Safe State - joshi66aryan/5143-Operating-System GitHub Wiki
In operating systems, the concept of safe and unsafe states is used to manage resource allocation and avoid deadlocks.
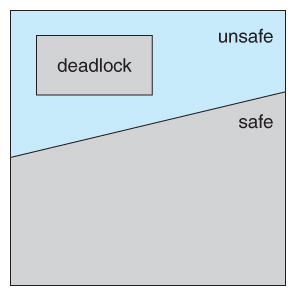
Figure - Safe, unsafe, and deadlocked state spaces.
A state is considered safe if:
- The system can allocate all resources requested by every process (up to their maximum needs) without entering a deadlock.
- A safe sequence of processes exists, defined as: { P0, P1, P2, ... PN}
In this sequence:
- Each process 𝑃𝑖 can complete using the resources currently allocated to it and those released by processes 𝑃𝑗 , where 𝑗 < 𝑖.
- Once 𝑃𝑖 completes, it releases its resources, making them available for subsequent processes in the sequence.
- A state is unsafe if no safe sequence exists.
-
Important:
- An unsafe state may lead to deadlock, but it does not guarantee that a deadlock will occur.
- Conversely, all safe states are guaranteed to be deadlock-free.
Consider a system with 12 tape drives and the following allocations:
| Process | Maximum Needs | Current Allocation |
|---|---|---|
| P0 | 10 | 5 |
| P1 | 4 | 2 |
| P2 | 9 | 2 |
To determine if the system is in a safe state, follow these steps:
- Check the available resources:
- Total resources = 12
- Current allocation = 5+2+2=9
- Available resources = 12−9=3.
- Evaluate possible sequences:
- Process P1: Needs 4−2=2, which can be satisfied with the available 3. After P1 finishes, it releases 2 more, making the total available = 3+2=5.
- Process P0: Needs 10−5=5, which can now be satisfied. After P0 finishes, it releases 5, making the total available = 5+5=10.
- Process P2: Needs 9−2=7, which can now be satisfied with the available 10.
- Safe Sequence: P1,P0,P2.
| Process | Maximum Needs | Current Allocation |
|---|---|---|
| P0 | 10 | 5 |
| P1 | 4 | 2 |
| P2 | 9 | 3 |
Updated Calculation:
-
Available resources = 12 − ( 5 + 2 + 3 ) = 2
-
Process P1: Needs 4−2=2, which can be satisfied. After P1 finishes, it releases 2, making the total available = 2+2=4.
-
Process P0: Needs 10−5=5, which cannot be satisfied with the available 4.
No safe sequence exists; the system is now in an unsafe state.