intern_database_requirement.md - brainchildservices/curriculum GitHub Wiki
Slide 1
Before we learn about a database, let us understand -
What is Data?
In simple words, data can be facts related to any object in consideration. For example, your name, age, height, weight, etc. are some data related to you. A picture, image, file, pdf, etc. can also be considered data.
Slide 2
Database
A database is a systematic collection of data. They support electronic storage and manipulation of data. Databases make data management easy.
Let us discuss a database example: An online telephone directory uses a database to store data of people, phone numbers, and other contact details. Your electricity service provider uses a database to manage billing, client-related issues, handle fault data, etc.
Let us also consider Facebook. It needs to store, manipulate, and present data related to members, their friends, member activities, messages, advertisements, and a lot more. We can provide a countless number of examples for the usage of databases.
Slide 3
What is a Database Management System (DBMS)?
Database Management System (DBMS) is a collection of programs that enable its users to access databases, manipulate data, report, and represent data. It also helps to control access to the database. Database Management Systems are not a new concept and, as such, had been first implemented in the 1960s.
Slide 4
Why use a database?
Databases are useful in many different scenarios for storing data. It is typical to use a database when different sets of data needs to be linked together, such as:
- Pupils in a school and their grades
- Customer records and sales information
- Patients’ and doctors’ records
- Transactions between different bank accounts
- Taxpayers and income tax payments
Slide 5
SQL Server
SQL is a database computer language designed for the retrieval and management of data in a relational database. SQL stands for Structured Query Language. This tutorial will give you a quick start to SQL. It covers most of the topics required for a basic understanding of SQL and to get a feel of how it works.
Why to Learn SQL?
SQL is Structured Query Language, which is a computer language for storing, manipulating and retrieving data stored in a relational database.
SQL is the standard language for Relational Database System. All the Relational Database Management Systems (RDMS) like MySQL, MS Access, Oracle, Sybase, Informix, Postgres and SQL Server use SQL as their standard database language.
Slide 6
Also, they are using different dialects, such as −
- MS SQL Server using T-SQL,
- Oracle using PL/SQL,
- MS Access version of SQL is called JET SQL (native format) etc.
Applications of SQL
As mentioned before, SQL is one of the most widely used query language over the databases. I'm going to list few of them here:
- Allows users to access data in the relational database management systems.
- Allows users to describe the data.
- Allows users to define the data in a database and manipulate that data.
- Allows to embed within other languages using SQL modules, libraries & pre-compilers.
- Allows users to create and drop databases and tables.
- Allows users to create view, stored procedure, functions in a database.
- Allows users to set permissions on tables, procedures and views.
SQL Server 2019 Developer is a full-featured free edition, Click here to Download
Slide 7
Various Syntax in SQL
SQL CREATE DATABASE Statement
CREATE DATABASE database_name;
SQL INSERT INTO Statement
INSERT INTO table_name( column1, column2....columnN)
VALUES ( value1, value2....valueN);
Slide 8
SQL UPDATE Statement
UPDATE table_name
SET column1 = value1, column2 = value2....columnN=valueN
[ WHERE CONDITION ];
SQL DELETE Statement
DELETE FROM table_name
WHERE {CONDITION};
Slide 9
- Database Table creation should follow below given Details:
Table creation is an easy process when using SQL Server or Visual Studio for your Database purpose. Expand your respective Database and right click on Table, and then click on Add New Table
Slide 10
Or you can Enter your SQL query to create a table as shown below
SQL CREATE TABLE Statement
CREATE TABLE table_name(
column1 datatype,
column2 datatype,
column3 datatype,
.....
columnN datatype,
PRIMARY KEY( one or more columns )
);
Slide 11
Slide 11 Downwards
- Creation Process to follow:
-
Pull to main branch
-
Create new branch Database
-
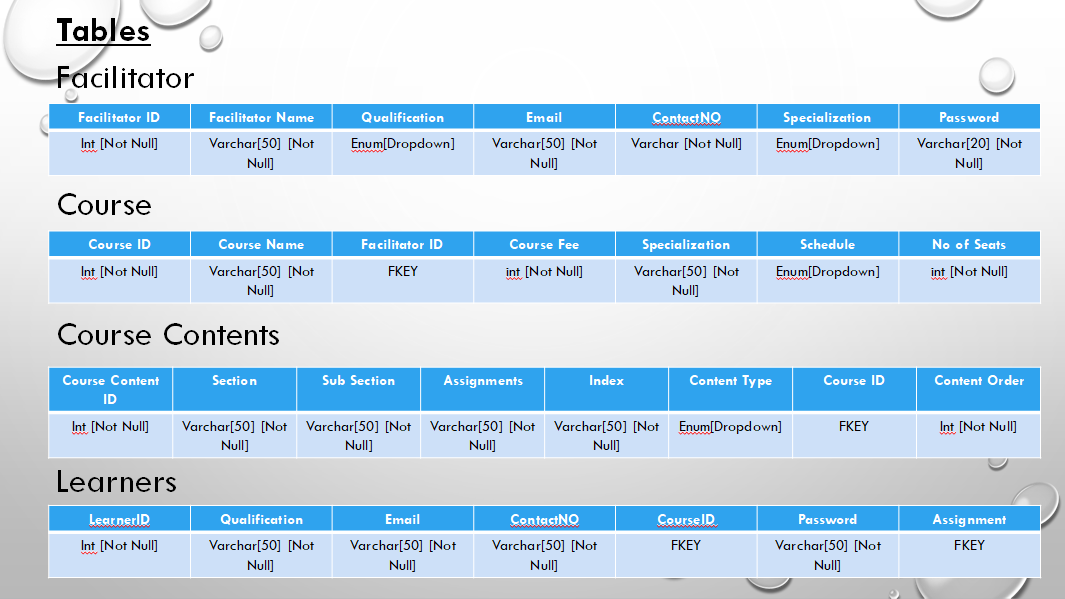
Create Table Facilitator: Fields: FacilitatorID(int), FacilitatorName(varchar50), Qualification(Enum), Email(varchar50), ContactNO(varchar), Specialization(Enum), Password(varchar(20))
Qualification(Enum): Btech, Mtech, BCA, MCA, BSc, PhD, Others Specialization(Enum): C#, HTML, CSS, JAVASCRIPT, SQL, ADO.NET, ASP.NET
Slide 11 Downwards
-
Create INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, SELECT SQL Commands for table Facilitator
-
Add dummy data to Facilitator, test SQL Commands for table Facilitator
-
Create Table Course: Fields: CourseID(int), CourseName(varchar(50)), FacilitatorID(FKEY), CourseFee(int), Specialization(FKey), Schedule(Enum), No of Seats(int)
Schedule(Enum): Fulltime, Parttime
-
Create Table CourseContent: Fields: CourseContentID(int), Section(nvarchar(50)), SubSection(nvarchar(50)),Assignments(nvarchar(50)),Index(nvarchar(50)), ContentType(enum), CourseID(Fkey), Content Order(int) ContentType(enum): HTML, PDF, Mark Down, Youtube Video, Assignments, Images
Slide 11 Downwards
- Create Table Learner: Fields: LearnerID(int), Qualification (nvarchar(50)), Email(nvarchar(50)), ContactNO(nvarchar(50)), CourseID(FKey), Password((nvarchar(20)), Assignment(FKey)
- Insert dummy data on to the tables and
- Inside Database folder create another folder table include the create sql query of tables one by one inside that folder. The file names to be saved as dbo.Name.sql 11.Inside Database folder create another folder SQLCommands include the create sql query commands that were used on the dummy data
Commit and create pull request