gitandversioncontrol.md - brainchildservices/curriculum GitHub Wiki
SLIDE- 1
- GIT
- Git is an open-source, version control tool created in 2005 by developers working on the Linux operating system;
- Git is a version control system that developers use all over the world.
- It helps you track different versions of your code and collaborate with other developers.
- it is a version control system that you download onto your computer.
- In order to check if you already have Git installed on your computer you can type the command git --version in the terminal.
SLIDE- 2
-
VERSION CONTROL
-
Version control allows you to keep track of your work and helps you to easily explore the changes you have made, be it data, coding scripts, notes, etc.
-
With version control software such as Git, version control is much smoother and easier to implement.
-
Using an online platform like Github to store your files means that you have an online back up of your work, which is beneficial for both you and your collaborators.
-
BENEFITS
-
Having a GitHub repo makes it easy for you to keep track of collaborative and personal projects - all files necessary for certain analyses can be held together and people can add in their code, graphs, etc.
-
You can review other people’s code, add comments to certain lines or the overall document, and suggest changes.
-
For collaborative projects, GitHub allows you to assign tasks to different users, making it clear who is responsible for which part of the analysis.
-
You can also ask certain users to review your code.
-
For personal projects, version control allows you to keep track of your work and easily navigate among the many versions of the files you create, whilst also maintaining an online backup.
-
SLIDE- 3
- GITHUB
- GitHub is a company founded in 2008 that makes tools which integrate with git.
- GitHub is a product that allows you to host your Git projects on a remote server somewhere (or in other words, in the cloud).
- GitHub is a code hosting platform for version control and collaboration.
- It lets you and others work together on projects from anywhere.
- Register yourself to github -> (https://github.com/) .. connect to the world of developers.
SLIDE- 4
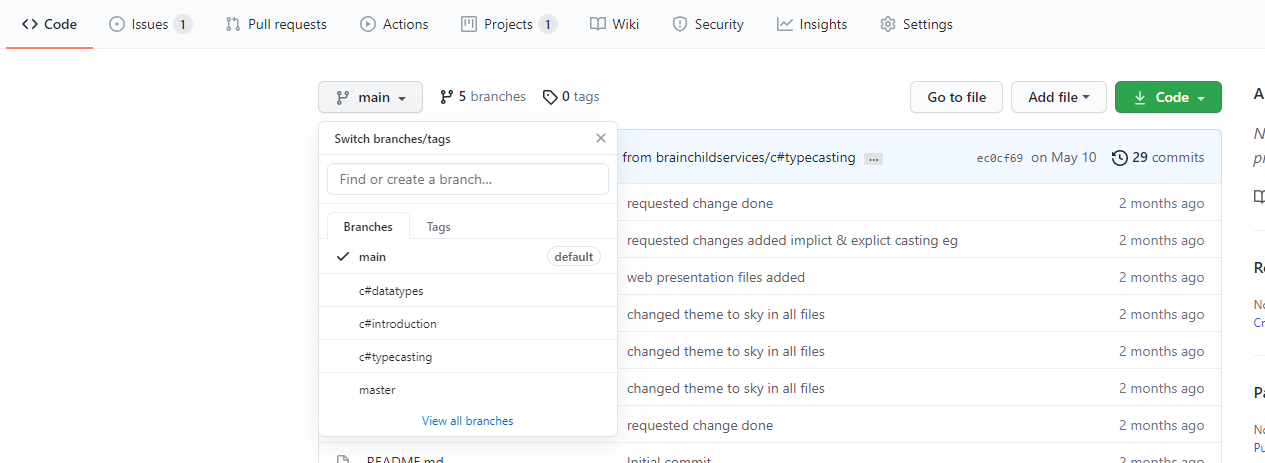
- Github Branches
- Branching is the way to work on different versions of a repository at one time.
- By default your repository has one branch named main which is considered to be the definitive branch. We use branches to experiment and make edits before committing them to main.
- Here at GitHub, our developers, writers, and designers use branches for keeping bug fixes and feature work separate from our main (production) branch.
- When a change is ready, they merge their branch into main.
- You can View/access your github repository branches from Github like,
SLIDE- 5
- Commit changes
- On GitHub, saved changes are called commits.
- Each commit has an associated commit message, which is a description explaining why a particular change was made.
- Commit messages capture the history of your changes, so other contributors can understand what you’ve done and why.
SLIDE- 6
- Pull Request
- Pull Requests are the heart of collaboration on GitHub.
- When you open a pull request, you’re proposing your changes and requesting that someone review and pull in your contribution and merge them into their branch.
- Pull requests show diffs, or differences, of the content from both branches.
- The changes, additions, and subtractions are shown in green and red.
- As soon as you make a commit, you can open a pull request and start a discussion, even before the code is finished.
- You can even open pull requests in your own repository and merge them yourself. It’s a great way to learn the GitHub flow before working on larger projects.
- Merge your Pull Request
- In this final step, it’s time to bring your changes together – merging your created branch into the main branch.
SLIDE- 7
- GIT INSTALLATION
- Get 'git' intalled using -> (https://git-scm.com/)
- Below are some recommended installation instructions, to keep things simple. However, if you know what these options do, and want to change them to suit you, go ahead:
-
-
For “Select Components”, check:
- “Git Bash Here”
- “Git GUI Here”
- “Git LFS (Large File Support)”
- “Associate .git* …”
- “Associate .sh …”
-
When prompted to choose the default editor, pick Notepad or if available, Notepad++ (a free graphical text editor designed for coding you can download here).
-
For “Adjusting the name of the initial branch in new repositories”, select: “Override the default…” and write in “main”.
-
For “Adjust your PATH environment”, select: “Git from the command line and also…”
-
For “Choose HTTPS transport backend”, select: “Use the OpenSSL library”
-
For “Configuring the line ending conversions”, select: “Checkout Windows-style,…”
-
For “Choose the default behavior of git pull”, select: “Default (fast-forward or merge)”
-
For “Choose a credential helper”, select: “Git Credential Manager Core”
-
For “Configure the terminal emulator …”, select: “Use MinTTY …”
-
For “Configure extra options”, select:
- “Enable file system caching”
For any configurations not listed here, select the default option.
SLIDE- 8
GETTING STARTED WITH GIT
-
You need to do this step the first time you use git on a computer. - Setup your profile:
Your name and email: git config --global user.name "yourGitHubUserName" git config --global user.email "yourGitHubEmail"
SLIDE- 9
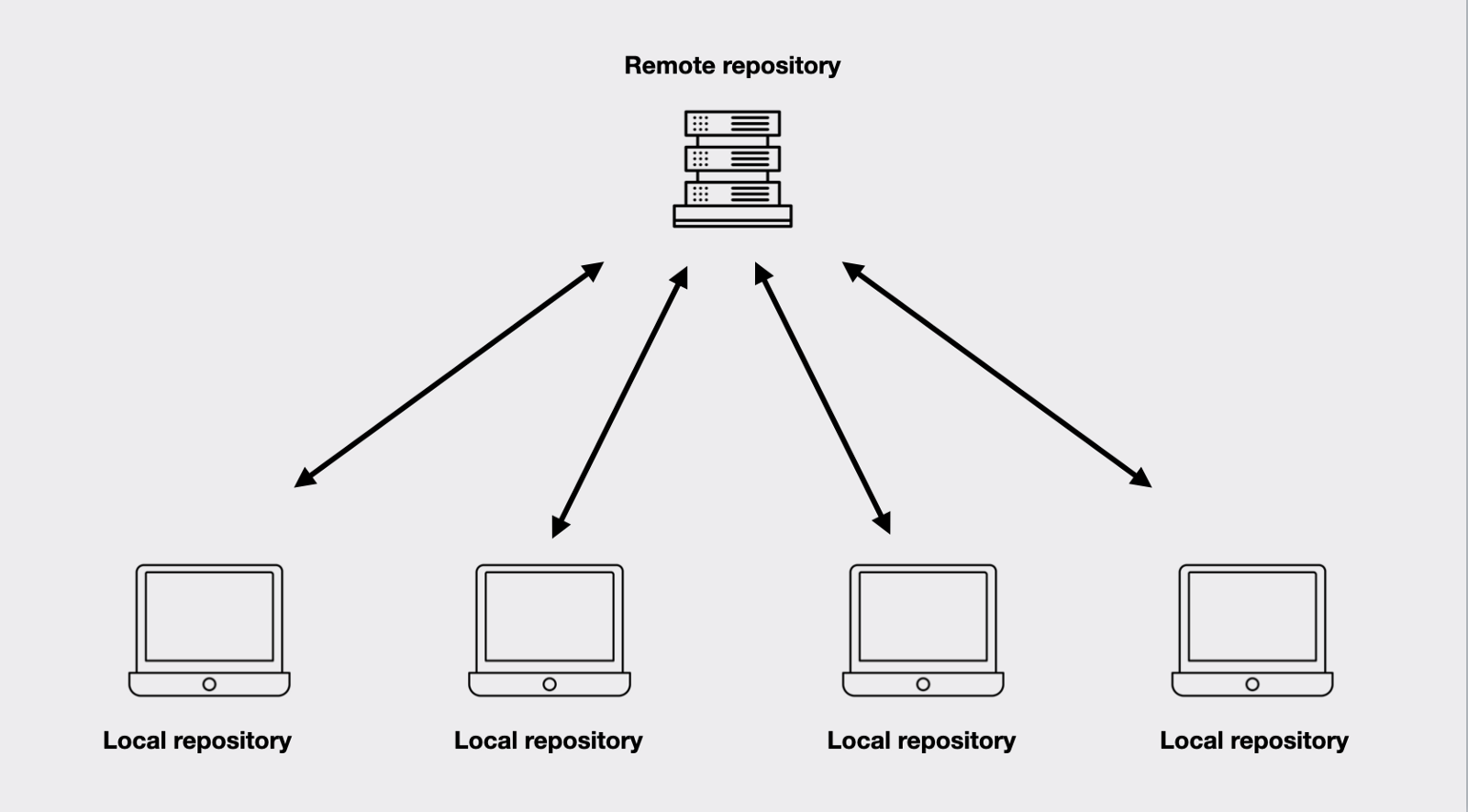
- WHAT IS A GIT REPOSITORY
-
The repository is the .git folder inside our project folder. It will track all the changes made to the files in our project and record that history over time.
-
The repository that we have on our computer is referred to as the local repository.
-
When we push (in other words upload) our local repository to one of code hosting services(here GitHub), then the repository that resides in these service in the cloud is referred to as the remote repository.
-
It is important to use a remote repository in order to be able to collaborate with other people as well as to backup our projects in case something happens to our laptop or computer.
-
-
SLIDE- 10
-
THE COMMIT,PULL,PUSH MANTRA
-
Will help you in git workflow.
-
Commit
- Once you’ve saved your files, you need to commit them - this means the changes you have made to files in your repo will be saved as a version of the repo, and your changes are now ready to go up on GitHub (the online copy of the repository).
-
Pull(git pull)
- Now, before you send your changes to Github, you need to pull, i.e. make sure you are completely up to date with the latest version of the online version of the files - other people could have been working on them even if you haven’t. You should always pull before you start editing and before you push.
-
Push(git push)
- Once you are up to date, you can push your changes - at this point in time your local copy and the online copy of the files will be the same.
-
-
REF Link:
- https://ourcodingclub.github.io/tutorials/git/
- https://www.earthdatascience.org/workshops/intro-version-control-git/basic-git-commands/
- https://www.javatpoint.com/how-to-install-git-on-windows (refer for git gui installation process images)