File Allocation Methods - aryanjoshi0823/5143-Operating-System GitHub Wiki
The allocation methods define how the files are stored in the disk blocks. There are three main disk space or file allocation methods.
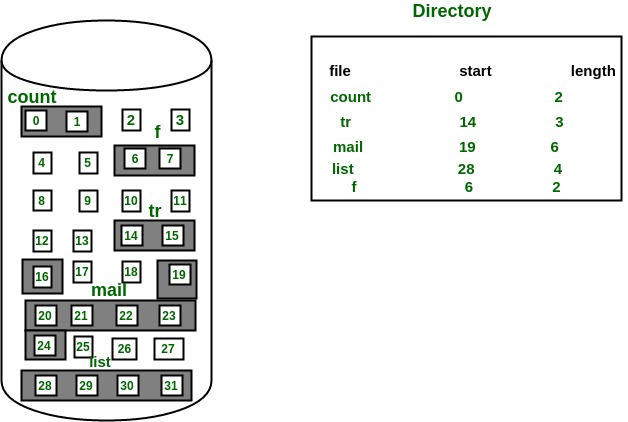
a) Contiguous Allocation:
-
In this scheme, each file occupies a contiguous set of blocks on the disk. For example, if a file requires n blocks and is given a block b as the starting location, then the blocks assigned to the file will be: b, b+1, b+2,……b+n-1.
-
This means that given the starting block address and the length of the file (in terms of blocks required), we can determine the blocks occupied by the file.
-
The directory entry for a file with contiguous allocation contains Address of starting block Length of the allocated portion.
-
The file ‘mail’ in the following figure starts from the block 19 with length = 6 blocks. Therefore, it occupies 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24 blocks.
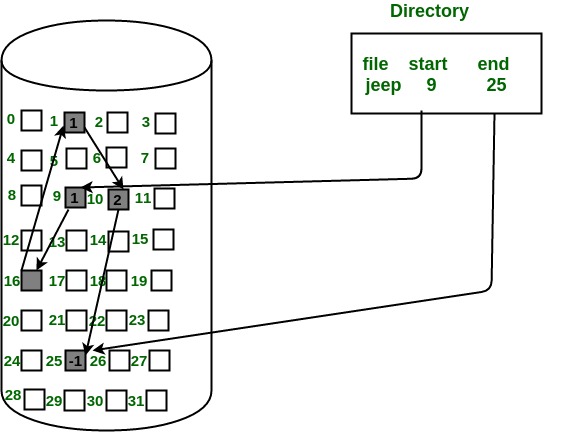
b) Linked Allocation:
-
In this scheme, each file is a linked list of disk blocks which need not be contiguous. The disk blocks can be scattered anywhere on the disk. The directory entry contains a pointer to the starting and the ending file block. Each block contains a pointer to the next block occupied by the file.
-
The file ‘jeep’ in following image shows how the blocks are randomly distributed. The last block (25) contains -1 indicating a null pointer and does not point to any other block.
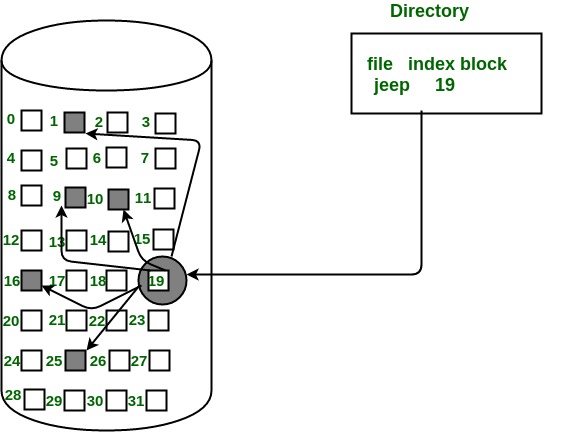
c) Indexed Allocation:
- In this scheme, a special block known as the Index block contains the pointers to all the blocks occupied by a file. Each file has its own index block. The ith entry in the index block contains the disk address of the ith file block. The directory entry contains the address of the index block as shown in the image: