HowToOperator.md - brainchildservices/curriculum GitHub Wiki
Slide 1
Different Types of JavaScript Operator
- Assignment Operators
- Arithmetic Operators
- Comparison Operators
- Logical Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- String Operators
- Other Operators
Slide 2
- JavaScript Assignment Operators
Assignment operators are used to assign values to variables. For example,
const x = 5;
Here, the = operator is used to assign value 5 to variable x.
Here's a list of commonly used assignment operators:
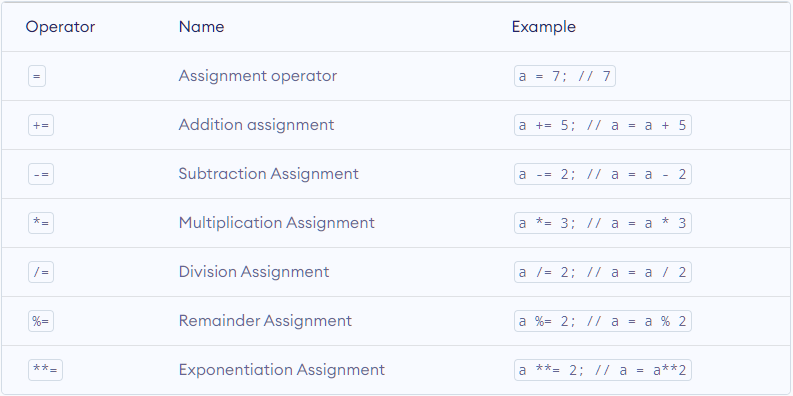
Note: The commonly used assignment operator is `=`. You will understand other assignment operators such as `+=`, `-=`, `*=` etc.
once we learn arithmetic operators.
Slide 3
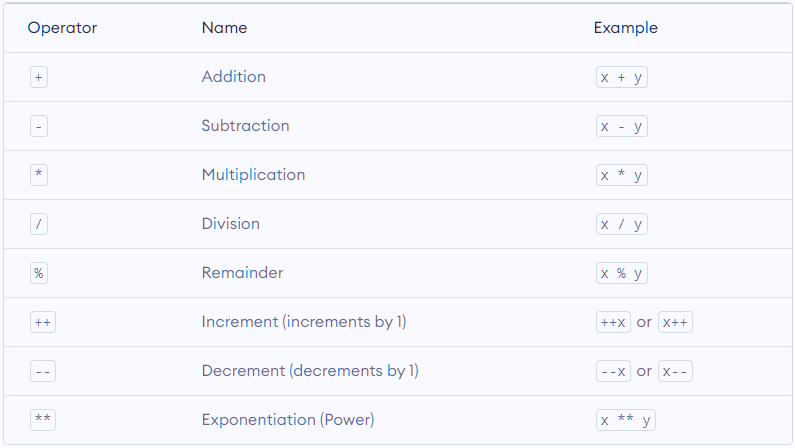
- JavaScript Arithmetic Operators
Arithmetic operators are used to perform arithmetic calculations. For example,
const number = 3 + 5; // output :- 8
Here, the + operator is used to add two operands.
Here's a list of Comparison Operators:
Example 1: Arithmetic operators in JavaScript
let x = 5;
let y = 3;
//Addition
console.log('x + y = ', x + y); // 8
//subtraction
console.log('x - y = ', x - y); // 2
//multiplication
console.log('x * y = ', x * y); // 15
//division
console.log('x / y = ', x / y); // 1.6666666666666667
//remainder
console.log('x % y = ', x % y); // 2
//increment
console.log('++x = ', ++x); // x is now 6
console.log('x++ = ', x++); // prints 6 and then increased to 7
console.log('x = ', x); // 7
//decrement
console.log('--x = ', --x); // x is now 6
console.log('x-- = ', x--); // prints 6 and then decreased to 5
console.log('x = ', x); // 5
Slide 3
-
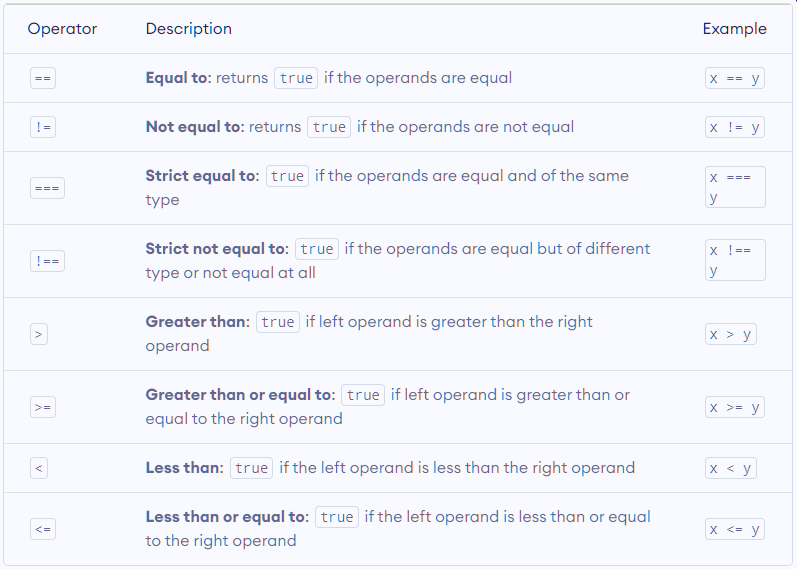
JavaScript Comparison Operators
Comparison operators compare two values and return a boolean value, either
trueorfalse. For example,const a = 5, b = 2; console.log(a>b); //True
Here, the comparison operator > is used to compare whether a is greater than b.
Here's a list of Comparison Operators:
Slide 3 DownWards
Example 2: Comparison operators in JavaScript
//equal operator
console.log(3 != 2); // true
console.log(2 == '2'); // true
// not equal operator
console.log(2 == 2); // true
console.log('hello' != 'Hello'); // true
// strict equal operator
console.log(2 === 2); // true
console.log(2 === '2'); // false
// strict not equal operator
console.log(2 !== '2'); // true
console.log(2 !== 2); // false
Slide 4
- JavaScript Logical Operators
Logical operators perform logical operations and return a boolean value, either true or false. For example,
const x = 5, y = 3;
(x < 6) && (y < 5); // true
Here, && is the logical operator AND. Since both x < 6 and y < 5 are true, the result is true.
Here's a list of Logical Operators:
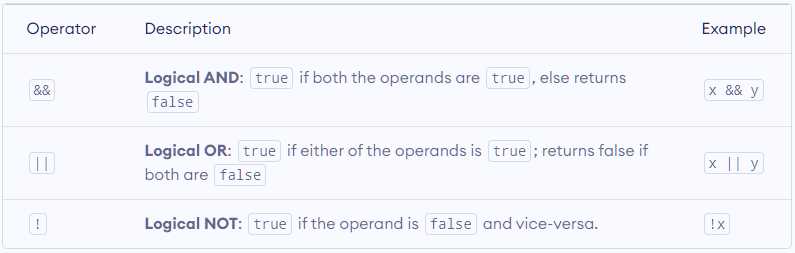
Example 3: Logical Operators in JavaScript
// logical AND
console.log(true && true); // true
console.log(true && false); // false
// logical OR
console.log(true || false); // true
// logical NOT
console.log(!true); // false
Logical operators are used in decision making and loops. You will learn about the use of logical operators in detail in later tutorials.
Slide 5
- JavaScript Bitwise Operators
Bitwise operators perform operations on binary representations of numbers.
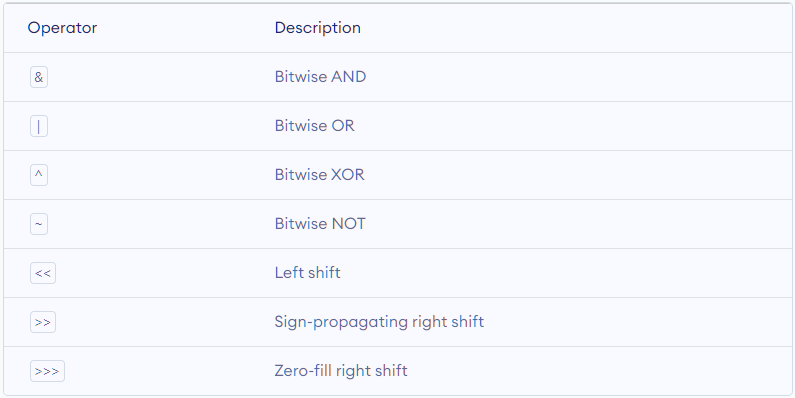
Bitwise operators are rarely used in everyday programming.
Slide 6
- JavaScript String Operators
In JavaScript, you can also use the + operator to concatenate (join) two or more strings.
Example 4: String operators in JavaScript
// concatenation operator
console.log('hello' + 'world');
let a = 'JavaScript';
a += ' tutorial'; // a = a + ' tutorial';
console.log(a);
Output
helloworld
JavaScript tutorial
Slide 7
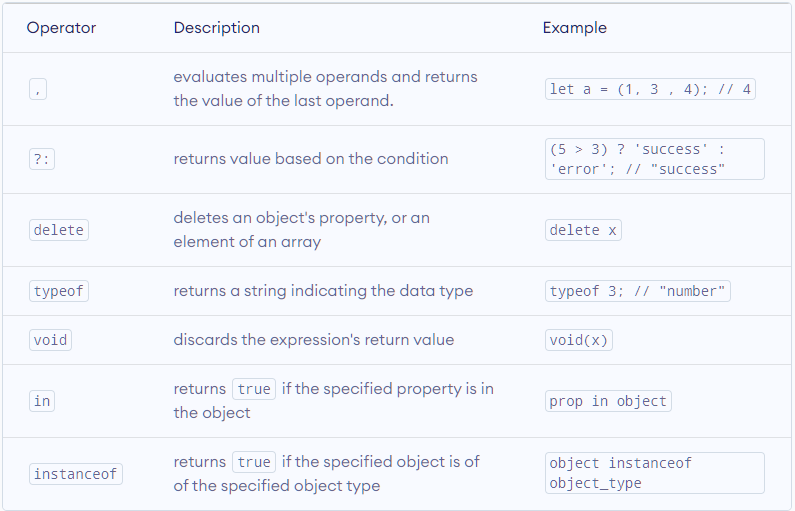
- Other JavaScript Operators
Here's a list of other operators available in JavaScript. You will learn about these operators in later tutorials.