csharp_types.md - brainchildservices/curriculum GitHub Wiki
SLIDE-1
- DATATYPES
- C# is a strongly-typed language. It means we must declare the type of a variable that indicates the kind of values it is going to store
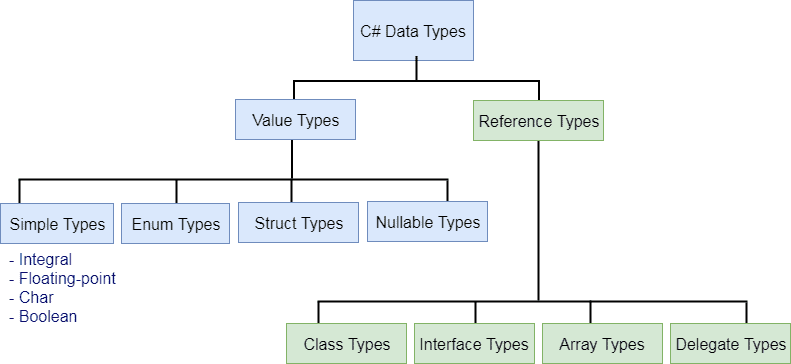
- C# mainly categorized data types in two types:
- Value types and Reference types.
- Value types include simple types (such as int, float, bool, and char), enum types, struct types, and Nullable value types.
- Reference types include class types, interface types, delegate types, and array types.
SLIDE-1(DOWNWARD)
SLIDE-2
- Value Type
- A data type is a value type if it holds a data value within its own memory space. It means the variables of these data types directly contain values.
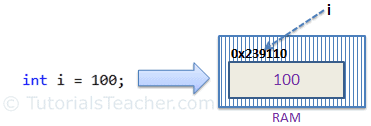
- For example, consider integer variable int i = 100;
- The system stores 100 in the memory space allocated for the variable i. The following image illustrates how 100 is stored at some hypothetical location in the memory (0x239110) for 'i':
SLIDE-3
-
Passing Value Type Variables
-
When you pass a value-type variable from one method to another, the system creates a separate copy of a variable in another method.
-
If value got changed in the one method, it wouldn't affect the variable in another method.
static void ChangeValue(int x) { x = 200; Console.WriteLine(x); } static void Main(string[] args) { int i = 100; Console.WriteLine(i); ChangeValue(i); Console.WriteLine(i); } Output: 100 200 100
-
SLIDE-3(DOWNWARDS)
-
This is how the value type getting stored.
-
-
The following data types are all of value type:
- bool
- byte
- char
- decimal
- double
- enum
- float
- int
- long
- sbyte
- short
- struct
- uint
- ulong
- ushort
-
SLIDE-4
- Reference Type
-
Unlike value types, a reference type doesn't store its value directly. Instead, it stores the address where the value is being stored.
-
In other words, a reference type contains a pointer to another memory location that holds the data.
-
For example, consider the following string variable:
string s = "Hello World!!";
-
SLIDE-4(DOWNWARD)
-
The following image shows how the system allocates the memory for the above string variable.
-
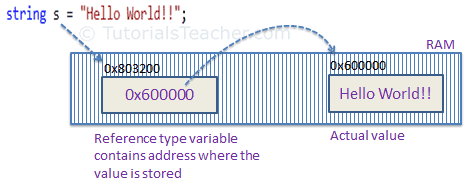
- As you can see in the above image, the system selects a random location in memory (0x803200) for the variable s. The value of a variable s is 0x600000, which is the memory address of the actual data value. Thus, reference type stores the address of the location where the actual value is stored instead of the value itself.
SLIDE-5
- Passing Reference Type Variables
-
When you pass a reference type variable from one method to another, it doesn't create a new copy; instead, it passes the variable's address.
-
So, If we change the value of a variable in a method, it will also be reflected in the calling method.
static void ChangeReferenceType(Student std2) { std2.StudentName = "Steve"; } static void Main(string[] args) { Student std1 = new Student(); std1.StudentName = "Bill"; ChangeReferenceType(std1); Console.WriteLine(std1.StudentName); } Output: Steve
-
SLIDE-6
-
The followings are reference type data types:
- String
- Arrays (even if their elements are value types)
- Class
- Delegate
-
Contents already in slide:
- table with details of simple datatypes: http://127.0.0.1:5500/003datatypes.html#/1
- different simple datatype syntax explaining. starting from : http://127.0.0.1:5500/003datatypes.html#/2
-
REF link: