FDD - allikvaleria/Phyton GitHub Wiki
Feature-Driven Development

History of Feature-Driven Development (FDD)
Feature-Driven Development (FDD) was introduced in 1997 by Jeff De Luca and his team at United Overseas Bank (UOB) in Singapore. It was developed as a response to the challenges they faced in large-scale software development projects that required a structured and systematic approach to deliver results on time and within budget.
The method was first applied to a real-world application for a large project involving 50 people with a strict 15-month timeline. The success of this project helped to refine the methodology and eventually, FDD was formally introduced to the software development community.
In 1999, FDD was discussed in the book Java Modeling in Color with UML, which further popularized the methodology within the software development world. Since then, FDD has grown to be widely used in large-scale projects due to its structured approach to managing feature development and delivering results incrementally.
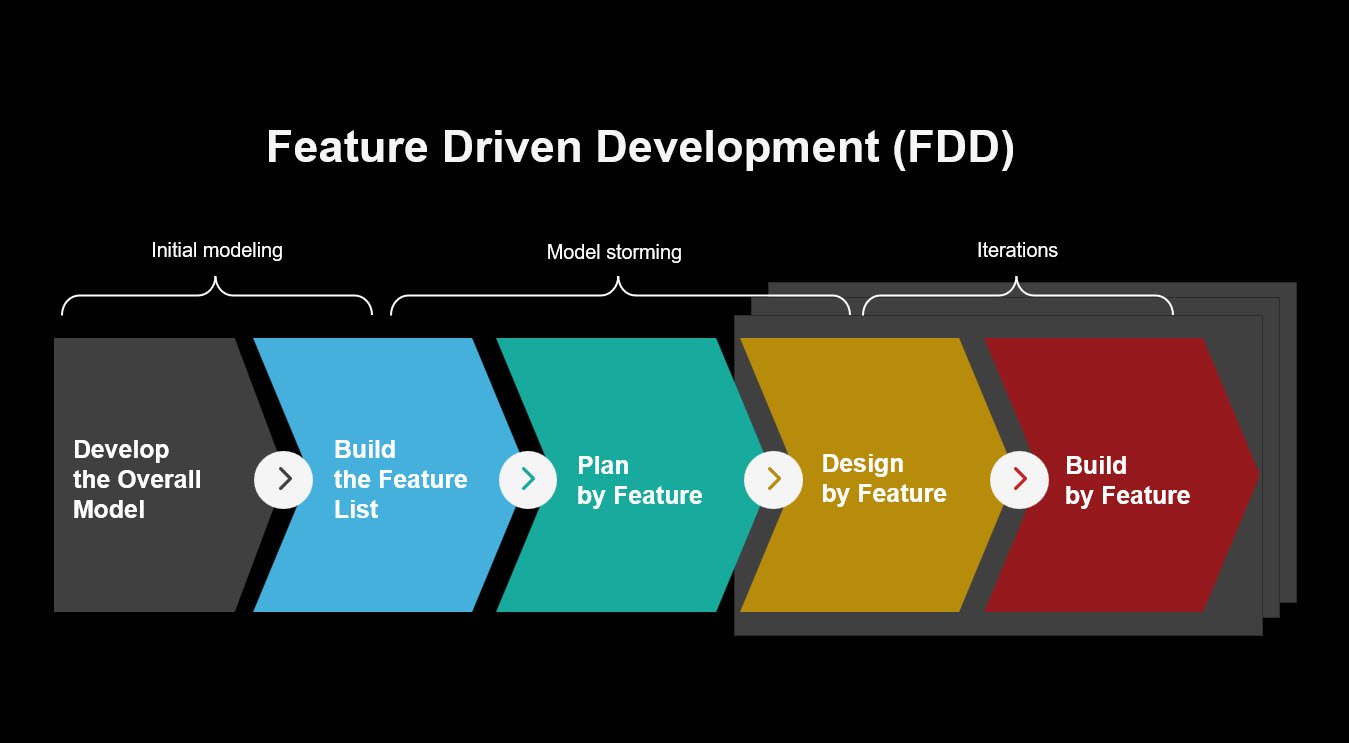
FDD Lifecycle
FDD is characterized by its strong emphasis on developing features, where each feature is typically a small, client-valued function that can be completed in 2 weeks or less. The FDD lifecycle is divided into a series of well-defined steps:
-
Build Overall Model: This is the initial step where the team builds a high-level model of the system. This model serves as a foundation for the features to be developed later. It includes understanding the domain and the system architecture.
-
Build Feature List: After the overall model is completed, the team breaks down the system into a list of features. These features are typically small, client-valued pieces of functionality that can be developed in 2 weeks or less. This list acts as the blueprint for the system’s development.
-
Plan by Feature: Once the feature list is ready, the development team organizes the features and plans the work. Each feature is assigned to a developer, and the schedule is set according to the team's capacity. The planning phase ensures that work is done incrementally, with clear goals for each feature.
-
Design by Feature: In this phase, the design team focuses on designing each feature in detail. The design work is done incrementally, with the design for each feature being finalized before development begins. This phase ensures that the features are well thought out and ready for development.
-
Build by Feature: Finally, the actual development work begins. Each feature is developed independently, and once completed, it is integrated into the overall system. The development process follows a rigorous process to ensure that each feature meets the specified requirements and functions as intended.
-
Generic Modeling Creation: In this initial phase, the team creates a high-level model of the system that serves as the foundation for future feature development. It includes domain and system architecture studies.
-
Creating a list of functionalities: Once the overall model is complete, the team breaks the system down into a list of functionalities, each representing a small feature that can be implemented in two weeks or less. This list serves as the system development plan.
-
Planning by feature: Once the list of features is ready, the team organizes the work for each feature. Each capability is assigned to a different developer, and a schedule is established to match the team's capabilities.
-
Design by Functional Capability: In this phase, the team designs each functional capability in detail. The design is done in phases and each capability is designed separately before development begins.
-
Feature-by-feature development: This is the actual development phase where each feature is designed and integrated into the system. The development follows a rigorous process to ensure that each feature meets the requirements and works properly.
Characteristics of FDD
- Short iterative: FDD lifecycle works in simple and short iterations to efficiently finish the work on time and gives good pace for large projects.
- Customer focused: This agile practice is totally based on inspection of each feature by client and then pushed to main build code.
- Structured and feature focused: Initial activities in lifecycle builds the domain model and features list in the beginning of timeline and more than 70% of efforts are given to last 2 activities.
- Frequent releases: Feature-driven development provides continuous releases of features in the software and retaining continuous success of the project.
The benefits and drawbacks of Feature-Driven Development (FDD):
| Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|
| Increased Efficiency: FDD breaks down development into smaller, manageable tasks, allowing teams to deliver software features more efficiently. | Requires Significant Planning: FDD needs careful upfront planning to create the feature list and model, which can take time. |
| Improved Team Coordination: FDD ensures that all team members are aligned and on the same page, enhancing collaboration. | May Not Be Suitable for Small Projects: FDD is designed for large-scale projects, so it might be overkill for small teams or simple projects. |
| Customer Satisfaction: The methodology focuses on delivering features that are valuable to the customer, ensuring their satisfaction. | Feature-Centric: Focusing primarily on features may sometimes overlook broader system concerns, such as technical debt or scalability. |
| Quality: FDD places a strong emphasis on maintaining high-quality standards throughout the development process, helping deliver reliable, bug-free software. | Rigid Structure: The process can sometimes feel rigid, especially if the project requires flexibility or changes to the feature list mid-development. |
Application of FDD in various industries
-
Software Development: FDD is used to manage the development of software products where it is important to clearly define functionality and iterate quickly to achieve results.
-
Financial Technology: For large-scale fintech projects where a high degree of accuracy and compliance with customer requirements is important, FDD helps to systematize and accelerate development processes, allowing faster adaptation of the product to market needs.
-
Mobile applications: For mobile applications where new features need to be added quickly with regular updates, FDD provides a convenient model for working on small but valuable features that can be released regularly.
-
Government and large corporations: In large and often bureaucratic organizations, FDD helps structure processes, simplifying project control and improving communication between different teams and levels.
Comparison of FDD with other development methodologies
| Methodology | Description | Comparison with FDD |
|---|---|---|
| Agile | A flexible, iterative approach focused on customer collaboration and rapid delivery. | Both Agile and FDD promote adaptability and frequent delivery. However, FDD is more structured, emphasizing modeling and planning around individual features. |
| Scrum | An Agile framework using short, time-boxed iterations (sprints) and daily team collaboration. | While Scrum focuses on delivering work in sprints, FDD centers on building specific, well-defined features. FDD offers more formal processes, which can benefit larger teams. |
| Waterfall | A linear, sequential development process with distinct phases (e.g., requirements, design, implementation). | Unlike Waterfall, FDD is iterative and allows for quicker adaptation to change through regular feature releases. |
FDD Full Form: Conclusion
In conclusion. Feature Driven Development (FDD) is a powerful and flexible software development methodology that emphasises iterative and incremental development, regular progress reporting, and code ownership. FDD is designed to deliver business value by focusing on delivering features or functionalities in a structured and organized manner. By following the five core principles of FDD. software development teams can deliver high-quality software products that meet the needs of their customers and provide value to their businesses. While FDD may not be suitable for every software development project, its flexibility and adaptability make it an attractive option for many organizations.