Chapter 10 Strategy 알고리즘을 모두 바꾸기 - brodieroy/Study GitHub Wiki
0. 알고리즘을 모두 바꾸기 - Strategy 패턴
1. 무작정 소스를 다운받아서 봅시다. A1, A4, Q4, Sample가 있더군요.
2. Sample을 봅시다.
Hand.java
public class Hand {
public static final int HANDVALUE_GUU = 0; // 주먹
public static final int HANDVALUE_CHO = 1; // 가위
public static final int HANDVALUE_PAA = 2; // 보
public static final Hand[] hand = { // 가위바위보를 표시하는 3개의 인스턴스
new Hand(HANDVALUE_GUU),
new Hand(HANDVALUE_CHO),
new Hand(HANDVALUE_PAA),
};
private static final String[] name = { // 문자열표현
"주먹", "가위", "보",
};
private int handvalue; // 가위바위보 손의 값
private Hand(int handvalue) {
this.handvalue = handvalue;
}
public static Hand getHand(int handvalue) { // 값에서 인스턴스를 얻는다.
return hand[handvalue];
}
public boolean isStrongerThan(Hand h) { // this가 인스턴스를 이길경우 true
return fight(h) == 1;
}
public boolean isWeakerThan(Hand h) { // this가 h에게 질경우 true
return fight(h) == -1;
}
private int fight(Hand h) { // 무승부는 0, this의 승이면 1, h의 승이면 -1
if (this == h) {
return 0;
} else if ((this.handvalue + 1) % 3 == h.handvalue) {
return 1;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
public String toString() { // 문자열 표현으로 변환
return name[handvalue];
}
}
Strategy.java
public interface Strategy {
public abstract Hand nextHand();
public abstract void study(boolean win);
}
ProbStrategy.java
import java.util.Random;
public class ProbStrategy implements Strategy {
private Random random;
private int prevHandValue = 0;
private int currentHandValue = 0;
private int[][] history = {
{ 1, 1, 1, },
{ 1, 1, 1, },
{ 1, 1, 1, },
};
public ProbStrategy(int seed) {
random = new Random(seed);
}
public Hand nextHand() {
int bet = random.nextInt(getSum(currentHandValue));
int handvalue = 0;
if (bet < history[currentHandValue][0]) {
handvalue = 0;
} else if (bet < history[currentHandValue][0] + history[currentHandValue][1]) {
handvalue = 1;
} else {
handvalue = 2;
}
prevHandValue = currentHandValue;
currentHandValue = handvalue;
return Hand.getHand(handvalue);
}
private int getSum(int hv) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
sum += history[hv][i];
}
return sum;
}
public void study(boolean win) {
if (win) {
history[prevHandValue][currentHandValue]++;
} else {
history[prevHandValue][(currentHandValue + 1) % 3]++;
history[prevHandValue][(currentHandValue + 2) % 3]++;
}
}
}
WinningStrategy.java
import java.util.Random;
public class WinningStrategy implements Strategy {
private Random random;
private boolean won = false;
private Hand prevHand;
public WinningStrategy(int seed) {
random = new Random(seed);
}
public Hand nextHand() {
if (!won) {
prevHand = Hand.getHand(random.nextInt(3));
}
return prevHand;
}
public void study(boolean win) {
won = win;
}
}
Player.java
public class Player {
private String name;
private Strategy strategy;
private int wincount;
private int losecount;
private int gamecount;
public Player(String name, Strategy strategy) { // 이름과 전략을 할당 받는다.
this.name = name;
this.strategy = strategy;
}
public Hand nextHand() { // 전략의 지시를 받는다.
return strategy.nextHand();
}
public void win() { // 승
strategy.study(true);
wincount++;
gamecount++;
}
public void lose() { // 패
strategy.study(false);
losecount++;
gamecount++;
}
public void even() { // 무승부
gamecount++;
}
public String toString() {
return "[" + name + ":" + gamecount + " games, " + wincount + " win, " + losecount + " lose" + "]";
}
}
Main.java
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (args.length != 2) {
System.out.println("Usage: java Main randomseed1 randomseed2");
System.out.println("Example: java Main 314 15");
System.exit(0);
}
int seed1 = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int seed2 = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
Player player1 = new Player("Taro", new WinningStrategy(seed1));
Player player2 = new Player("Hana", new ProbStrategy(seed2));
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
Hand nextHand1 = player1.nextHand();
Hand nextHand2 = player2.nextHand();
if (nextHand1.isStrongerThan(nextHand2)) {
System.out.println("Winner:" + player1);
player1.win();
player2.lose();
} else if (nextHand2.isStrongerThan(nextHand1)) {
System.out.println("Winner:" + player2);
player1.lose();
player2.win();
} else {
System.out.println("Even...");
player1.even();
player2.even();
}
}
System.out.println("Total result:");
System.out.println(player1.toString());
System.out.println(player2.toString());
}
}
###UML표현
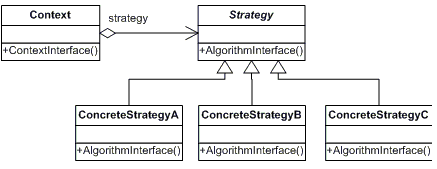
###정리
- 보통은 프로그래밍을 할 때 메소드 내부에 동화된 형태로 알고리즘을 구현하기 쉽습니다.
- 위임을 사용하고있다, 느슨한연결이다, API를 변경하지 않는 선에서 교체가 용이하다
- 실행중에 교체도가능하다(메모리, 속도, 환경 등)
- 같은 strategy를이용하여 검증이 가능하다(쓰래드? 도 될까?