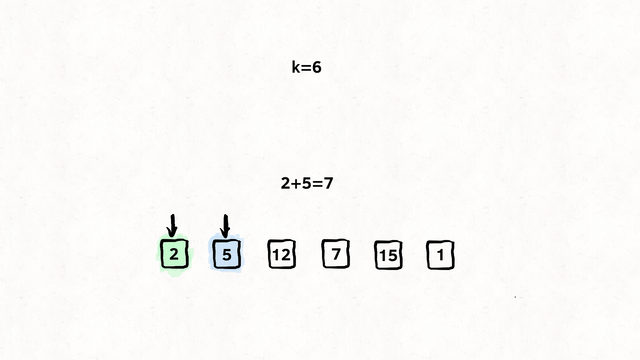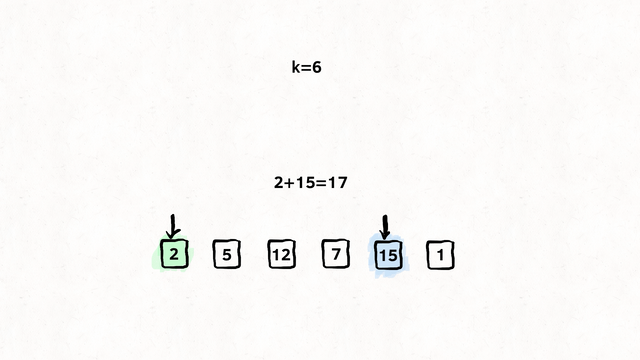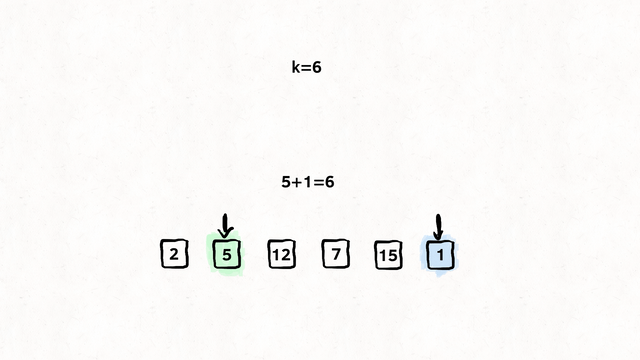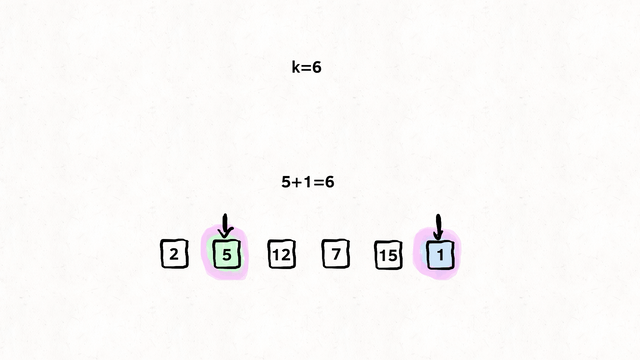Common Leetcode Techniques - dohdat/leetcode-practice GitHub Wiki

Planned Courses
- Algorithm 2
- Algorithm 3
- Graph Theory 1
- Graph Theory 2
- Graph Theory 3
- Binary Search 1
- Binary Search 2
- Binary Search 3
- Dynamic Programming 1
- Dynamic Programming 2
- Dynamic Programming 3
- Dynamic Programming 4
Given an array nums of distinct integers, return all the possible permutations. You can return the answer in any order.
Input: nums = [1,2,3]
Output: [[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]
var permute = function(nums) {
let res = [];
let cur = new Set();
function backtrack() {
if (cur.size === nums.length) {
res.push([...cur]);
return;
}
for (let n of nums) {
if (cur.has(n)) {
continue;
}
cur.add(n);
backtrack();
cur.delete(n);
}
}
backtrack();
return res;
};No Duplicates
Input: n = 4, k = 2
Output: [[1,2],[1,3],[1,4],[2,3],[2,4],[3,4]]
var combine = function(n, k) {
let res = [];
let cur = new Set();
function backtrack(index) {
if (cur.size === k) {
res.push([...cur]);
return;
}
for (let i = index; i <= n; i++) {
if (cur.has(i)) {
continue;
}
cur.add(i);
backtrack(i + 1);
cur.delete(i);
}
}
backtrack(1);
return res;
};Given a string s, find the length of the longest substring without repeating characters.
Input: s = "abcabcbb"
Output: 3
Explanation: The answer is "abc", with the length of 3.
var lengthOfLongestSubstring = function(s) {
let set = new Set();
let max = 0;
let left = 0;
for (let right = 0; right < s.length; right++) {
while (set.has(s[right])) {
set.delete(s[left++]);
}
set.add(s[right]);
max = Math.max(max, right - left + 1);
}
return max;
};Question:
Decode this string.
Input: s = "3[a]2[bc]"
Output: "aaabcbc"
const decodeString = s => {
const stack = [];
for (const char of s) {
if (char !== "]") { stack.push(char); continue; }
let cur = stack.pop();
let str = '';
while (cur !== '[') {
str = cur + str;
cur = stack.pop();
}
let num = '';
cur = stack.pop();
while (!Number.isNaN(Number(cur))) {
num = cur + num;
cur = stack.pop();
}
stack.push(cur);
stack.push(str.repeat(Number(num)));
}
return stack.join('');
};Question:
Determine valid parentheses.
Input: s = "()[]{}"
Output: true
var isValid = function(s) {
const stack = [];
const map = {
'(': ')',
'[': ']',
'{': '}'
}
for (let i = 0 ; i < s.length ; i++) {
let c = s[i];
if (map[c]) {
stack.push(map[c])
} else if (c !== stack.pop()) {
return false;
}
}
return !stack.length;
};Return the maximum amount of water a container can store.

Input: height = [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]
Output: 49
Explanation: The above vertical lines are represented by array [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]. In this case, the max area of water (blue section) the container can contain is 49.
var maxArea = function(height) {
let left = 0;
let right = height.length - 1;
let max = 0;
while (left <= right) {
let curArea = Math.min(height[left], height[right]) * (right - left);
if (height[left] <= height[right]) {
left++;
} else {
right--;
}
max = Math.max(max, curArea);
}
return max;
};Given the root of a binary tree, return the level order traversal of its nodes' values. (i.e., from left to right, level by level).

Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [[3],[9,20],[15,7]]
var levelOrder = function(root) {
if(!root) return [];
let q = [root];
let res = [];
while (q.length !== 0) {
let temp = [];
let len = q.length;
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
let c = q.shift();
temp.push(c.val);
c.left && q.push(c.left);
c.right && q.push(c.right);
}
res.push(temp);
}
return res;
};Whenever the problem asks for the shortest, minimum, nearest, quickest in a matrix/graph try BFS

Input: mat = [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]]
Output: [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]]
var updateMatrix = function(mat) {
let rows = mat.length;
let cols = mat[0].length;
let q = [];
let dir = [[1, 0], [-1, 0], [0, 1], [0, -1]];
function isValid(r, c) {
if (r < 0 || c < 0 || r >= rows || c >= cols) {
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}
for (let r = 0; r < rows; r++) {
for (let c = 0; c < cols; c++) {
if (mat[r][c] === 0) {
q.push([r, c]);
} else {
mat[r][c] = "#";
}
}
}
for (let [r, c] of q) {
for (let [dr, dc] of dir) {
let cr = r + dr;
let cd = c + dc;
if (isValid(cr, cd) && mat[cr][cd] === "#") {
mat[cr][cd] = mat[r][c] + 1;
q.push([cr, cd]);
}
}
}
return mat;
};Rotting Oranges

Input: grid = [[2,1,1],[1,1,0],[0,1,1]]
Output: 4
var orangesRotting = function(grid) {
let rows = grid.length;
let cols = grid[0].length;
let mins = 0;
let q = [];
let dir = [[1, 0], [-1, 0], [0, 1], [0, -1]];
let freshOranges = 0;
function isValid(r, c) {
if (r < 0 || c < 0 || r >= rows || c >= cols) {
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}
for (let r = 0; r < rows; r++) {
for (let c = 0; c < cols; c++) {
if (grid[r][c] === 2) {
q.push([r, c]);
} else if (grid[r][c] === 1) {
freshOranges++;
}
}
}
while (q.length && freshOranges) {
let len = q.length;
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
let [r, c] = q.shift();
for (let [dr, dc] of dir) {
let cr = r + dr;
let cd = c + dc;
if (isValid(cr, cd) && grid[cr][cd] === 1) {
grid[cr][cd] = 2;
freshOranges--;
q.push([cr, cd]);
}
}
}
mins++;
}
return freshOranges === 0 ? mins : -1;
};Left-> Root -> Right
Root-> Left -> Right
Left-> Right -> Root
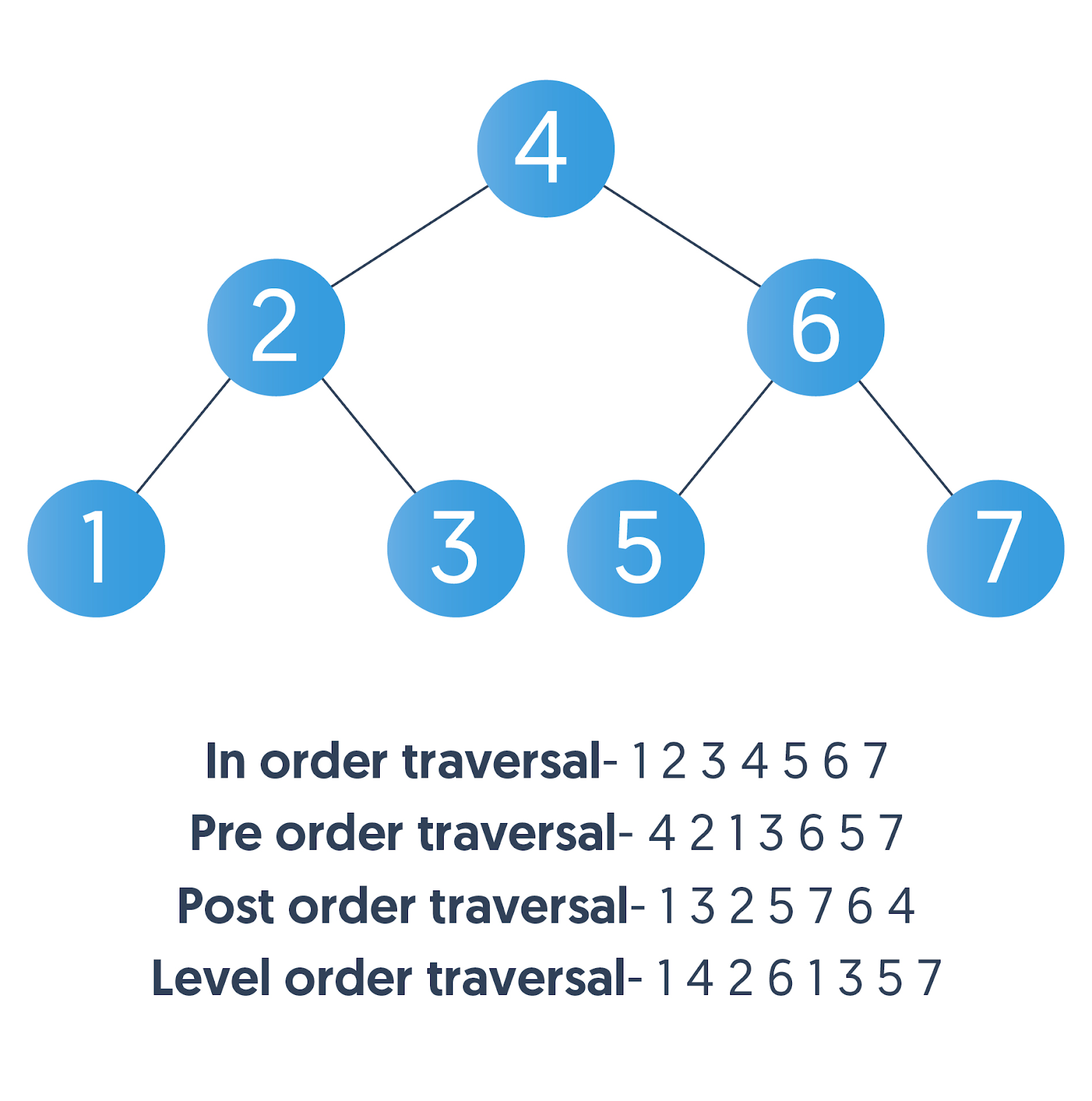
Question:
Find the total sum of all root-to-leaf numbers. A leaf node is a node with no children.

Input: root = [1,2,3]
Output: 25
Explanation:
The root-to-leaf path 1->2 represents the number 12.
The root-to-leaf path 1->3 represents the number 13.
Therefore, sum = 12 + 13 = 25.
var sumNumbers = function(root) {
let res = [];
function dfs(node, path) {
if (!node) {
return false;
}
path.push(node.val);
if (!node.left && !node.right) {
res.push(Number(path.join("")));
return true;
}
node.left && dfs(node.left, [...path]);
node.right && dfs(node.right, [...path]);
}
dfs(root, []);
let answer = res.reduce((a, b) => a + b);
return answer;
};Question
Merge 2 binary trees.

Input: root1 = [1,3,2,5], root2 = [2,1,3,null,4,null,7]
Output: [3,4,5,5,4,null,7]
var mergeTrees = function(t1, t2) {
if(!t1 && !t2) return null;
const root = new TreeNode((t1?.val || 0) + (t2?.val || 0));
root.left = mergeTrees(t1?.left, t2?.left);
root.right = mergeTrees(t1?.right, t2?.right);
return root;
};Question:

Output: 3
var numIslands = function(grid) {
let rows = grid.length;
let cols = grid[0].length;
let res = 0;
function dfs(r, c) {
if (r < 0 || c < 0 || r >= rows || c >= cols || !grid[r][c] || grid[r][c] === '0') {
return;
}
grid[r][c] = '0';
dfs(r - 1, c);
dfs(r + 1, c);
dfs(r, c - 1);
dfs(r, c + 1);
}
for (let r = 0; r < rows; r++) {
for (let c = 0; c < cols; c++) {
if (grid[r][c] === '1') {
res++;
dfs(r, c);
}
}
}
return res;
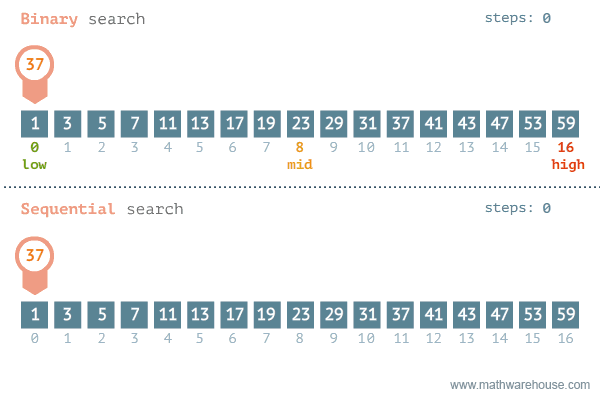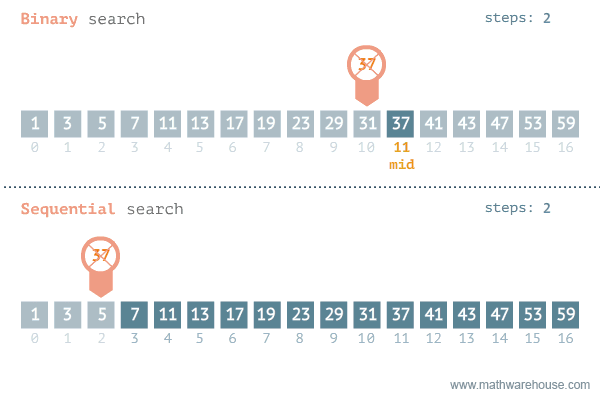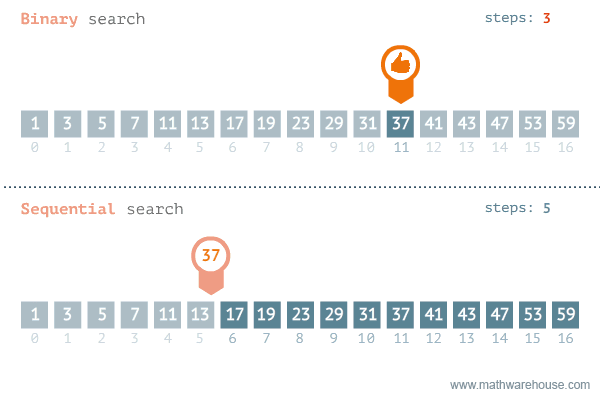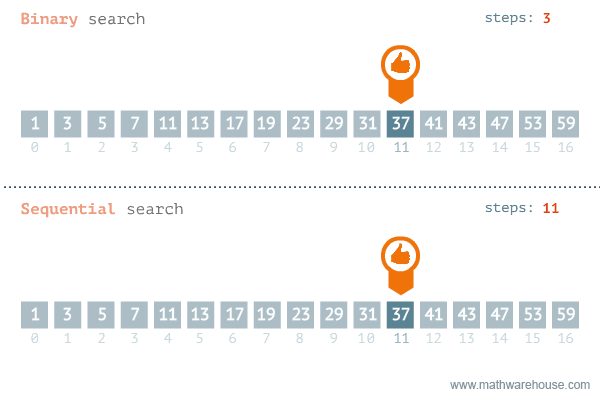
};Find if target exists in array. You must write an algorithm with O(log n) time complexity.
Input: nums = [-1,0,3,5,9,12], target = 9
Output: 4
Explanation: 9 exists in nums and its index is 4
var search = function(nums, target) {
let left = 0;
let right = nums.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
let mid = Math.floor((right + left) / 2);
if (nums[mid] === target) {
return mid;
}
if (nums[mid] > target) {
right = mid - 1;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return -1;
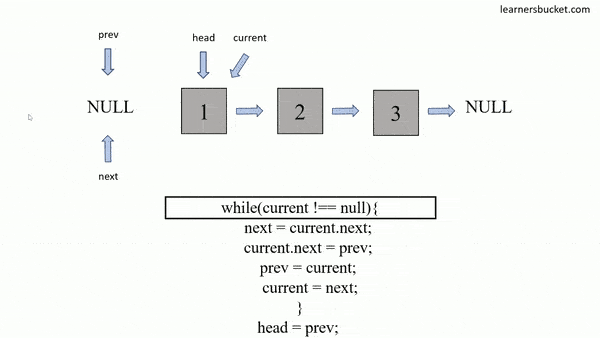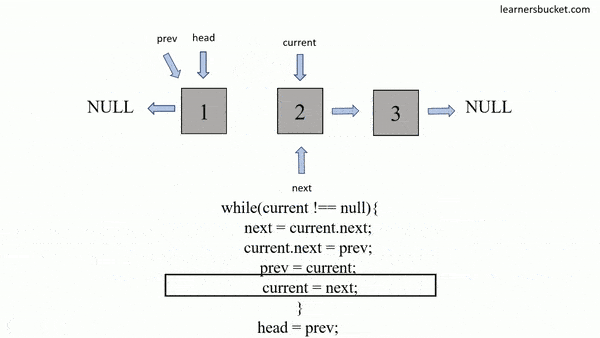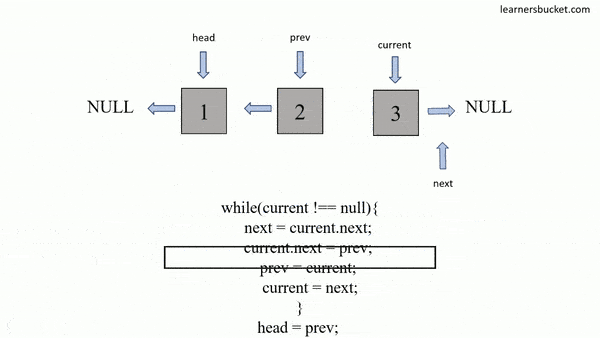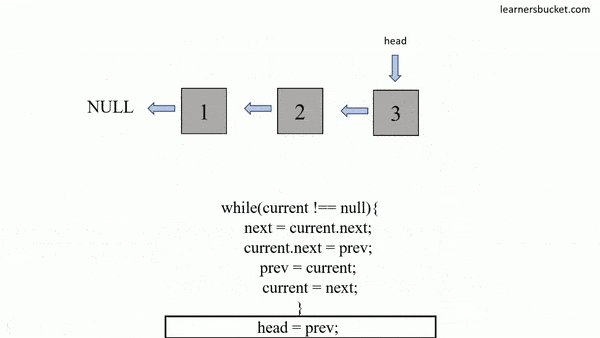
};How to traverse a linked list:
const arr = [];
let head = linkedList;
while (head !== null) {
arr.push(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
console.log(arr);
// [5, 3, 10]var hasCycle = function(head) {
let slow = head;
let fast = head;
while (fast && fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow === fast) return true;
}
return false;
};Traverse the linked list once with a temp variable to get the len of the linked list.
Traverse the head again, stop once we get to the middle.
var middleNode = function(head) {
if(head === null) return null;
let temp = head;
let len = 0;
while(temp !== null) {
len++;
temp = temp.next;
}
let mid = Math.floor(len/2);
let counter = 0;
while(head !== null) {
if(counter === mid) {
return head;
}
counter++;
head = head.next;
}
};Input: list1 = [1,2,4], list2 = [1,3,4]
Output: [1,1,2,3,4,4]
var mergeTwoLists = function(l1, l2) {
const head = new ListNode(null);
let cur = head;
while (l1 && l2) {
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
cur.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
cur.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = l1 || l2;
return head.next;
};Remove the Nth node from the end of list
Maintain two pointers and update one with a delay of n steps.

Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2
Output: [1,2,3,5]
var removeNthFromEnd = function(head, n) {
let dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
let left = dummy;
let right = head;
while(n > 0 && right) {
right = right.next;
n--;
}
while(right) {
left = left.next;
right = right.next;
}
left.next = left.next.next;
return dummy.next;
};var reverseList = function(head) {
let prev = null;
let cur = head;
while (cur) {
[cur.next, prev, cur] = [prev, cur, cur.next];
}
return prev;
};How to create a 2D array:
var minFallingPathSum = function(matrix) {
let rows = matrix.length;
let cols = matrix[0].length;
let arr = new Array(rows).fill().map(() => Array(cols));
};Get the index in a for let loop:
for (let [i,w] of words.entries()) {
}Find Intersection of Two Arrays
Input: nums1 = [4,9,5], nums2 = [9,4,9,8,4]
Output: [9,4]
Explanation: [4,9] is also accepted.
const set_intersection = (set1, set2) => {
let output = [];
const arr = Array.from(set1)
for (let s of arr)
if (set2.has(s)) {
output.push(s);
}
return output;
}
var intersection = function(nums1, nums2) {
let set1 = new Set(nums1);
let set2 = new Set(nums2);
if (set1.size < set2.size) {
return set_intersection(set1, set2);
}
else {
return set_intersection(set2, set1);
}
};The pop() method removes the last element from an array:
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
fruits.pop();
fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple"]const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
let fruit = fruits.pop();
fruit = "Mango"The push() method adds a new element to an array (at the end):
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
fruits.push("Kiwi");
fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango", "Kiwi"];The shift() method removes the first array element and "shifts" all other elements to a lower index.
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
fruits.shift();
fruits = ["Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];The unshift() method adds a new element to an array (at the beginning), and "unshifts" older elements:
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
fruits.unshift("Lemon");
fruits = ["Lemon","Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];The concat() method creates a new array by merging (concatenating) existing arrays:
const myGirls = ["Cecilie", "Lone"];
const myBoys = ["Emil", "Tobias", "Linus"];
const myChildren = myGirls.concat(myBoys);
myChildren = Cecilie,Lone,Emil,Tobias,LinusThe splice() method adds new items to an array.
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
fruits.splice(2, 0, "Lemon", "Kiwi");
fruits = Banana, Orange, Lemon, Kiwi, Apple, Mango
//The first parameter (2) defines the position where new elements should be added (spliced in).
//The second parameter (0) defines how many elements should be removed.
//The rest of the parameters ("Lemon" , "Kiwi") define the new elements to be added.The slice() method slices out a piece of an array.
const fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Lemon", "Apple", "Mango"];
const citrus = fruits.slice(1);
//This example slices out a part of an array starting from array element 1 ("Orange")
fruits = Orange, Lemon, Apple, MangoCreate an array from 0 to N
[...Array(10).keys()]How to remove an element from the array
for (let i = 0; i <= nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] === 0) {
nums.splice(i, 1);
}
}How to calculate the sum of an array
let total = nums.reduce((a, b) => a + b, 0);How to swap between 2 elements in the array:
Input: nums = [0,1,0,3,12]
Output: [1,3,12,0,0]
let index = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] !== 0) {
[nums[index], nums[i]] = [nums[i], nums[index]];
index++;
}
}indexOf but skip duplicates element:
indexOf(searchElement, fromIndex)
nums.indexOf(target, i + 1)
Check if a char is not a number
for (let c of s) {
if (isNaN(c)) {
console.log("Not a number");
}
}slice() extracts a part of a string and returns the extracted part in a new string.
The method takes 2 parameters: start position, and end position (end not included).
let text = "Apple, Banana, Kiwi";
let part = text.slice(7, 13);
return Bananalet text = "Apple, Banana, Kiwi";
let part = text.slice(7);
return Banana, KiwiThe indexOf() method returns the index of (position of) the first occurrence of a string in a string:
let str = "Please locate where 'locate' occurs!";
str.indexOf("locate");
return 7Time Complexity: O(n)
Break string into Array
let text = "How are you doing today?";
const myArray = text.split(" ");
Output: ["How","are","you","doing","today?"]Remove the first and last char of a string
let str = "Hello";
let newStr = str.slice(1,-1);
console.log(newStr);
Output: "ell"Find the interesection between 2 strings
let arr1 = ["a","b];
let arr2 = ["b","a","d"];
let filtered = arr1.filter(c => arr2.includes(c));
console.log(filtered);
Output: ["a","b"]
Creates a new Set
new Set()
const myArray = ["a","b","c"];
const letters = new Set(myArray);Adds a new element to the Set
letters.add("a");Removes an element from a Set
letters.delete("a");Returns true if a value exists in the Set
let res = letters.has("a");
res = trueReturns the number of elements in a Set
const myArray = ["a","b","c"];
const letters = new Set(myArray);
let size = letters.size;
size = 3Creates a new Map
const fruits = new Map();Sets the value for a key in a Map
const preMap = new Map();
for (let [crs, pre] of prerequisites) {
preMap.set(crs, (preMap.get(crs) || []).concat(pre));
}Gets the value for a key in a Map
const fruits = new Map();
// Set Map Values
fruits.set("apples", 500);
fruits.get("apples"); // Returns 500Removes a Map element specified by the key
fruits.delete("apples");Returns true if a key exists in a Map
fruits.has("apples");How to iterate through a hashmap
for(let [key, val] of preMap) {
console.log(key);
console.log(val);
}Returns the number of elements in a Map
console.log(fruits.size);Creates a new Set
new Set()
const myArray = ["a","b","c"];
const letters = new Set(myArray);Adds a new element to the Set
letters.add("a");Removes an element from a Set
letters.delete("a");Returns true if a value exists in the Set
let res = letters.has("a");
res = trueReturns the number of elements in a Set
const myArray = ["a","b","c"];
const letters = new Set(myArray);
let size = letters.size;
size = 3Creates a new Map
const fruits = new Map();Sets the value for a key in a Map
const preMap = new Map();
for (let [crs, pre] of prerequisites) {
preMap.set(crs, (preMap.get(crs) || []).concat(pre));
}Gets the value for a key in a Map
const fruits = new Map();
// Set Map Values
fruits.set("apples", 500);
fruits.get("apples"); // Returns 500Removes a Map element specified by the key
fruits.delete("apples");Returns true if a key exists in a Map
fruits.has("apples");How to iterate through a hashmap
for(let [key, val] of preMap) {
console.log(key);
console.log(val);
}Returns the number of elements in a Map
console.log(fruits.size);
O(1):
push and pop of stack/array
O(n):
Traversing an array
Linear search
O(log n):
O(log n) can be faster than O(n) on large data set.
Binary search
O(n log n):
Divide and Conquer Algorithms
O(n2):
Traversing 2D array
O(n!):
Generating all unrestricted permutations of a partially ordered set