Page Tables - joshi66aryan/5143-Operating-System GitHub Wiki
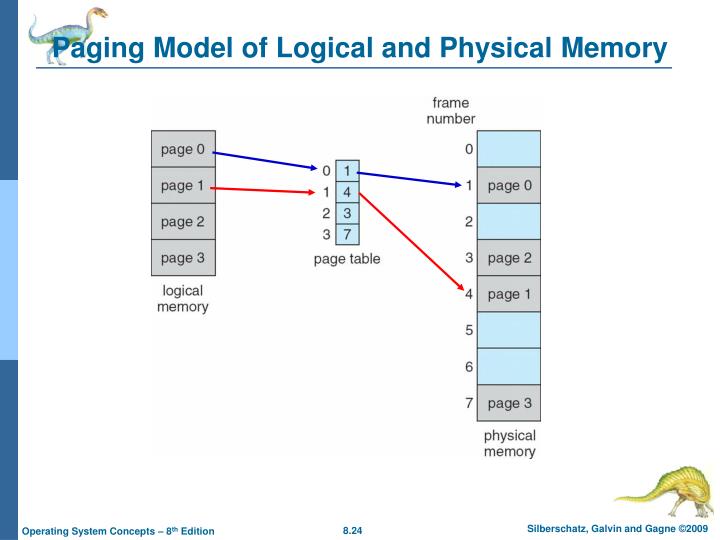
In operating systems, page tables are essential data structures that facilitate the mapping of a process's virtual addresses to physical memory addresses. This mechanism enables processes to operate within their own isolated address spaces, thereby enhancing both security and stability.
Key Components of a Page Table:
-
Page Number: Extracted from the higher-order bits of the virtual address, this number serves as an index into the page table.
-
Page Table Entry (PTE): Each entry contains crucial information, including:
- Frame Number: Identifies the specific physical memory frame corresponding to the virtual page.
- Control Bits: These may include:
- Present/Absent Bit: Indicates whether the page resides in physical memory or has been swapped out.
- Protection Bits: Define access permissions, such as read, write, or execute.
- Dirty Bit: Signals if the page has been modified since it was loaded into memory.
- Reference Bit: Shows whether the page has been accessed, aiding in page replacement decisions.
-
Page Offset: Derived from the lower-order bits of the virtual address, this offset specifies the exact byte within the page.
Address Translation Process:
When a process attempts to access a memory location, the system performs the following steps:
-
Virtual Address Breakdown:
- The virtual address is divided into two components:
- Page Number: Directs to the appropriate entry in the page table.
- Page Offset: Denotes the specific location within the page.
- The virtual address is divided into two components:
-
Page Table Lookup:
- The operating system consults the page table using the page number to find the corresponding PTE.
- If the Present Bit is set, the page is in physical memory, and the frame number is retrieved.
- If the Present Bit is not set, a page fault occurs, prompting the operating system to load the page from secondary storage into physical memory.
-
Physical Address Calculation:
- The frame number from the PTE is combined with the page offset to form the complete physical address.
-
Memory Access:
- The system accesses the physical memory at the calculated address to retrieve or store data.
Illustrative Diagram: