Custom Robot (2 Wheels) - dhanushshettigar/Getting-Started-With-ROS2 GitHub Wiki
This tutorial demonstrates how to design a simple robot using URDF (Unified Robot Description Format). The robot includes a chassis, two wheels, and a caster wheel. Below are the steps involved, along with the full XML code snippets.
- Create a Chassis (Base Link)
- Add the Right Wheel
- Align the Right Wheel
- Add the Left Wheel
- Add the Caster Wheel
- Conclusion
The chassis serves as the central structure (base) of the robot. We define it as a box-shaped link. The origin is offset slightly to ensure it rests above the ground.
<robot name="ros_bot">
<material name="blue">
<color rgba="0 0 0.5 1"/>
</material>
<link name="base_link">
<visual>
<geometry>
<box size="0.6 0.4 0.2"/>
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 0.1" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<material name="blue"/>
</visual>
</link>
</robot>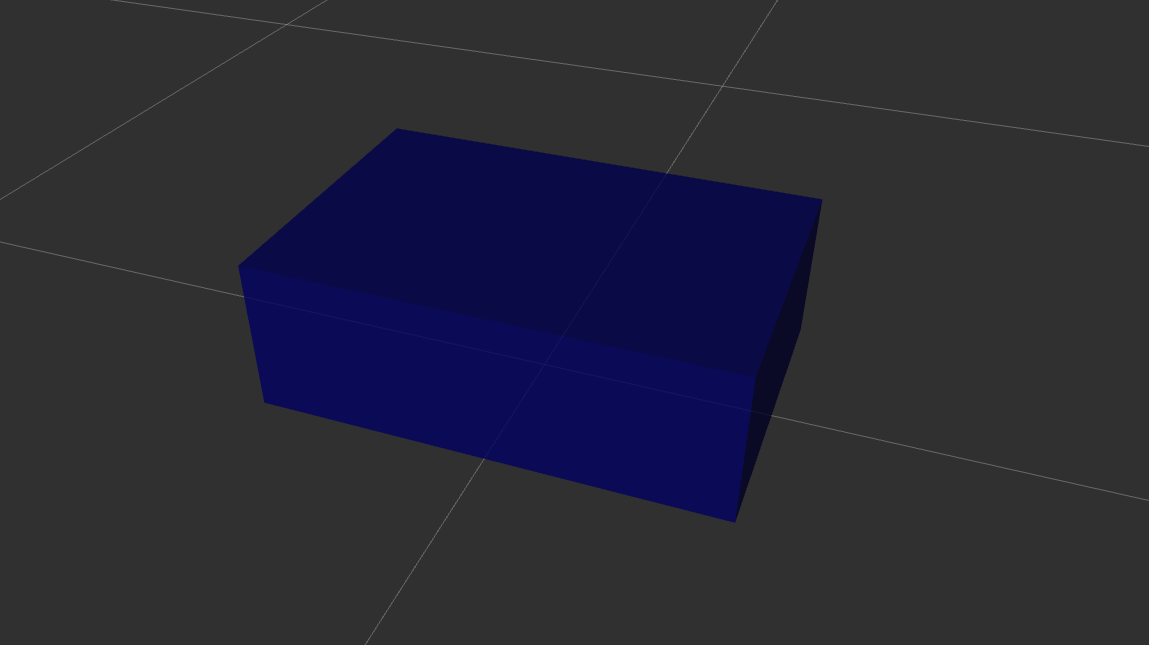
A cylinder geometry is used to represent the right wheel. We use a continuous joint type, which allows the wheel to rotate continuously.
<material name="grey">
<color rgba="0.5 0.5 0.5 1"/>
</material>
<link name="right_wheel_link">
<visual>
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="0.1" length="0.05"/>
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<material name="grey"/>
</visual>
</link>
<joint name="base_right_wheel_joint" type="continuous">
<parent link="base_link"/>
<child link="right_wheel_link"/>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<axis xyz="1 0 0"/>
</joint>
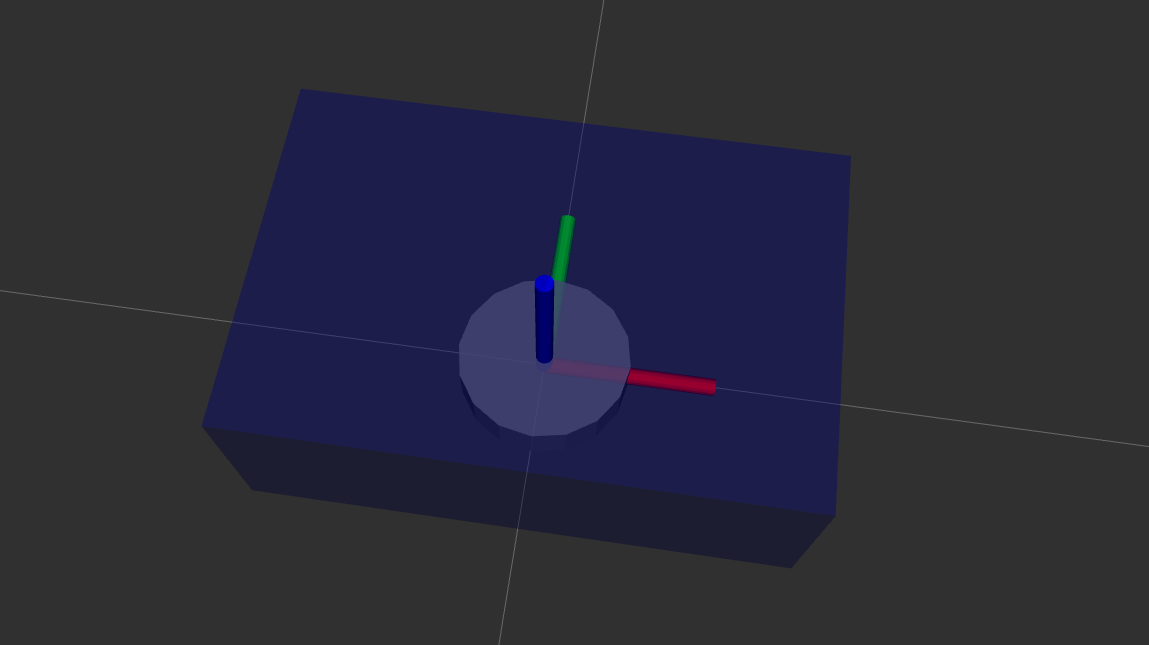
The right wheel is now rotated 90 degrees along the x-axis (rpy="1.57 0 0") so it aligns correctly with the chassis. We also position it on the right side of the base link using an offset in the origin tag.
<link name="right_wheel_link">
<visual>
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="0.1" length="0.05"/>
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="1.57 0 0"/>
<material name="grey"/>
</visual>
</link>
<joint name="base_right_wheel_joint" type="continuous">
<parent link="base_link"/>
<child link="right_wheel_link"/>
<origin xyz="-0.15 -0.225 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<axis xyz="0 1 0"/>
</joint>
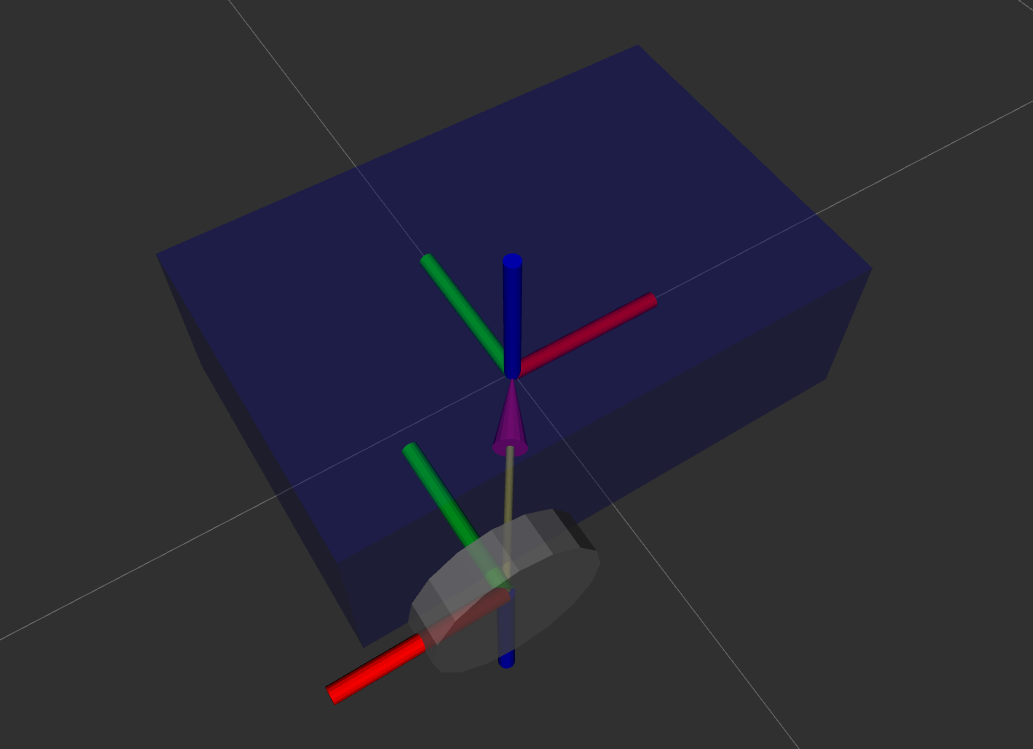
Similar to the right wheel, the left wheel is defined with a cylinder geometry. We rotate it 90 degrees for alignment and place it on the left side of the base.
<link name="left_wheel_link">
<visual>
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="0.1" length="0.05"/>
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="1.57 0 0"/>
<material name="grey"/>
</visual>
</link>
<joint name="base_left_wheel_joint" type="continuous">
<parent link="base_link"/>
<child link="left_wheel_link"/>
<origin xyz="-0.15 0.225 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<axis xyz="0 1 0"/>
</joint>
A sphere geometry represents the caster wheel, providing stability to the robot. The caster wheel is fixed to the base with a fixed joint since it doesn’t rotate or move independently.
<link name="caster_wheel_link">
<visual>
<geometry>
<sphere radius="0.05"/>
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<material name="grey"/>
</visual>
</link>
<joint name="base_caster_wheel_joint" type="fixed">
<parent link="base_link"/>
<child link="caster_wheel_link"/>
<origin xyz="0.2 0 -0.05" rpy="0 0 0"/>
</joint>
</robot>
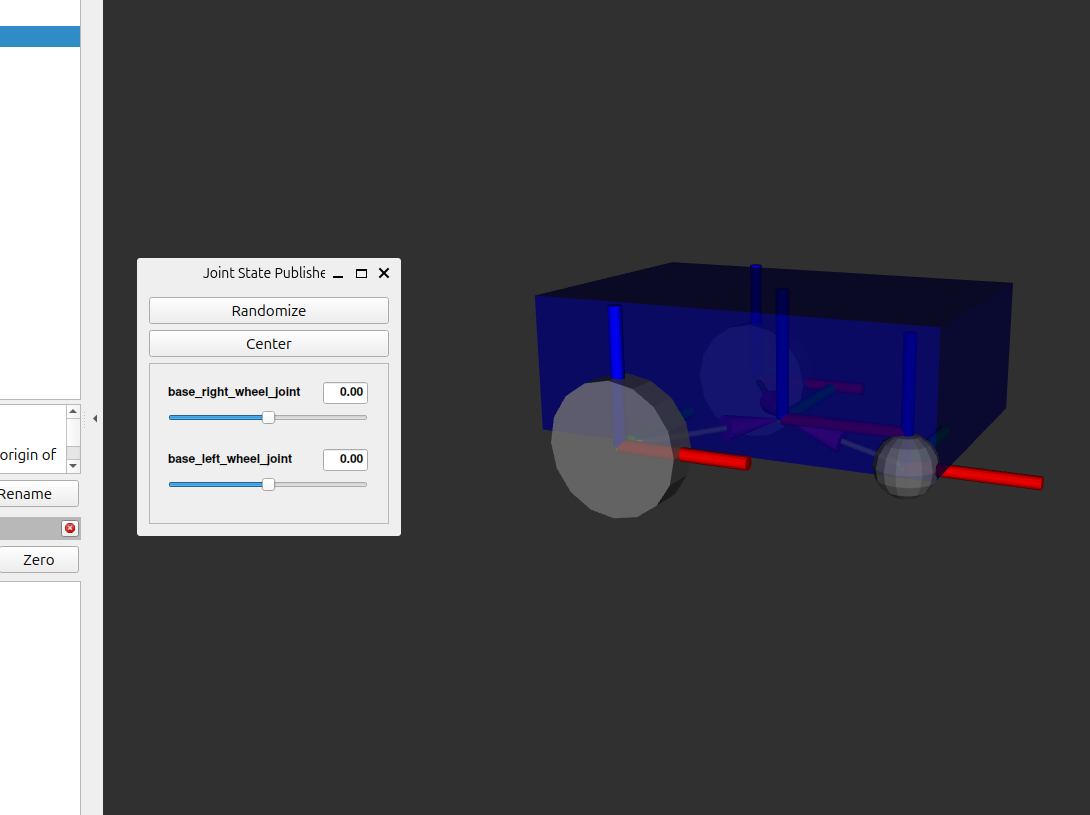
This URDF file defines a basic two-wheeled robot with a chassis, left and right wheels, and a caster wheel for stability. You can visualize this robot using RViz