CSharpArraySorting.md - brainchildservices/curriculum GitHub Wiki
Simple Exercise to be completed before learning Sorting Algorithms:
- Q1: Take the size of array as input from user. Prompt user to enter elements to the array. Prompt user to enter any number. Create a program that checks if the number input by the user is present in the array and at which index.
Test Data:
Enter the size of array: 4
Enter elements to array:
1
14
15
17
Enter the element to be searched: 17
Expected Output:
Found 17 at index 3
Enter the size of array: 3
Enter elements to array:
1
13
10
Enter the element to be searched: 17
Expected Output:
17 not found in the array
- Q2: Take the size of array as input from user. Prompt user to enter elements to the array. Prompt user to enter two index numbers. Write a program that the numbers at the index position provided by the user: Print the array with swapped numbers
Test Data:
Enter the size of array: 4
Enter elements to array:
1
14
15
17
Enter the index to be swapped:
1
3
Expected Output:
Array after swapping is
1 17 15 14
Enter the size of array: 6
Enter elements to array:
1
13
10
6
8
78
Enter the index to be swapped:
0
3
Expected Output:
Array after swapping is
6 13 10 1 8 78
- Q3.1: Take the size of array as input from user. Prompt user to enter elements to the array. Write a program to print the largest number in the array
Test Data:
Enter the size of array: 4
Enter elements to array:
1
14
15
17
Expected Output:
Largest number is: 17
- Q3.2: Take the size of array as input from user. Prompt user to enter elements to the array. Write a program to print the smallest number in the array
Test Data:
Enter the size of array: 4
Enter elements to array:
1
14
-15
17
Expected Output:
Smallest number is: -15
- Q4: Take the size of array as input from user. Prompt user to enter elements to the array. Write a program to print the second largest number in the array without completely sorting the array.
Test Data:
Enter the size of array: 4
Enter elements to array:
1
14
-15
17
Expected Output:
2nd largest number is: 14
- Q5: Take the size of array as input from the user. Prompt user to enter elements to the array. Write a program to reverse the array(without using another array) and print the array
Test Data:
Enter the size of array: 4
Enter elements to array:
1
14
-15
17
Expected Output:
The reversed array is : 17 -15 14 1
Consider the example of finding the sum of first N Natural numbers.
Case1: https://dotnetfiddle.net/zwKKen Using a for loop and adding each term to the sum.
But if we put one more zero, dotn't fiddle can no longer handle it as Execute time goes over 10 seconds.
Case2: https://dotnetfiddle.net/R82no9
Here we have used the arithmetic expression formula to calculate the sum of N terms. Since there is no for loop involved, the execution time is more fast and we can find the answer for larger and larger numbers.
The purpose of programming is not just to write some code, but to write code that has good performance and efficiency.
Finding out the time complexity of your code can help you develop better programs that run faster.
How to calculate the time complexity of any algorithm or program?
The most common metric is using Big O notation.
- Big O notation cares about the worst-case scenario. E.g., when you want to sort and elements in the array are in reverse order for some sorting algorithms or the loop has to run all the iterations to complete the sorting.
- It helps us to find the amount of work the CPU has to do (time complexity) as the input size grows (towards infinity).
- Big O = Big Order function. Drop constants and lower order terms. E.g. O(3*n^2 + 10n + 10) becomes O(n^2).
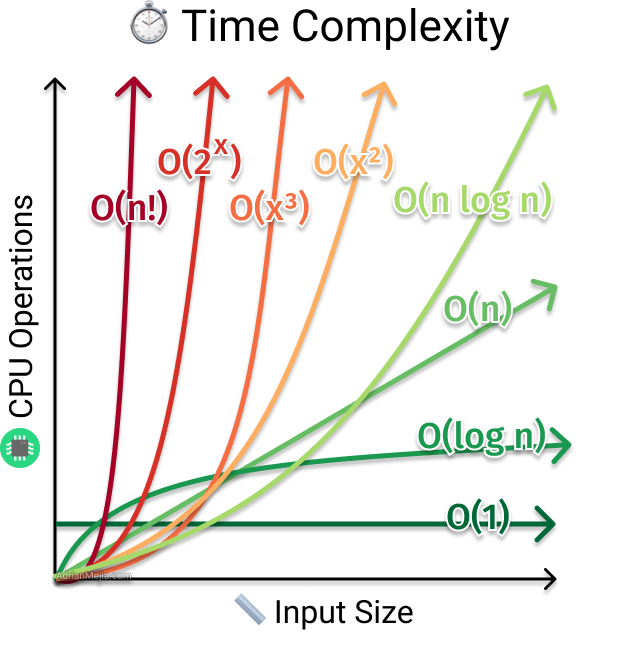
-
O(1): Simple assignment statements, reading a variable etc
https://dotnetfiddle.net/8J7ehJ -
O(log(n)): Binary Search of a sorted array
-
O(sqrt(n)) : A program that finds the square root of perfect squares https://onlinegdb.com/YVrMS0gjo
https://dotnetfiddle.net/iYRjej -
O(n): Printing all the elements of an array of size n
https://dotnetfiddle.net/vCRlIh -
O(nlog(n)) : Merge Sort
-
O(n2) : Nested for loops that run from 0 to n, Selection Sort https://dotnetfiddle.net/2UcPYC
-
O(2n) : Recursive calling of the Fibonacci series
-
O(n!): Any algorithm that calculates all permutation of a given array.
Sorting Algorithms:
Sorting algorithms are a set of instructions that take an array or list as an input and arrange the items into a particular order.
Some of the most common sorting algorithms we are going to learn are :
- Selection Sort : Smallest number is found and saved to the start of the index on first iteration. In the next iteration, the next smallest number is found and is saved to the second index and so on.
Time Complexity: O(n2) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GUDLRan2DWM&t=321s
Method1 : Finding the index of the smallest number and swapping the numbers after the inner for loop iteration completes
https://dotnetfiddle.net/2enz3R
Method2: Swapping the numbers between start of the unsorted array section and the number as soon as a smaller number is found https://dotnetfiddle.net/D6SWh9
- Bubble Sort :In Bubble Sort adjacent elements are compared and least of which is moved towards left. After first iteration highest number is at the last index. After second iteration the second highest element is at second last position. So inside for loop becomes (j = 0; j < n - i - 1; j++)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Jdtq5uKz-w4&list=PL2_aWCzGMAwKedT2KfDMB9YA5DgASZb3U&index=4
Case1: Not optimized
https://dotnetfiddle.net/3InKV9
Case2: Optimized: The outloop stops if there is no swap inside the inner for loop
https://dotnetfiddle.net/SzFLze
Time Complexity: O(n2)
- Insertion Sort :
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TzeBrDU-JaY&list=PL2_aWCzGMAwKedT2KfDMB9YA5DgASZb3U&index=5
Here we create a hole and move it towards the start. The hole value is compared with all the elements to the left of it and if an element is larger it is moved one place to right. https://dotnetfiddle.net/XbpgMU
- Merge Sort
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0nlPxaC2lTw&list=PL2_aWCzGMAwKedT2KfDMB9YA5DgASZb3U&index=6
- Quick Sort
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=COk73cpQbFQ