Full Stack Development - blockchainpsu/blockchain-essentials-spring2020 GitHub Wiki
Introduction
You've probably heard of full-stack development before.
Briefly, it's a ubiquitous term that encapsulates both backend and frontend development (server-side and client-side, respectively) into one neat developer.
There are some arguments that go into the effectiveness of such a model for development, but that's neither here nor there.
Additionally, throughout this module, we'll be making a full-stack suggestion-app to apply our concepts into practice.
As a precursor to writing blockchains, smart contracts, and decentralized apps, we need to go back to basics.
We will cover the following:
Stacks
Stacks are essentially a group of sufficiently important frameworks used to create different applications. To go "full-stack" means to have the ability to work with all layers of frameworks within a stack—frontend to backend to database.
For example, in our workshop, we use the MERN stack to create web applications. MERN stands for MongoDB, Express, React and Node. As you may already know, React will be used for the frontend, Node and Express for the backend, and MongoDB for the database.
Information Flow
Before we begin creating a web app, we need to understand the fundamentals and, more importantly, the flow of information through your app.
Full-stack development involves the creation and maintainence of several layers behind your app. In most cases, there will be three layers: the client (frontend), server (backend), and database. Web sequence diagrams are very helpful when trying to understand how information moves from one layer to the next.
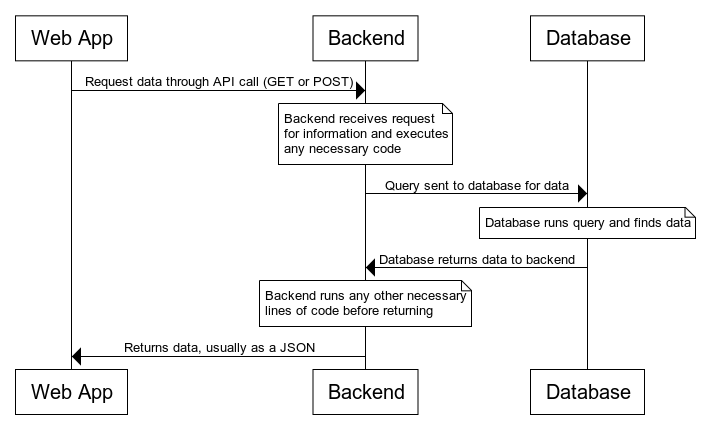
Consider the above image. When a user interacts with the browser or UI, the UI creates a request that moves to the backend—the server. Often, it's a request that will GET data or POST data (we'll cover these under Requests). The backend processes the request and then asks the database for the requested data. The database processes the query, finds the requested data (or throws an error), and gives the backend the data. From there, the backend sends the data back to the frontend UI, and the UI will process the data as it sees fit.
Environment Setup
If you're eager to learn about these technologies, you definitely have to start with a functional development environment.
- Download Git, if you haven't already. We'll use this for version control and pushing files to GitHub. After downloading, check that everything works by running
git --versionin the terminal; there should be no errors. - Download Node.js. We'll use this for our applications' backend. Check that everything works by running
node -vandnpm -vin the terminal; they should only output the version number. NPM, in particular, will be used to download different dependencies per project. - Download MongoDB. We'll use this as the framework for our database.
- Download an IDE that you're familiar with. We recommend using Visual Studio Code if you're unsure about what you want.
Additional Information
If you're looking for different resources, we highly recommend the following:
- Mozilla's MDN houses a number of beginner-friendly tutorials to web development. Their HTML, CSS, and JavaScript guides are good for a starting point. For something more comprehensive, look at their beginner's tutorial.
- Can't stop highly recommending University of Helsinki's open Full-Stack Development course. They cover React, NodeJS, Express, MongoDB, Redux, and GraphQL. It's extremely comprehensive, understandable, and structured like a course. After each section, there are accompanying exercises to test your knowledge. If you're serious about learning, definitely take this course.
- For all other topics, NodeSchool.io houses several tutorials that can be installed onto your local machine via npm.