Lambda - devian-al/AWS-Solutions-Architect-Prep GitHub Wiki
Lambda Simplified
- AWS Lambda lets you
run code without provisioning or managing servers. - You pay only for the compute time you consume.
- With Lambda, you can run code for virtually any type of application or backend service - all with
zero administration - You upload your code and Lambda takes care of everything required to run and scale your code with high availability.
- You can set up your code to be automatically triggered from other AWS services or be called directly from any web or mobile app.
Lambda Key Details
- Lambda is a compute service where you upload your code as a function and AWS provisions the necessary details underneath the function so that the function executes successfully.
- AWS Lambda is the ultimate
abstraction layer. You only worry about code, AWS does everything else. - Lambda supports Go, Python, C#, PowerShell, Node.js, and Java
Each Lambda function maps to one request.- Automatic horizontal scalling.
- Lambda is priced on the number of requests;
1,000,00 are free.Each million afterwards is $0.20.
- Lambda is also
priced on the runtime of your code, rounded up to the nearest 100mb, and the amount of memory your code allocates. - Lambda works globally.
Lambda functions can trigger other Lambda functions.- You can use Lambda as an
event-driven servicethat executes based on changes in your AWS ecosystem. - You can also use Lambda as a
handler in response to HTTP events via API calls over the AWS SDK or API Gateway. - Environment variables - AWS Lambda
encrypts them using the AWS Key Management Service. - When your Lambda function is invoked, those values are decrypted and made available to the Lambda code.
The first time you create or update Lambda functions that use environment variables in a region, a default service key is created for you automatically within AWS KMS. This key is used to encrypt environment variables. However, if you wish to use encryption helpers and use KMS to encrypt environment variables after your Lambda function is created, you must create your own AWS KMS key and choose it instead of the default key.
- To enable your Lambda function to access resources inside a
private VPC, you must provide additional VPC-specific configuration information that includes VPC subnet IDs and security group IDs. - AWS Lambda uses this information to
set up elastic network interfaces (ENIs) that enable your function to connect securely to other resources within a private VPC. AWS X-Ray allows you to debug your Lambda functionin case of unexpected behavior.
How it Works
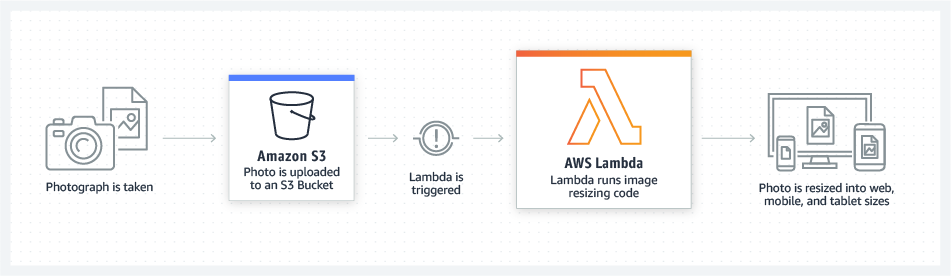
- Invoking Functions
- Lambda
supports synchronous and asynchronous invocation of a Lambda function. You can control the invocation type only when you invoke a Lambda function (referred to as on-demand invocation). - An event source is the entity that publishes events, and a Lambda function is the custom code that processes the events.
Event source mappingmaps an event source to a Lambda function.- It enables
automatic invocation of your Lambda function when events occur.
- It enables
- Lambda provides event source mappings for the following services.
- Amazon Kinesis
- Amazon DynamoDB
- Amazon S3
- Lambda
Lambda@Edge
-
You can use Lambda@Edge to allow your Lambda functions to customize the content that CloudFront delivers.
-
It adds compute capacity to your CloudFront edge locations and
allows you to execute the functions in AWS locations closer to your application's viewers. -
The functions run in response to CloudFront events, without provisioning or managing servers. You can use Lambda functions to change CloudFront requests and responses at the following points
- After CloudFront receives a request from a viewer (viewer request)
- Before CloudFront forwards the request to the origin (origin request)
- After CloudFront receives the response from the origin (origin response)
- Before CloudFront forwards the response to the viewer (viewer response)
How it Works
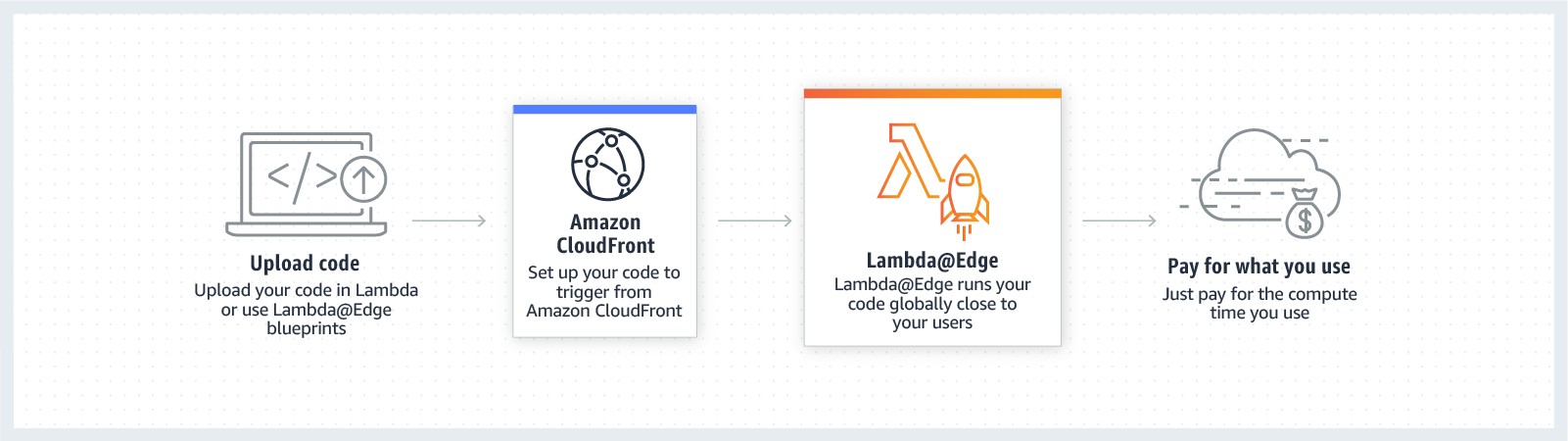
-
You'd use Lambda@Edge to simplify and reduce origin infrastructure.
Use Cases
Website Security and Privacy- You can trigger a Lambda function to add HTTP security headers on all origin responses without having to modify your application code on your origin. This helps improve security and privacy for your users and content providers, while using CloudFront to deliver the content at low latencies.

- You can trigger a Lambda function to add HTTP security headers on all origin responses without having to modify your application code on your origin. This helps improve security and privacy for your users and content providers, while using CloudFront to deliver the content at low latencies.
Dynamic Web Application at the Edge- By combining Lambda@Edge with other AWS services, developers can build powerful web applications at the edge that automatically scale up and down—with zero origin infrastructure and administrative effort required for automatic scaling, backups, or data center redundancy.

- By combining Lambda@Edge with other AWS services, developers can build powerful web applications at the edge that automatically scale up and down—with zero origin infrastructure and administrative effort required for automatic scaling, backups, or data center redundancy.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)- You can use Lambda@Edge to improve search engine optimization (SEO) for your website. For example, you can trigger a Lambda function to deliver a pre-rendered HTML page stored in Amazon S3 when the user-agent is a search engine bot such as Googlebot or Bingbot.

- You can use Lambda@Edge to improve search engine optimization (SEO) for your website. For example, you can trigger a Lambda function to deliver a pre-rendered HTML page stored in Amazon S3 when the user-agent is a search engine bot such as Googlebot or Bingbot.
Intelligently Route Across Origins and Data Centers- By using Lambda@Edge to dynamically route requests to different origins based on different viewer characteristics, you can balance the load on your origins, while improving the performance for your users. For example, you can route requests to origins within a home region, based on a viewer's location.

- By using Lambda@Edge to dynamically route requests to different origins based on different viewer characteristics, you can balance the load on your origins, while improving the performance for your users. For example, you can route requests to origins within a home region, based on a viewer's location.
Bot Mitigation at the Edge- Lambda@Edge can help you block unwanted bots at the edge, and let the authorized traffic go through. By intelligently mitigating these automated processes, you can help protect your origin infrastructure from unhelpful web crawlers and bots, while improving performance for real users.

- Lambda@Edge can help you block unwanted bots at the edge, and let the authorized traffic go through. By intelligently mitigating these automated processes, you can help protect your origin infrastructure from unhelpful web crawlers and bots, while improving performance for real users.
IMPROVED USER EXPERIENCE- Lambda@Edge can help improve your users' experience with your websites and web applications across the world, by letting you personalize content for them without sacrificing performance.
Real-time Image Transformation- You can customize your users' experience by transforming images on the fly based on the user characteristics. For example, you can resize images based on the viewer's device type—mobile, desktop, or tablet. You can also cache the transformed images at CloudFront Edge locations to further improve performance when delivering images.

- You can customize your users' experience by transforming images on the fly based on the user characteristics. For example, you can resize images based on the viewer's device type—mobile, desktop, or tablet. You can also cache the transformed images at CloudFront Edge locations to further improve performance when delivering images.
A/B Testing- You can test and serve different versions of your website to the users without re-directs or changing the browser URL. This allows you to seamlessly release updates to your website to improve your website's overall experience while continuing to deliver responsiveness for users.

- You can test and serve different versions of your website to the users without re-directs or changing the browser URL. This allows you to seamlessly release updates to your website to improve your website's overall experience while continuing to deliver responsiveness for users.
User Authentication and Authorization- You can use Lambda@Edge to help authenticate and authorize users for the premium pay-wall content on your website, filtering out unauthorized requests before they reach your origin infrastructure. For example, you can trigger a Lambda function to authorize each viewer request by calling authentication and user management service such as Amazon Cognito.
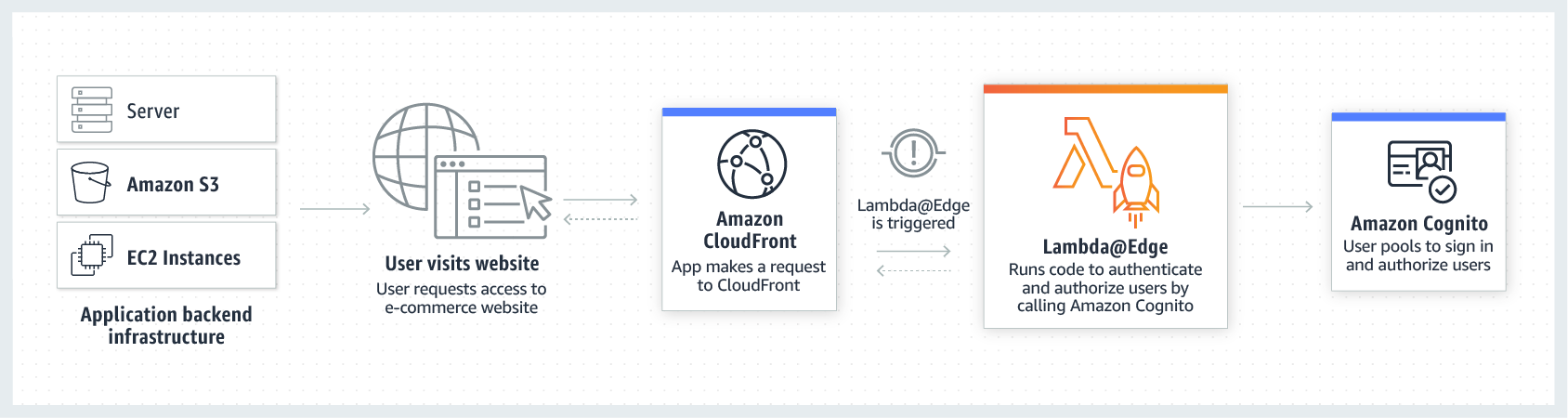
- You can use Lambda@Edge to help authenticate and authorize users for the premium pay-wall content on your website, filtering out unauthorized requests before they reach your origin infrastructure. For example, you can trigger a Lambda function to authorize each viewer request by calling authentication and user management service such as Amazon Cognito.
User Prioritization- Lambda@Edge can help you to control and prioritize access to your website by routing users to different pages and experiences. For example, you can trigger a Lambda function that runs code to prioritize premium and paid users on your e-commerce website as the traffic surges during shopping sales. You can also redirect other shoppers to a temporary “waiting room”— an alternate site with branding and marketing deals where they can wait for a turn to access your main retail site.

- Lambda@Edge can help you to control and prioritize access to your website by routing users to different pages and experiences. For example, you can trigger a Lambda function that runs code to prioritize premium and paid users on your e-commerce website as the traffic surges during shopping sales. You can also redirect other shoppers to a temporary “waiting room”— an alternate site with branding and marketing deals where they can wait for a turn to access your main retail site.
User Tracking and Analytics- By using Lambda@Edge and Kinesis together, you can process real-time streaming data so that you can track and analyze globally-distributed user activity on your website and mobile applications, including click stream analysis.

- By using Lambda@Edge and Kinesis together, you can process real-time streaming data so that you can track and analyze globally-distributed user activity on your website and mobile applications, including click stream analysis.