Sum of Left Leaves - codepath/compsci_guides GitHub Wiki
Problem Highlights
- 🔗 Leetcode Link: Sum of Left Leaves
- 💡 Problem Difficulty: Easy
- ⏰ Time to complete: 15 mins
- 🛠️ Topics: Binary Trees, Depth-First-Search
- 🗒️ Similar Questions: Path Sum II, Smallest String Starting From Leaf, Binary Tree Paths, Path Sum
1: U-nderstand
Understand what the interviewer is asking for by using test cases and questions about the problem.
- Established a set (2-3) of test cases to verify their own solution later.
- Established a set (1-2) of edge cases to verify their solution handles complexities.
- Have fully understood the problem and have no clarifying questions.
- Have you verified any Time/Space Constraints for this problem?
- Can the input tree be Null?
- No, there is at least one node.
- What is the space and time complexity?
- Time is
O(N)and Space isO(1)excluding the recursion stack.
- Time is
HAPPY CASE
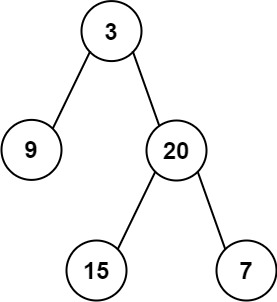
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: 24
Explanation: There are two left leaves in the binary tree, with values 9 and 15 respectively.
Input: root = [1,2,3]
Output: 2
Explanation: There is one left leaf. 2.

EDGE CASE
Input: root = [1]
Output: 0
2: M-atch
Match what this problem looks like to known categories of problems, e.g. Linked List or Dynamic Programming, and strategies or patterns in those categories.
If you are dealing with Binary Trees some common techniques you can employ to help you solve the problem:
- Think about appropriate Tree Traversal: Pre-Order, In-Order, Post-Order, Level-Order
- Choosing a specific tree traversal helps identify a left leaf.
- Store nodes within a HashMap to refer to later
- We don’t have a specific way of referring to previous nodes in a path that could be used in a HashMap. So, a HashMap would not help us as much in this context.
- Using Binary Search to find an element
- We are not working with a Binary Search Tree.
- Applying a level-order traversal with a queue
- Using this approach may complicate our code
3: P-lan
Plan the solution with appropriate visualizations and pseudocode.
General Idea: Lets pass information from parent as to whether it's a left child or right child. Only left child leaf will add to sum.
1. Create a helper function to recursively progress through the nodes.
a. Basecase, root is None. Can't operate function on None
b. If left child and leaf, then add node's value to total
c. Check left side and mark as left child
d. Check right side and mark as right child
3. Create the total variable to store sum
4. Recursively call helper
5. Return total
⚠️ Common Mistakes
- Failing to recognize the need for a helper function to store results during recursive processing of nodes.
4: I-mplement
Implement the code to solve the algorithm.
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def sumOfLeftLeaves(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
# Create a helper function to recursively progress through the nodes.
def helper(root:Optional[TreeNode], isLeftChild:bool):
nonlocal total
# Basecase, root is None. Can't operate function on None
if not root:
return
# If left child and leaf, then add node's value to total
if isLeftChild and not root.left and not root.right:
total += root.val
return
# Check left side and mark as left child
helper(root.left, True)
# Check right side and mark as right child
helper(root.right, False)
# Create the total variable to store sum
total = 0
# Recursively call helper
helper(root, False)
# Return total
return total
class Solution {
// Create the total variable to store sum
int sum=0;
public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) {
// Recursively call helper
helper(root,false);
// Return total
return sum;
}
// Create a helper function to recursively progress through the nodes
public void helper(TreeNode root,boolean isLeft){
// Basecase, root is None. Can't operate function on None
if(root==null ) return;
if(root.left==null && root.right==null) {
// If left child and leaf, then add node's value to total
if(isLeft)
sum+=root.val;
}
// Check left side and mark as left child
helper(root.left,true);
// Check right side and mark as right child
helper(root.right,false);
}
}
5: R-eview
Review the code by running specific example(s) and recording values (watchlist) of your code's variables along the way.
- Trace through your code with an input to check for the expected output
- Catch possible edge cases and off-by-one errors
6: E-valuate
Evaluate the performance of your algorithm and state any strong/weak or future potential work.
Assume N represents the number nodes in tree
- Time Complexity:
O(N)because we need to visit each node in binary tree. - Space Complexity:
O(1)if we do not count the recursion stack. The recursion stack will cost usO(N)if we have a linked list like tree.O(logN)in the average case.