Crud.md - brainchildservices/curriculum GitHub Wiki
Slide 1
CRUD
Any organizations that tracks data (like accounts, payment information, or other records) need systems that provide persistent storage, which is usually organized into a database. A relational database consists of data organized by rows and columns.
CRUD (create, read, update, delete) is an acronym that refers to the four functions we use to implement persistent storage applications and relational database applications, including the Oracle Database, Microsoft SQL Server, and MySQL.
Slide 2
The table below summarizes what each CRUD operation means.
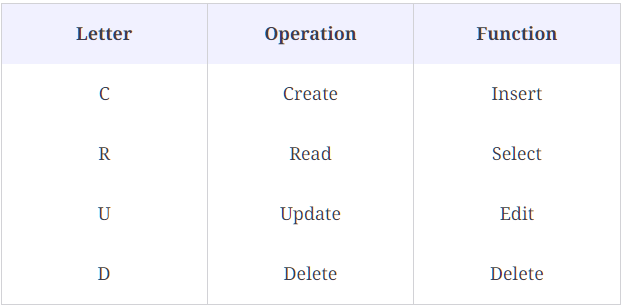
Slide 3
Why is CRUD so important?
CRUD is constantly used for anything related to database and database design. Software developers can’t get anything done without CRUD operations. Website development, for example, uses REST (Representational State Transfer), which is a superset of CRUD used for HTTP resources.
On the other end, CRUD is just as important for end-users. Without it, things like registering for websites, creating blogs, or bookmarks would be impossible. Most applications we use let us add or create new entries, search for existing ones, make changes to them or delete them.
CRUD offers many benefits including:
- It facilitates security control by satisfying the various access requirements
- It simplifies and facilitates application design making it more scalable
- It has better performance compared to ad-hoc SQL statements