Launching Gazebo in ROS2 - dhanushshettigar/Getting-Started-With-ROS2 GitHub Wiki
This document explains how to launch Gazebo from a ROS 2 launch system using a custom launch file. The steps include creating a package, modifying URDF files to include inertia properties, and handling errors related to missing inertia tags.
- Create New Package
- Modify URDF to Include Inertia Tags
- Error Handling for Missing Inertia Tags
- Final Steps
Inside your ROS workspace's source folder, create a new package named my_robot_bringup.
cd <Your-ROS-Workspace-Path>/src
ros2 pkg create my_robot_bringup --build-type ament_python
cd my_robot_bringup && code .Create a launch folder and a new file named my_robot_gazebo.launch.py.
from launch import LaunchDescription
from launch_ros.actions import Node
from launch.actions import IncludeLaunchDescription
from launch.launch_description_sources import PythonLaunchDescriptionSource
from launch.substitutions import Command
from ament_index_python.packages import get_package_share_directory
import os
def generate_launch_description():
# Path to URDF file
urdf_path = os.path.join(
get_package_share_directory('my_robot_description'),
'urdf', 'my_robot.urdf.xacro'
)
# Launch the robot_state_publisher
robot_state_publisher_node = Node(
package='robot_state_publisher',
executable='robot_state_publisher',
parameters=[{
'robot_description': Command(['xacro ', urdf_path])
}]
)
# Include Gazebo Harmonic (ros_gz_sim) launch file
gazebo_launch = IncludeLaunchDescription(
PythonLaunchDescriptionSource([
os.path.join(get_package_share_directory('ros_gz_sim'), 'launch', 'gz_sim.launch.py')
])
)
# Spawn robot in Gazebo Harmonic using ros_gz's `create` service
spawn_robot = Node(
package='ros_gz_sim',
executable='create',
arguments=['-name', 'my_robot', '-topic', 'robot_description'],
output='screen'
)
# Launch RViz2 without configuration file
rviz_node = Node(
package='rviz2',
executable='rviz2',
output='screen',
)
# Return the launch description
return LaunchDescription([
robot_state_publisher_node,
gazebo_launch,
spawn_robot,
rviz_node
])Edit your package.xml to include the necessary dependencies.
<exec_depend>my_robot_description</exec_depend>
<exec_depend>robot_state_publisher</exec_depend>
<exec_depend>ros_gz_sim</exec_depend>
Modify your setup.py to include the launch file.
data_files=[
('share/ament_index/resource_index/packages',
['resource/' + package_name]),
('share/' + package_name, ['package.xml']),
('share/' + package_name + '/launch', ['launch/my_robot_gazebo.launch.py']),
],
Build your package in the workspace.
colcon build --packages-select my_robot_bringupSource the install files.
source install/setup.bashSet the necessary environment variables.
export QT_QPA_PLATFORM=xcbLaunch the package using the following command.
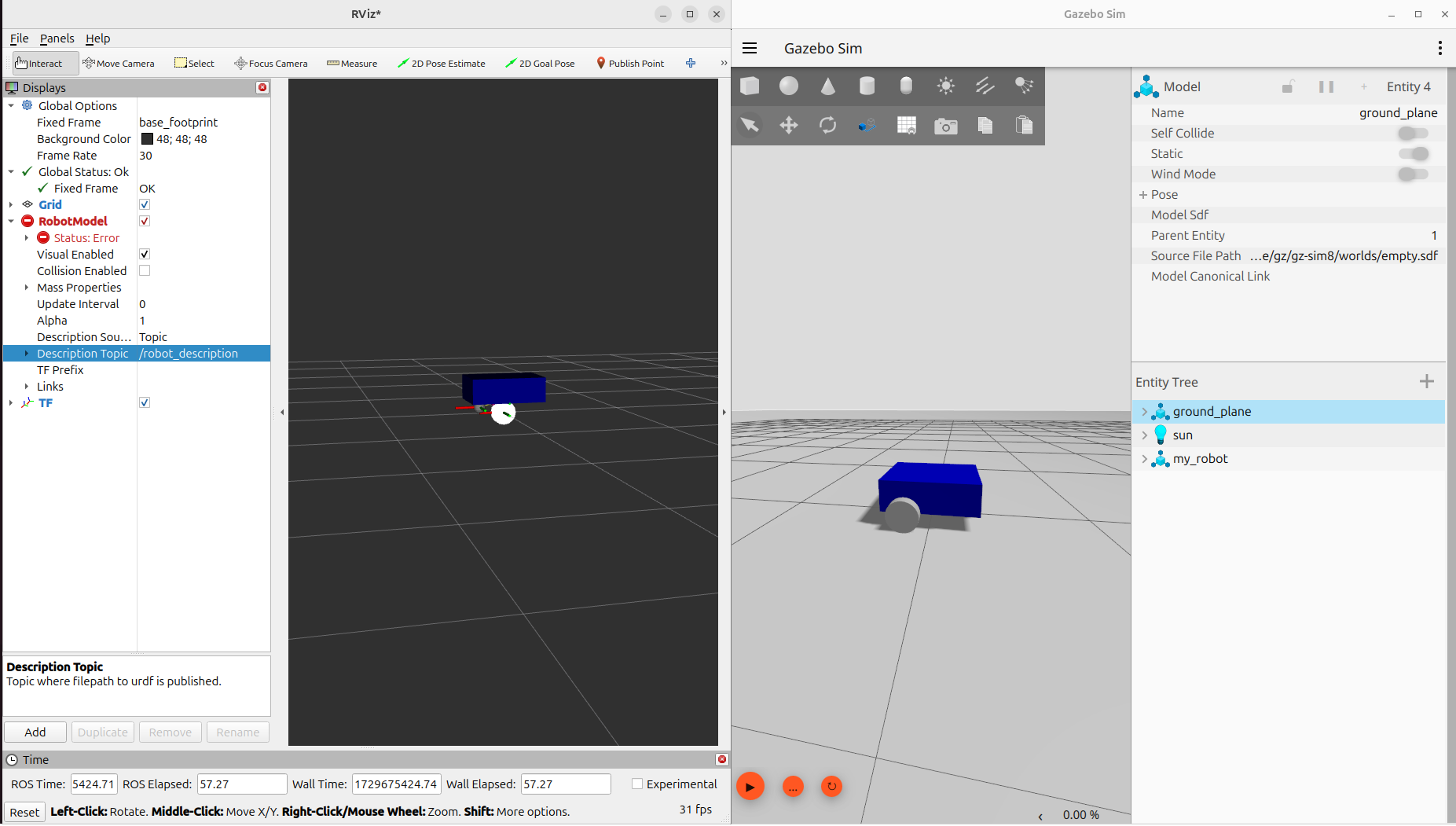
ros2 launch my_robot_bringup my_robot_gazebo.launch.pyIf you run the launch file without adding inertia tags in your URDF, you may encounter an error similar to:
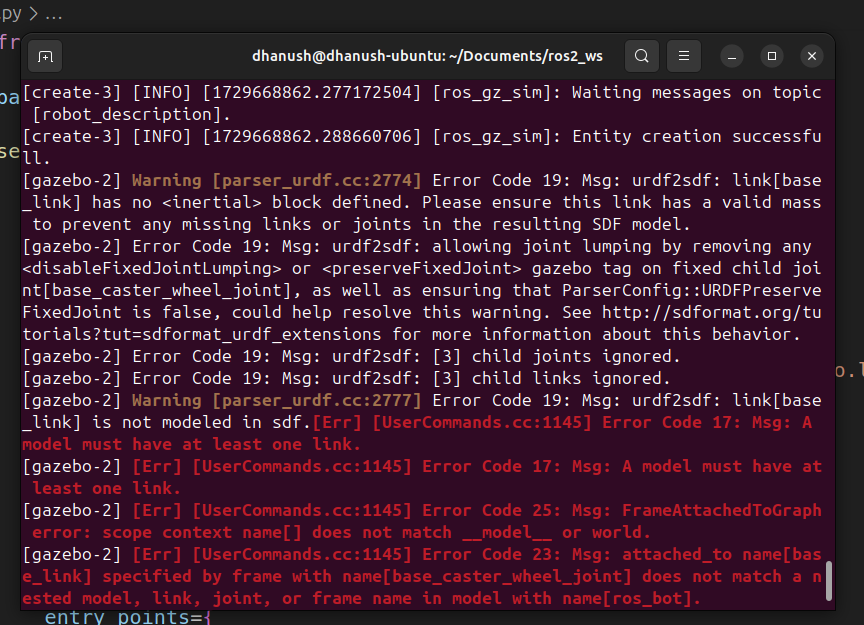
This error indicates that Gazebo requires inertia properties for the robot model to accurately simulate its physical behavior. To resolve this issue, you need to add inertia tags in your URDF files.
For more information on adding inertia properties to URDF models, refer to the following links:
Go to your existing package, my_robot_description.
cd <Your-ROS-Workspace-Path>/src && cd my_robot_description
code .Edit the common_properties.xacro file in the urdf folder to include inertia tags.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<robot xmlns:xacro="http://www.ros.org/wiki/xacro">
<material name="blue">
<color rgba="0 0 0.5 1" />
</material>
<material name="grey">
<color rgba="0.5 0.5 0.5 1" />
</material>
<xacro:macro name="box_inertia" params="m l w h xyz rpy">
<inertial>
<origin xyz="${xyz}" rpy="${rpy}" />
<mass value="${m}" />
<inertia ixx="${(m/12) * (h*h + l*l)}" ixy="0" ixz="0"
iyy="${(m/12) * (w*w + l*l)}" iyz="0"
izz="${(m/12) * (w*w + h*h)}" />
</inertial>
</xacro:macro>
<xacro:macro name="cylinder_inertia" params="m r h xyz rpy">
<inertial>
<origin xyz="${xyz}" rpy="${rpy}" />
<mass value="${m}" />
<inertia ixx="${(m/12) * (3*r*r + h*h)}" ixy="0" ixz="0"
iyy="${(m/12) * (3*r*r + h*h)}" iyz="0"
izz="${(m/2) * (r*r)}" />
</inertial>
</xacro:macro>
<xacro:macro name="sphere_inertia" params="m r xyz rpy">
<inertial>
<origin xyz="${xyz}" rpy="${rpy}" />
<mass value="${m}" />
<inertia ixx="${(2/5) * m * r * r}" ixy="0" ixz="0"
iyy="${(2/5) * m * r * r}" iyz="0"
izz="${(2/5) * m * r * r}" />
</inertial>
</xacro:macro>
</robot>Add inertia properties to your robot's URDF file.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<robot name="my_robot" xmlns:xacro="http://www.ros.org/wiki/xacro">
<xacro:include filename="common_properties.xacro" />
<xacro:property name="base_length" value="0.6" />
<xacro:property name="base_width" value="0.4" />
<xacro:property name="base_height" value="0.2" />
<xacro:property name="wheel_radius" value="0.1" />
<xacro:property name="wheel_length" value="0.05" />
<link name="base_footprint" />
<link name="base_link">
<visual>
<geometry>
<box size="${base_length} ${base_width} ${base_height}" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 ${base_height / 2.0}" rpy="0 0 0" />
<material name="blue" />
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<box size="${base_length} ${base_width} ${base_height}" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 ${base_height / 2.0}" rpy="0 0 0" />
</collision>
<xacro:box_inertia m="5.0" l="${2*base_length}" w="${2*base_width}" h="${2*base_height}"
xyz="0 0 ${base_height / 2.0}" rpy="0 0 0" />
</link>
<xacro:macro name="wheel_link" params="prefix">
<link name="${prefix}_wheel_link">
<visual>
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${wheel_radius}" length="${wheel_length}" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="${pi / 2.0} 0 0" />
<material name="grey" />
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${wheel_radius}" length="${wheel_length}" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="${pi / 2.0} 0 0" />
</collision>
<xacro:cylinder_inertia m="1.0" r="${2*wheel_radius}" h="${2*wheel_length}"
xyz="0 0 0" rpy="${pi / 2.0} 0 0" />
</link>
</xacro:macro>
<xacro:wheel_link prefix="right" />
<xacro:wheel_link prefix="left" />
<link name="caster_wheel_link">
<visual>
<geometry>
<sphere radius="${wheel_radius / 2.0}" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<material name="grey" />
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<sphere radius="${wheel_radius / 2.0}" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
</collision>
<xacro:sphere_inertia m="0.5" r="${2*wheel_radius / 2.0}"
xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
</link>
<joint name="base_joint" type="fixed">
<parent link="base_footprint" />
<child link="base_link" />
<origin xyz="0 0 ${wheel_radius}" rpy="0 0 0"/>
</joint>
<joint name="base_right_wheel_joint" type="continuous">
<parent link="base_link" />
<child link="right_wheel_link" />
<origin xyz="${-base_length / 4.0} ${-(base_width + wheel_length) / 2.0} 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<axis xyz="0 1 0" />
</joint>
<joint name="base_left_wheel_joint" type="continuous">
<parent link="base_link" />
<child link="left_wheel_link" />
<origin xyz="${-base_length / 4.0} ${(base_width + wheel_length) / 2.0} 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<axis xyz="0 1 0" />
</joint>
<joint name="base_caster_wheel_joint" type="fixed">
<parent link="base_link" />
<child link="caster_wheel_link" />
<origin xyz="${base_length / 3.0} 0 ${-wheel_radius / 2.0}" rpy="0 0 0" />
</joint>
</robot>
After modifying the URDF files, follow the steps to build and launch the package again.
cd <Your-ROS-Workspace-Path> && colcon build --packages-select my_robot_bringup my_robot_descriptionsource install/setup.bashLaunch the package using the same command as before.
ros2 launch my_robot_bringup my_robot_gazebo.launch.py
By following these steps, you will have successfully set up your Gazebo environment with a ROS 2 package that includes inertia properties for your robot model.