Intro To Gazebo - dhanushshettigar/Getting-Started-With-ROS2 GitHub Wiki
Intro To Gazebo
Table of Contents
- What is Gazebo?
- Installing Gazebo (gz harmonic)
- Running the Gazebo Simulator
- Running Quick Start Examples
- References
What is Gazebo?
Gazebo is an advanced robotics simulator that enables users to create 3D worlds and simulate robot behavior in a virtual environment. It provides physics simulation, sensor modeling, and interfaces to integrate with ROS (Robot Operating System).
Why use Gazebo Harmonic?
Gazebo Harmonic is the latest version with improved features, faster performance, and better support for ROS 2 integration. Unlike Gazebo Classic, it ensures smoother transitions for modern robotics applications.
Installing Gazebo (gz harmonic)
Reminder: We are NOT installing Gazebo Classic.
Gazebo Classic is now deprecated, and we use Gazebo Harmonic for better performance, improved support, and active development.
Step 1: Install Necessary Tools
Before installing Gazebo, update your package lists and install essential tools:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install curl lsb-release gnupg
- curl: A tool to download files from the web.
- lsb-release: Used to determine the Ubuntu version you are running.
- gnupg: Provides cryptographic tools for handling GPG keys.
Step 2: Install Gazebo Harmonic
Next, install Gazebo Harmonic using the official OSRF repository.
sudo curl https://packages.osrfoundation.org/gazebo.gpg --output /usr/share/keyrings/pkgs-osrf-archive-keyring.gpg
echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/pkgs-osrf-archive-keyring.gpg] http://packages.osrfoundation.org/gazebo/ubuntu-stable $(lsb_release -cs) main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/gazebo-stable.list > /dev/null
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install gz-harmonic
- GPG Key: This ensures the repository is secure and trusted.
- Repository Setup: The commands add Gazebo’s stable repository based on your system architecture and Ubuntu version.
- Package Installation: The final step installs gz-harmonic, which is the core Gazebo Harmonic simulator.
After installation, all libraries should be ready for use.
Step 3: Set Environment Variable
Before running the simulator, you need to set an environment variable to ensure the graphical interface loads correctly:
export QT_QPA_PLATFORM=xcb
Why is this needed? The Gazebo simulator (gz sim) uses Qt, a cross-platform framework for UI development. Without this setting, some systems may encounter issues rendering the UI properly.
Step 4: Run the Gazebo Simulator
To launch Gazebo, use the following command:
gz sim
What to expect? Gazebo will open with a 3D environment where you can place, move, and interact with robots and objects. On slower systems, it may take time to load—click Wait if a warning message appears.
Running Quick Start Examples
Gazebo includes built-in examples to help you get familiar with the interface and controls. One of these is the NAO Joint Control example.
Step 1: Run NAO Joint Control
From the Quick Start menu, select the NAO Joint Control example.
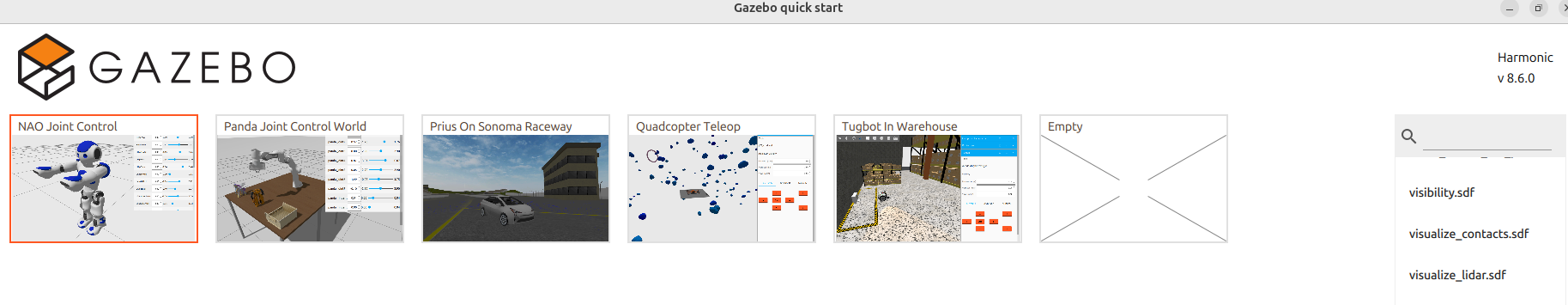
The NAO robot is a popular humanoid robot used for research and education.
Step 2: Explore Control Windows
Inspect the various control windows to see how different joints of the robot can be manipulated.
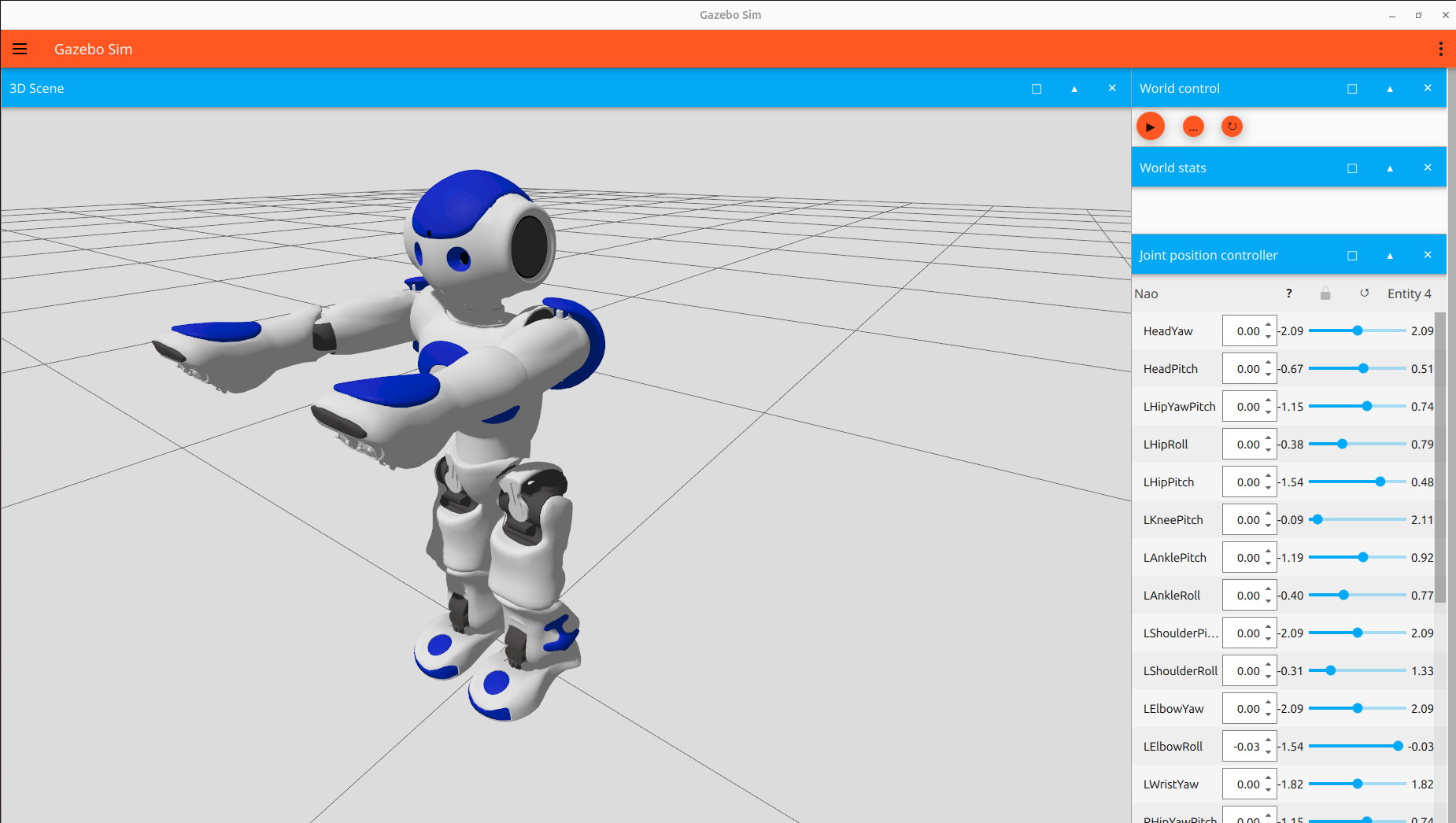
Step 3: Simulate and Adjust Controls
Run the simulation and experiment by changing the robot's position controls.
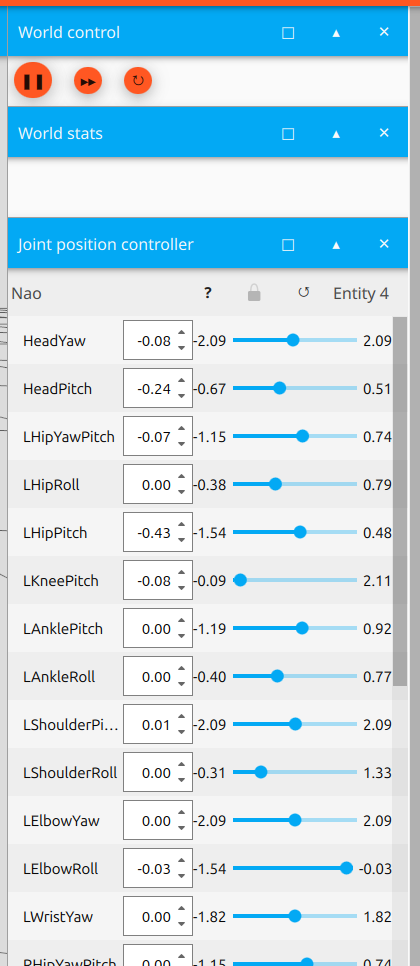
This helps you understand how the robot responds to different commands and movements.