methodOverriding.md - brainchildservices/curriculum GitHub Wiki
Slide 1
C# Method Overriding
Case 1
: Base class has Method1 and Derived class Method2
https://dotnetfiddle.net/aYNCBv
Base class and Derived class has two different methods and we try to access each method using 3 objects created: Following are the points we can notice.
- Base class object of type base class can access members in the base class
- Derived class object of type derived class can access members of both base class and derived class(also depends on access modifiers)
- Derived class object of type base class can access only the members of the base class.
- Derived class object of type base class points to the Method1 of the base class
Slide 2
Case2: Base class has Method1 and Derived class has Method1 and Method2
https://dotnetfiddle.net/peUY0S
Following are the points we can notice.
- Base class object of type base class can access members in the base class
- Derived class object of type derived class can access members of both base class and derived class(also depends on access modifiers)
- Derived class object of type base class can access only the members of the base class.
- We got a warning message on Method1 of Derived class: Method1 of base class hides the Method1 of the derived class.
- Derived class object of type derived class points to the Method1 of the derived class.
- Derived class object of type base class points to the Method1 of the base class
Slide 3
Case3: Base class has Method1 and Derived class has Method1 and Method2 with new keyword to Method1 of derived class(Method Hiding)
https://dotnetfiddle.net/1riUAF
Following are the points we can notice.
- Base class object of type base class can access members in the base class
- Derived class object of type derived class can access members of both base class and derived class(also depends on access modifiers)
- Derived class object of type base class can access only the members of the base class.
- Derived class object of type derived class points to the Method1 of the derived class.
- Derived class object of type base class points to the Method1 of the base class
- The only change we can notice is that the warning message is gone from case 2. So it means that in case 2, the system was automatically hiding the Method1 of Base class.
Slide 4
Case4: Base class has Method1 and Derived class has Method1 and Method2 with virtual keyword to Method1 of base class and override keyword to Method1 of Derived class.(Method Overriding)
https://dotnetfiddle.net/9F3sU3
Following are the points we can notice.
- Base class object of type base class can access members in the base class
- Derived class object of type derived class can access members of both base class and derived class(also depends on access modifiers)
- Derived class object of type base class can access the overridden member of the base class.
- Derived class object of type derived class points to the Method1 of the base class.
- Derived class object of type base class points to the Method1 of the derived class
Slide 5
Using var to initialize a class:
var can be used to initialize an object that would let the compiler decide what type to be assigned for the object.
Learn more about var on another section.
When we are creating an object of type var for a derived class, the object will have the following features,
- It would be able to access the methods of both derived class and base class,
- It would be able to access the methods of the derived class
- If there is a method that is overridden, the object would point to the method in the derived class.
https://dotnetfiddle.net/qwJjIQ
Slide 6
A practical example of method overloading:
We have a base class Animal. Almost all animals walk on four lege. So we create a method walk that prints. "I walk on four legs."
We create a derived class Tiger which inherits class Animal. It has some methods of its own.
We create an object of Tiger which references Animal type. We call the method Walk and it prints. "I walk on four legs."
We create an object of Kangaroo which references Animal type. We call the method Walk and it prints. "I walk on four legs."
But Kangaroos don't walk on four legs. So we need to override the method.
So we make the Walk method in Animal virtual and create a Walk method with override in Kangaroo that prints. "I walk on four legs."
https://dotnetfiddle.net/pSFYlJ
Slide 7
-
Q1. What is method overriding?
The process of re-implementing a base class non-static method in the derived class with the same signature as defined in the superclass is called Function Overriding or Method Overriding in C#. -
Q2. When do we need to override a method in C#?
If the base class method logic is not fulfilling the derived business requirements, then the derived class needs to override that method with the required business logic. Eg: The case where most animals walk on four legs but the Kangaroo walks on two legs. -
Q3. How to achieve method overriding?
In order to override a method:
- You need to add virtual keyword to the method in the base class
- You need to add override keyword to the same method in the derived class.
- Create an object of derived class with reference to the base class.
Slide 7 Downwards
-
Q4. What is runtime polymorphism?
Method Overriding is a type of polymorphism. It has several names like “Run Time Polymorphism” or “Dynamic Polymorphism” and sometimes it is called “Late Binding”. When you compile your program the reference variable of the base class gets memory and the compiler checks all the methods in that class. So it checks all the base class methods but not the child class methods. Now at runtime when the object is created, only checked methods can run. In case a method is overridden in the child class that function runs. Child class other functions aren't run because the compiler hasn't recognized them at the compile time. runtime polymorphism -
Q5. What are differences in creating an object like Child C=new Child(); and Parent C=new Child(); ?
When the object is created as Child C=new Child(); it is called Child object which references the Child class.In this case:
** Object C has access to members of the base class as well members of the Child class.
When the object is created as Parent C=new Child(); it is called Child object which references the Parent class.In this case:
** Object C has access to members of the parents class and only the overridden members of the Child class.
Slide 7 Downwards
-
Q6. What happens when the derived class and base class has the same member name?
** You get a warning message that the derived class members override the base class members. -
Q8. What is method hiding?
When the base class and derived class both have the same method name and signature, the compiler automatically hides the method in base class and gives out a warning message. Adding the new keyword to the method in derived class would explicitly hide the base class method and remove the warning message. This is called method hiding. -
Q9. What does the base keyword do? Base keyword is used to access the members of the base class in the derived class that have been overridden or hidden.
Slide 7 Downwards
-
Q10. What is the difference between method overloading and method overriding?
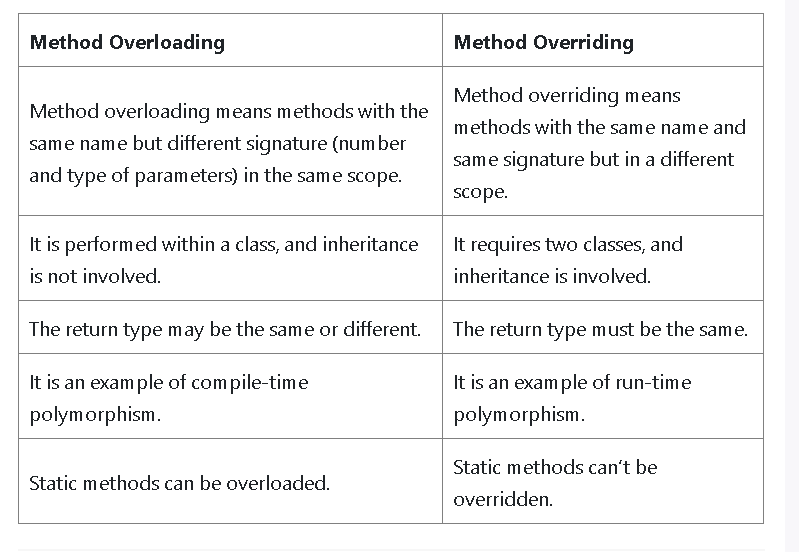
-
Q11. What do you do if you have to access an overridden member of a base class in the derived class? We can access the overridden member using the base keyword.
When we call an overridden method in the derived class, it will only call the method in the derived class.
Here inside Method 3, we are calling Method1. The call goes to Method1 of the derived class.
https://dotnetfiddle.net/gWeADH
Putting base.Method1 will make the compiler call the Method1 in the base class rather than the derived class.
https://dotnetfiddle.net/gWeADH
Slide 8
Exercises:
Q1. Implement the following classes: Dog, Frog, Cat, Kitten and Tomcat. All of them are animals (Animal). Animals are characterized by age, name and gender. Each animal makes a sound (use a virtual method in the Animal class). Create an array of different animals and print on the console their name, age and the corresponding sound each one makes
Q2. Create a class named Astrodroid that provides a virtual method called GetSound which returns a string. The default sound should be the words "Beep beep".
Implement a method called 'MakeSound' which writes the result of the GetSound method to the Console followed by a new line.
Create a derived class named R2 that inherits from Astrodroid.
Override the GetSound method on the R2 class so that it returns "Beep bop".
MCQ Exercises: https://www.sanfoundry.com/csharp-mcqs-method-overloading/
When do we use Parent C=new Child()?
Slide 9
What is Upcasting?
Difference between abstract and virtual? The purpose of the virtual access modifier is to allow you to provide a default implementation of your property on your base class that can optionally be overriden on your derived class. It is similar to the abstract keywords, but carries optional semantics instead of required semantics.
https://www.interviewsansar.com/up-casting-and-down-casting-in-csharp-interview-qa/
https://www.c-sharpcorner.com/article/polymorphism-up-casting-and-down-casting/
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/method-hiding-in-c-sharp/
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/difference-between-method-overriding-and-method-hiding-in-c-sharp/
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/csharp/programming-guide/classes-and-structs/knowing-when-to-use-override-and-new-keywords
https://www.sanfoundry.com/csharp-mcqs-inheritance-implementation/