exceptionseHow are handled.md - brainchildservices/curriculum GitHub Wiki
Slide 1
Throw keyword
Previously we were seeing how to handle exceptions which are automatically raised by CLR.
An exception can be raised manually by using the throw keyword. Any type of exceptions which is derived from Exception class can be raised using the throw keyword. The throw statement allows you to create a custom error.
Case1: Normal showing the exception message:
using System;
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = new int[]{1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7};
try
{
arr[10] = 12;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
}
Slide 2
Case2: Use throw to specify exception we like
using System;
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = new int[]{1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7};
try
{
arr[10] = 12;
}
catch (Exception)
{
throw new Exception("I name this exception");
}
}
}
Slide 2 Downwards
OR
using System;
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = new int[]{1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7};
try
{
arr[10] = 12;
}
catch (Exception)
{
throw new IndexOutOfRangeException("I name this exception");
}
}
}
Slide 2 Downwards
OR
using System;
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = new int[]{1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7};
try
{
arr[10] = 12;
}
catch (IndexOutOfRangeException)
{
throw new IndexOutOfRangeException("I name this exception");
}
}
}
The catch parameter can be any specific exception that we want to catch.
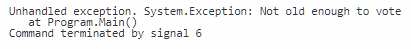
Example program to throw exception if age less than 18:
Slide 2 Downwards
using System;
//A program to throw a custom error message if the age of user is under 18 public class Program { public static void Main() { int age = 17; if (age < 18) { throw new Exception("Not old enough to vote"); } else { Console.WriteLine("You can vote"); } } }
Output