example_bouncingBall - almarklein/visvis GitHub Wiki
#!/usr/bin/env python
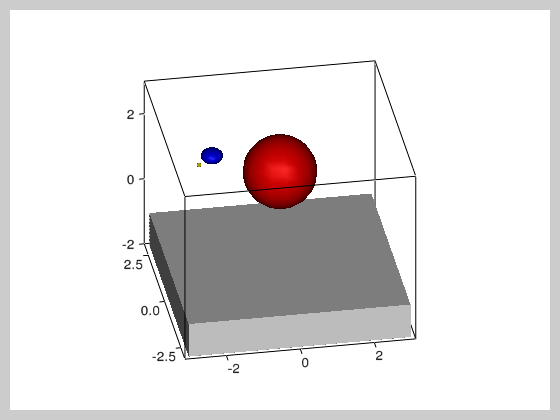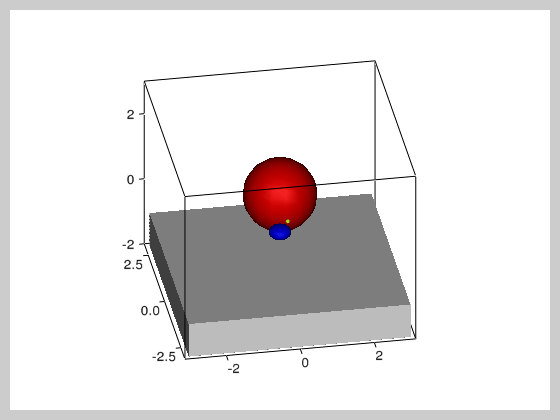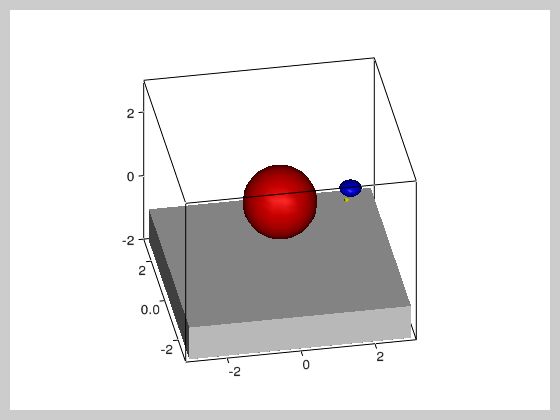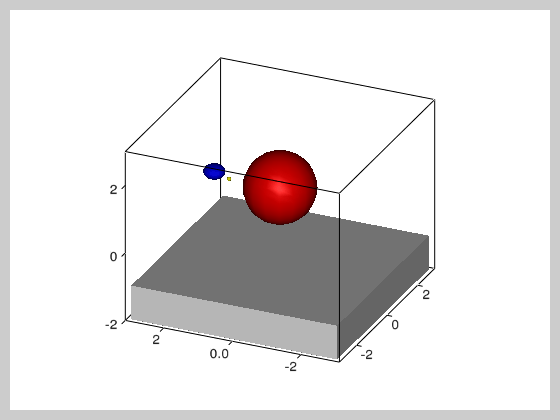
""" This example shows a ball that bounces on a surface and has
two balls rotating around it. It illustrates the use of timers
and how object hierarchy can be used to build (and move) complex
models consisting of multiple simple objects.
"""
import visvis as vv
# Create floor
floor = vv.solidBox((0,0,-1.5), (6,6,1))
# Create hierachy objects
sun = vv.solidSphere()
earth = vv.solidSphere((2,0,0),(0.3,0.3,0.2))
moon = vv.solidSphere((2,0,0),scaling=(0.2, 0.2, 0.3))
moon.parent = earth
earth.parent = sun
# Add transformations
sunTrans = sun.transformations[0]
earthRot = vv.Transform_Rotate(20)
moonRot = vv.Transform_Rotate(20)
earth.transformations.insert(0,earthRot)
moon.transformations.insert(0,moonRot)
# Set appearance
earth.faceColor = 'b'
moon.faceColor = 'y'
sun.faceColor = 'r'
# Set axes settings
axes = vv.gca()
axes.SetLimits(rangeZ=(-2,3))
# Define timer func
sun.zSpeed = 0.2
def onTimer(event):
# Move moon
moonRot.angle += 20
if moonRot.angle > 360:
moonRot.angle = 0
# Move earth
earthRot.angle += 5
if earthRot.angle > 360:
earthRot.angle = 0
# Move sun
sun.zSpeed -= 0.01
sunTrans.dz += sun.zSpeed
# Detect bounce
if sunTrans.dz < 0:
sun.zSpeed *= -1
sunTrans.dz = 0
# Update!
axes.Draw()
# Create time and enter main loop
timer = vv.Timer(axes, 100, False)
timer.Bind(onTimer)
timer.Start()
app = vv.use()
app.Run()
