Language - borkdominik/bigER GitHub Wiki
📖 Table of Contents
Last updated for: v0.3.0
ER models are specified in .erd files with the erdiagram keyword and a model name. After the header follows an optional notation, before specification of the model elements (i.e. entities and relationships).
Syntax Graph (click to open)

// header (required)
erdiagram Name
// notation (optional)
notation=default
// model elements
entity E1 { id1 key }
entity E2 { id2 key }
relationship Rel { E1 -> E2 } The notation option changes the representation in the ER diagram to a specific notation.
Syntax Graph (click to open)
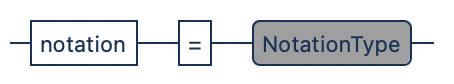
| Notation Type | Description |
|---|---|
default |
Default Notation |
chen |
Chen Notation |
bachman |
Bachman Notation |
crowsfoot |
Crow's Foot Notation |
See Notations for more information.
Single-line and multi-line comments are supported.
// single-line comment
/*
multi-line comment
*/An entity includes a name and attributes within curly braces.
Syntax Graph (click to open)
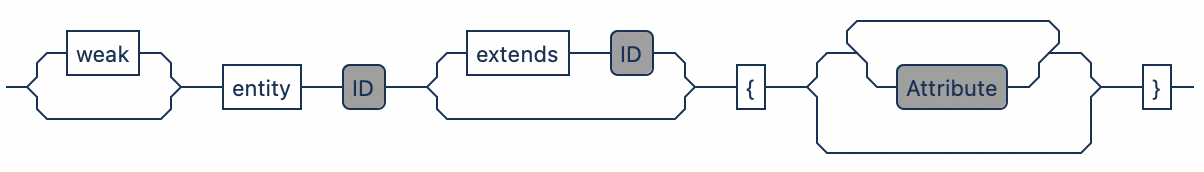
// Basic Entity
entity Basic {}
// Entity with Attributes
entity WithAttr {
attr1 key
attr2
}The preceding weak keyboard defines a weak entity. While a key attribute is used in strong entities, weak entities use a partial-key for identification. The dependency is declared with an additional weak relationship.
entity StrongEntity {
attr key
}
weak entity WeakEntity {
attr partial-key
}
weak relationship depends {
WeakEntity -> StrongEntity
}
⚠️ (experimental)
entity Vehicle {
manufacturer
cost
}
entity Car extends Vehicle {
serial_nr
}
Syntax Graph (click to open)
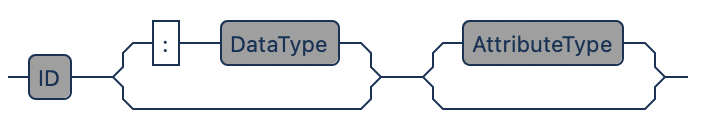
// Basic
attr
// Datatype
attr: VARCHAR(255)
attr : integer
// Classifiers
attr key
attr partial-key
attr derivedSyntax Graph (click to open)
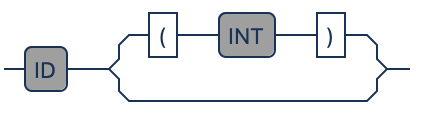
| Classifier | Description |
|---|---|
none |
Simple |
key |
Key attributes uniquely identify entities |
partial-key |
Partial key, used for weak entities |
derived |
Can be derived from another attribute (e.g., age from birthday) |
Syntax Graph (click to open)
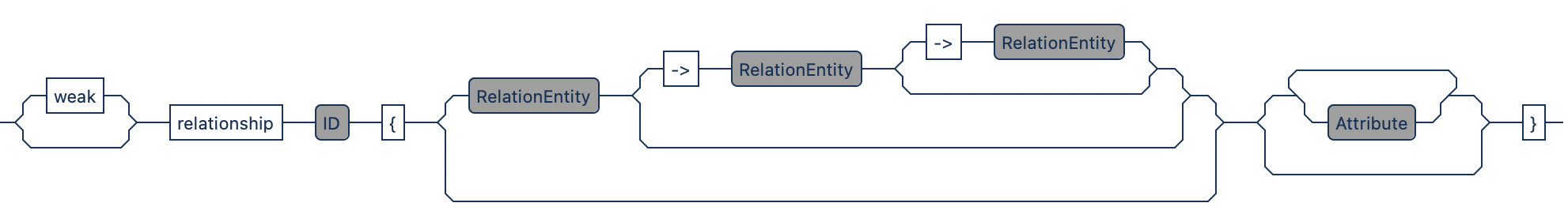

relationship Binary {
E1 -> E2
}
relationship Ternary {
E1 -> E2 -> E3
}
relationship Recursive {
E1 -> E1
}
Cardinality corresponds to the maximum constraint in the number of allowed entity instances. The value for cardinality can be either 1 (one) or N (many).
// 1-1 (One-To-One)
relationship Rel1 {
E1[1] -> E2[1]
}
// 1-N (One-To-Many)
relationship Rel2 {
E1[1] -> E2[N]
}
// N-N (Many-To-Many)
relationship Rel3 {
E1[N] -> E2[N]
}
Participation corresponds to the minimum constraint and can be either 0 or 1.
// zero-or-one (0..1) -> one-and-only-one (1..1)
relationship Rel1 {
Entity1[0..1] -> Entity2[1..1]
}
// [1..1] is the same as [1] (one)
relationship Rel2 {
Entity3[1..1] -> Entity4[1]
}
// zero-or-more (0..N) -> one-or-more (1..N)
relationship Rel3 {
Entity5[0..N] -> Entity6[1..N]
}
// [1..N] is the same as [N] (many)
relationship Rel4 {
Entity7[1..N] -> Entity8[N]
}Roles can be specified after cardinality- and participation constraints.
relationship Rel {
E1[ 1 | "role1" ] -> E2[ 1..N | "role2" ]
}