser up to date. Out of date browsers could have dangerous vulnerabilities that could be exploited. Updating your browser is a quick and simple task that can help you stay safe on the internet. Finally, don't give out your personal information on any untrustworthy websites. The best way to keep yourself safe is by using trustworthy websites and keeping personal information off of illegitimate sites. To learn more, check out some of the sources below.
Sources
www.phishing.org
www.phishprotection.com
www.consumer.ftc.gov/articles/how-recognize-and-avoid-phishing-scams
Author
- Brian Anderson