深入理解WindowInsets - finalxiaoxiao/study GitHub Wiki
在WMS学习过程中,我们会发现窗口的布局、控件树的布局、config的更新诸多流程都会遇到WindowInset的逻辑处理, 因此学习WindowInsets是每个系统工程师在窗口管理模块成长中的的必经之路。
本文将基于Android T版本,从WindowInsets的更新、派发、控制等角度,对WindowInsets一探究竟。
Insets描述的是对Rect的变更,它将会从四周对矩形区域进行裁剪,用于Rect的边缘偏移。
因此WindowInsets描述的是特定不可修改的区域对应用布局frame的裁剪,开发者应该拿到这些信息进行布局调整。
举个例子,如果状态栏的frame为[0,0][1080,96],屏幕的frame为[0,0][1080,2412],那么状态栏Insets就为Insets{left=0, top=96, right=0, bottom=0}。
| 方法签名 | 方法简介 |
|---|---|
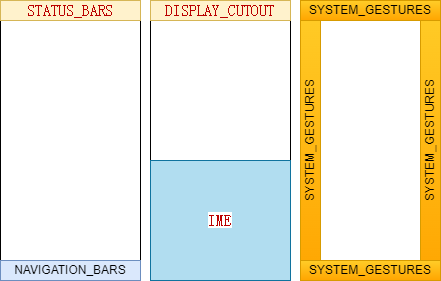
public static @InsetsType int statusBars() |
状态栏类型 |
public static @InsetsType int navigationBars() |
导航栏类型 |
public static @InsetsType int captionBar() |
标题栏类型 |
public static @InsetsType int ime() |
输入法类型 |
public static @InsetsType int systemGestures() |
系统手势类型 |
public static @InsetsType int mandatorySystemGestures() |
系统强制手势类型 |
public static @InsetsType int tappableElement() |
系统可点击类型 |
public static @InsetsType int displayCutout() |
挖孔区类型 |
public static @InsetsType int systemBars() |
系统栏类型(系统Bar类型,包括状态栏、导航栏、标题栏) |
| 方法签名 | 方法简介 |
|---|---|
public Insets getInsets(@InsetsType int typeMask) |
获取指定Insetstype集合的Insets。 例如我们可以传入WindowInsets#Type#systemBars() 获取状态栏、导航栏、标题栏合并所占Insets。 |
public Insets getInsetsIgnoringVisibility(@InsetsType int typeMask) |
获取指定Insetstype集合的Insets(忽视可见性)。 如果状态栏和导航栏隐藏时,getInsetsIgnoringVisibility依然可以获取它们的frame大小,而getInsets获取的是0。 |
public boolean isVisible(@InsetsType int typeMask) |
获取insets可见性。 只有所有的类型都可见时,才返回true |
public DisplayCutout getDisplayCutout() |
获取挖孔区信息。 |
public RoundedCorner getRoundedCorner(@RoundedCorner.Position int position) |
获取圆角信息 |
public @Nullable Rect getPrivacyIndicatorBounds() |
获取隐私指示器区域 |
Insets区域可能会影响应用的布局,例如我们不能让交互的控件和导航栏区域发生重叠。框架提供了主动获取Insets和监听Insets的接口, 下面将介绍一下如何正确使用这些API。
| 方法签名 | 方法简介 |
|---|---|
public WindowInsets getRootWindowInsets() |
获取窗口的WindowInsets,这个insets是未经派发消费的。 需要在View attach到窗口之后才能获取,否则会返回null值。因此建议在Activity或者View的onAttachedToWindow中获取WindowInsets。 |
public void setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(OnApplyWindowInsetsListener listener) |
监听WindowInsets的派发。 我们可以通过这个方法实时获取该View最新的insets并调整布局。在控件树重新大刷新、WindowInsets发生变更时, 框架会计算新的WindowInsets并将其派发至整个控件树。 如果主动设置了监听,View自身的派发逻辑onApplyWindowInsets将会被代替。 |
public @NonNull WindowInsets onApplyWindowInsets(@NonNull View view,@NonNull WindowInsets insets) |
处理Insets的派发。 参数view代表当前派发的控件,参数insets是派给view的WindowInsets。 返回值决定了是否中断派发。返回WindowInsets#CONSUMED,代表中断自身和自身子树的派发。 |
安卓P开始谷歌开始 支持刘海屏,前置摄像头会影响应用布局。
框架侧提供了API让开发者可以获取当前设备的DisplayCutout——挖孔区信息,以及设置layoutInDisplayCutoutMode——挖孔区布局模式
| 方法签名 | 方法简介 |
|---|---|
public @NonNull Insets getWaterfallInsets() |
获取瀑布屏的曲面Insets大小。 |
|
public int getSafeInsetTop() public int getSafeInsetBottom() public int getSafeInsetLeft() public int getSafeInsetRight() |
获取DisplayCutout的Insets的top/bottom/left/right值。 |
|
public List<Rect> getBoundingRects() public @NonNull Rect getBoundingRectLeft() public @NonNull Rect getBoundingRectTop() public @NonNull Rect getBoundingRectRight() public @NonNull Rect getBoundingRectBottom() |
获取DisplayCutout的frame集合(Top/Bottom/Left/Right frame)。 |
public @Nullable Path getCutoutPath() |
获取挖孔区的路径。 |
| Filed | Filed简介 |
|---|---|
public int layoutInDisplayCutoutMode = LAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_DEFAULT; |
是否布局在挖孔区。 该值会影响窗口的frame。 |
public static final int LAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_DEFAULT = 0; |
默认挖孔区布局模式。 窗口进入全屏时,框架直接裁剪窗口的frame。 |
public static final int LAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_SHORT_EDGES = 1; |
扩展短边挖孔区布局模式。 当挖孔区处于短边时,frame不会被裁剪,长边依然会裁剪(谷歌要求挖孔区在短边,很少有设备具有长边挖孔区)。 |
public static final int LAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_NEVER = 2; |
从不扩展挖孔区布局模式。 在所有的情况下,frame都会被挖孔区裁剪 |
public static final int LAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYS = 3; |
始终扩展挖孔区布局模式。 在所有的情况下,frame都不会被挖孔区裁剪 |
从android S开始,谷歌引入 圆角Insets, 开发者可以通过WindowInsets获取圆角,调整自身布局,以免内容被截断。 圆角信息是硬件决定的,但也会受到系统其它Insets及Task的影响。
| 方法签名(Filed) | 方法(Filed)简介 |
|---|---|
|
public static final int POSITION_TOP_LEFT = 0; public static final int POSITION_TOP_RIGHT = 1; public static final int POSITION_BOTTOM_RIGHT = 2; public static final int POSITION_BOTTOM_LEFT = 3; |
圆角的四个位置: 左上,右上,右下,左下。 |
public @Position getPosition() |
获取圆角位置 |
public Point getCenter() |
获取圆角圆心。 |
有一部分Insets是具有可见性的,如状态栏、导航栏、输入法。
| 方法签名(Filed) | 方法(Filed)简介 |
|---|---|
void show(@InsetsType int types) |
显示WindowInsets。 types是类型集合,目前可以操控的Insets类型——状态栏、导航栏、输入法。 |
void hide(@InsetsType int types) |
隐藏WindowInsets。 其余同上。 |
WindowInsetsController的appearance是指状态栏和导航栏的显示模式。其中透明样式由框架侧来控制,应用侧负责控制状态栏字体颜色和背景色。
| 方法签名(Filed) | 方法(Filed)简介 |
|---|---|
|
@hide int APPEARANCE_OPAQUE_STATUS_BARS = 1; |
状态栏不透明。 框架侧控制,如分屏场景会带有这个flag。 |
|
@hide int APPEARANCE_OPAQUE_NAVIGATION_BARS = 1 << 1; |
导航栏不透明。 其余同上。 |
|
@hide int APPEARANCE_LOW_PROFILE_BARS = 1 << 2; |
低调模式。 状态栏和导航栏会加载更少的图标,变暗,谷歌建议应用直接使用hide来达到沉浸状态。 |
int APPEARANCE_LIGHT_STATUS_BARS = 1 << 3; |
亮色状态栏(状态栏反色)。 正常情况下,状态栏和导航栏是黑底白字,在背景色亮色的情况下字体会不清晰,需要使用亮色flag将字体调整为黑色。 |
int APPEARANCE_LIGHT_NAVIGATION_BARS = 1 << 4; |
亮色导航栏(导航栏反色)。 其余同上 |
|
@hide int APPEARANCE_SEMI_TRANSPARENT_STATUS_BARS = 1 << 5; |
状态栏半透明。 框架侧控制,在letterbox场景,为了避免letterbox显示使得状态栏字体不清晰,因此改为半透。 |
|
@hide int APPEARANCE_SEMI_TRANSPARENT_NAVIGATION_BARS = 1 << 6; |
导航栏半透明。 其余同上。 |
void setSystemBarsAppearance(@Appearance int appearance, @Appearance int mask); |
设置Appearance |
@Appearance int getSystemBarsAppearance(); |
获取Appearance |
| 方法签名(Filed) | 方法(Filed)简介 |
|---|---|
int BEHAVIOR_DEFAULT = 1; |
默认行为模式 用手势唤起被隐藏的导航栏、状态栏之后,它们不会再被自动隐藏。 |
int BEHAVIOR_SHOW_TRANSIENT_BARS_BY_SWIPE = 2; |
短暂行为模式 用手势唤起被隐藏的导航栏、状态栏之后会短暂停留,之后被自动隐藏。 |
void setSystemBarsBehavior(@Behavior int behavior); |
设置系统栏行为模式 |
@Behavior int getSystemBarsBehavior(); |
获取系统栏行为模式 |
对于可控制的Insets,它们在显示与隐藏的时候,框架会为其执行动画。框架支持定制动画,并且会通知应用动画更新时的insets。
| 方法签名(Filed) | 方法(Filed)简介 |
|---|---|
|
void onControllableInsetsChanged(@NonNull WindowInsetsController controller, @InsetsType int typeMask); |
当应用可以控制的Insets类型更新,框架回调此方法。 typeMask 表示支持应用自定义动画的insets类型集合,这取决于当前应用是否能够获取insets控制权(和是否在前台、是否是焦点,是否是多窗口有关)。 |
| 方法签名(Filed) | 方法(Filed)简介 |
|---|---|
|
void addOnControllableInsetsChangedListener( @NonNull OnControllableInsetsChangedListener listener); |
添加Insets控制权变更的监听。 |
|
void addOnControllableInsetsChangedListener( @NonNull OnControllableInsetsChangedListener listener); |
移除Insets控制权变更的监听。 |
|
void controlWindowInsetsAnimation(@InsetsType int types, long durationMillis, @Nullable Interpolator interpolator, @Nullable CancellationSignal cancellationSignal, @NonNull WindowInsetsAnimationControlListener listener); |
控制自定义Insets动画。 types 是Insets类型集合。durationMillis 是动画时长,interpolator 是动画插值器。 cancellationSignal 是动画中断器,可以主动中断insets动画。 listener 是动画执行的回调。在onReady中准备动画,onFinished和onCancel中清理状态。 |
| 方法签名(Filed) | 方法(Filed)简介 |
|---|---|
|
void onReady(@NonNull WindowInsetsAnimationController controller, @InsetsType int types); |
动画ready。通常在该方法中,使用controller准备动画。 |
void onFinished(@NonNull WindowInsetsAnimationController controller); |
动画结束 |
void onCancelled(@Nullable WindowInsetsAnimationController controller); |
动画取消 |
| 方法签名(Filed) | 方法(Filed)简介 |
|---|---|
@NonNull Insets getHiddenStateInsets(); |
获取完全隐藏的Insets。通常使用这个值作为动画的初始/结束Insets |
@NonNull Insets getShownStateInsets(); |
获取完全显示的Insets。 |
@NonNull Insets getCurrentInsets(); |
获取当前的动画Insets。 |
float getCurrentFraction(); |
获取当前的动画进度 |
float getCurrentAlpha(); |
获取当前的动画alpha |
@InsetsType int getTypes(); |
获取动画的Insets类型 |
void setInsetsAndAlpha(@Nullable Insets insets, @FloatRange(from = 0f, to = 1f) float alpha, @FloatRange(from = 0f, to = 1f) float fraction); |
设置动画Insets值,该值最终会作用在动画leash上。 |
void finish(boolean shown); |
结束动画 |
default boolean isReady() |
动画是否ready |
boolean isFinished(); |
动画是否结束 |
boolean isCancelled(); |
动画是否被取消 |
findViewById(R.id.id_test_1).setOnClickListener(v -> {
WindowInsetsController insetsController = getWindow().getInsetsController();
insetsController.controlWindowInsetsAnimation(WindowInsets.Type.navigationBars(), 2000, null, null,
new WindowInsetsAnimationControlListener() {
@Override
public void onReady(@NonNull WindowInsetsAnimationController controller,
int types) {
Log.d(TAG, "onReady: ");
prepareInsetsAnimation(controller);
}
@Override
public void onFinished(@NonNull WindowInsetsAnimationController controller) {
Log.d(TAG, "onFinished: ");
}
@Override
public void onCancelled(@Nullable WindowInsetsAnimationController controller) {
Log.d(TAG, "onCancelled: ");
}
});
});
private void prepareInsetsAnimation(@NonNull WindowInsetsAnimationController controller) {
ValueAnimator mAnimator = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(0, 1f);
mAnimator.setDuration(2000);
Insets hiddenInsets = controller.getHiddenStateInsets();
Insets shownStateInsets = controller.getShownStateInsets();
boolean show = getWindow().getDecorView().getRootWindowInsets()
.isVisible(WindowInsets.Type.navigationBars());
mAnimator.addUpdateListener(animation -> {
float rawFraction = animation.getAnimatedFraction();
//计算动画insets
Interpolator linearInterpolator = new LinearInterpolator();
Insets start = show ? hiddenInsets : shownStateInsets;
Insets end = show ? shownStateInsets : hiddenInsets;
TypeEvaluator<Insets> evaluator = (fraction, startValue, endValue) -> Insets.of(
(int) (startValue.left + fraction * (endValue.left - startValue.left)),
(int) (startValue.top + fraction * (endValue.top - startValue.top)),
(int) (startValue.right + fraction * (endValue.right - startValue.right)),
(int) (startValue.bottom + fraction * (endValue.bottom - startValue.bottom)));
Insets applyInsets = evaluator.evaluate(linearInterpolator.getInterpolation(rawFraction),
start, end);
//计算动画alpha
float alphaFraction = show ? rawFraction : 1 - rawFraction;
float applyAlpha = linearInterpolator.getInterpolation(alphaFraction);
//apply
controller.setInsetsAndAlpha(applyInsets, applyAlpha, rawFraction);
});
mAnimator.addListener(new AnimatorListenerAdapter() {
@Override
public void onAnimationEnd(@NonNull Animator animation, boolean isReverse) {
// 结束动画
controller.finish(show);
}
});
//开始动画
mAnimator.start();
}