v1.1 5. Battery Board - alanbjohnston/CubeSatSim GitHub Wiki
These instructions are to build and test the Battery board.
You will need these tools:
- Safety glasses (to protect eyes while soldering or trimming leads)
- Soldering iron and solder (I use lead-free solder, but leaded solder is easier to work with)
- Needle nose pliers (to bend leads and hold parts)
- Side cutters (to trim leads)
- Wire strippers or a blade (to remove insulation from wires)
- Heat gun or hairdryer (to secure heat shrink tubing over connector wires)
Other tools that are helpful:
- Multimeter (to read battery voltage)
Checklist
The BOM has a sheet "By Steps" which lists the parts needed for each step in order. https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1y94Ut4WlnfJ7ZC4sU9S5768G5_BMU9aPUGnHsb_djTI/edit?usp=sharing If you have a Google account, you can make a copy of this spreadsheet ("File" then "Make a Copy") and check off each part as you install it.
For example, here is the checklist for this step:
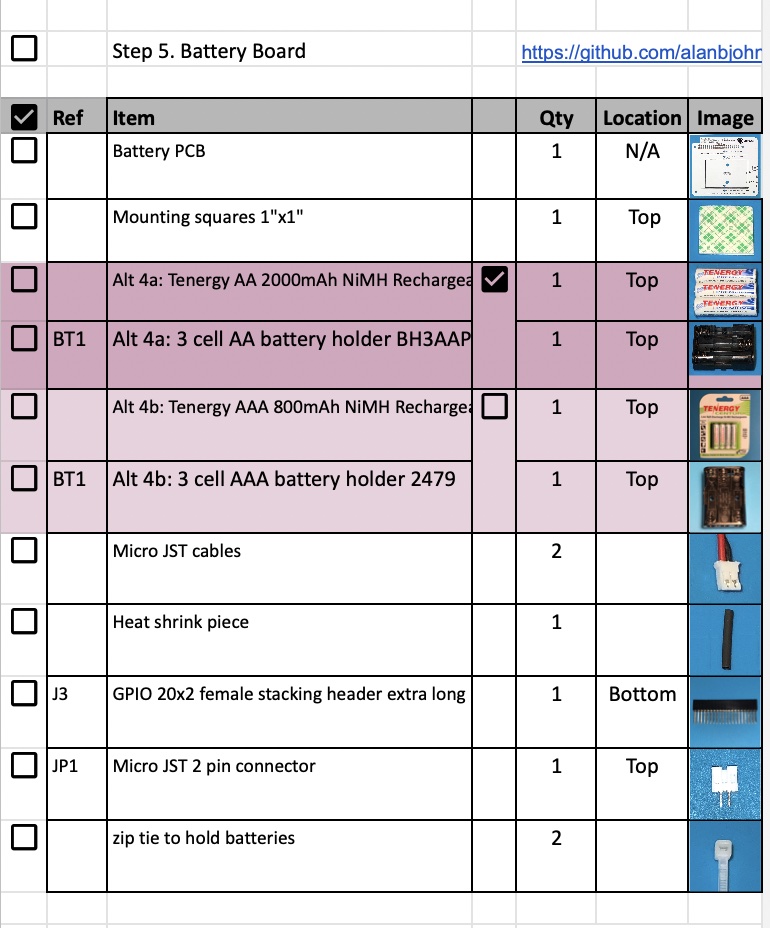
Battery Board Instructions
Video
Here is a video of this step: https://youtu.be/qfso6Rdalrw
Assembly
The Battery Board stacks on top of the main board.
Either AAA or AA batteries can be used. When doing public demos or events, I would recommend using AA batteries. The CubeSatSim will take over 3 hours to discharge and about the same time to recharge. I'd recommend AAA batteries for classroom demonstrations or videos where you want to see changes in battery voltage right away. The CubeSatSim will discharge in about an hour, and recharge in about the same time.
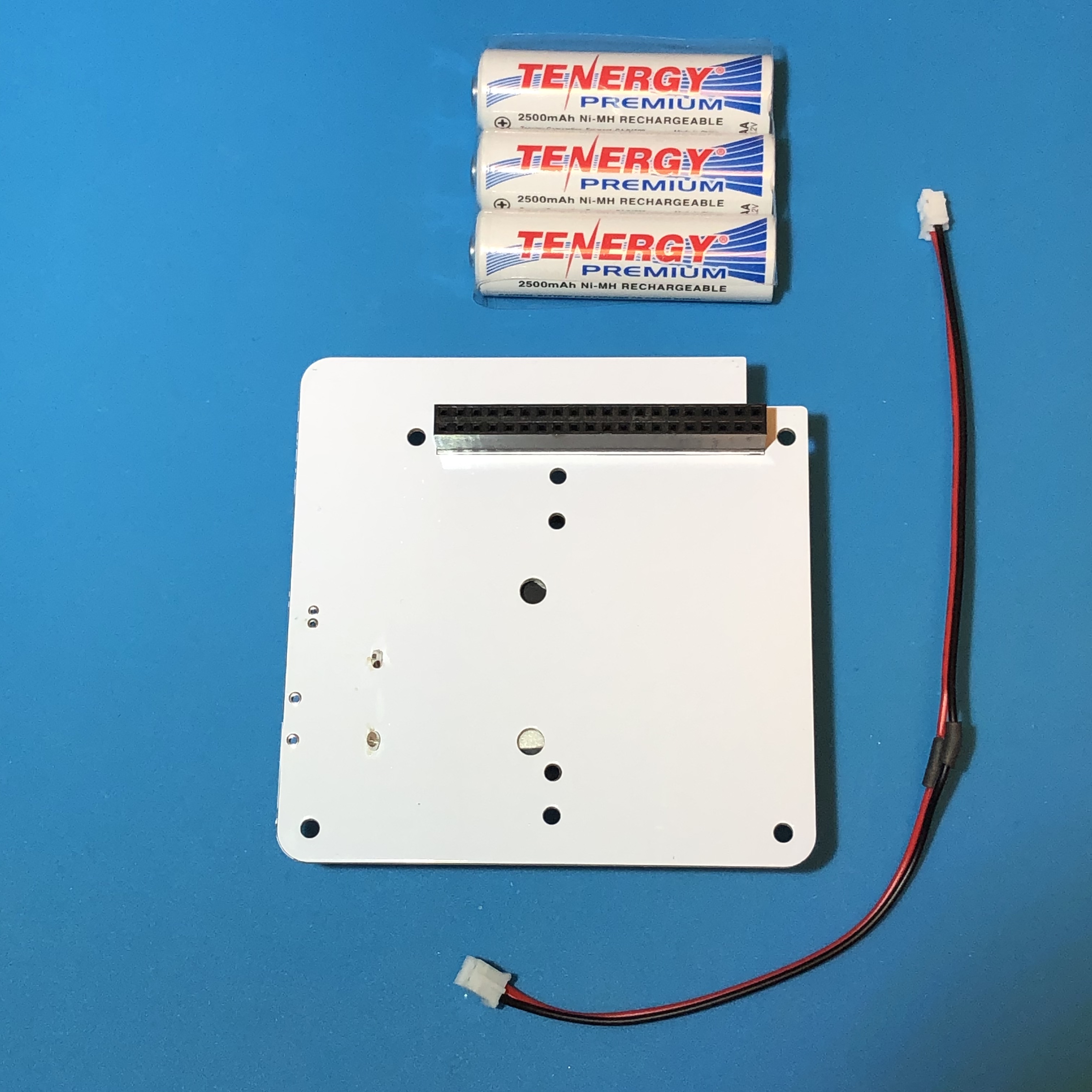
You will need the following parts to make the Battery board as described in the BOM https://cubesatsim.org/bom:
-
Battery PCB
-
Stacking GPIO header
-
Three Nickel Metal Hydride (NiMH) cells (either AA or AAA size)
-
Battery holder (either AA or AAA size)
-
Two JST 2.0 cables
-
JST 2.0 connector
-
A piece of heat shrink tube
-
Foam mounting square
-
Two small zip ties
The parts are shown here:
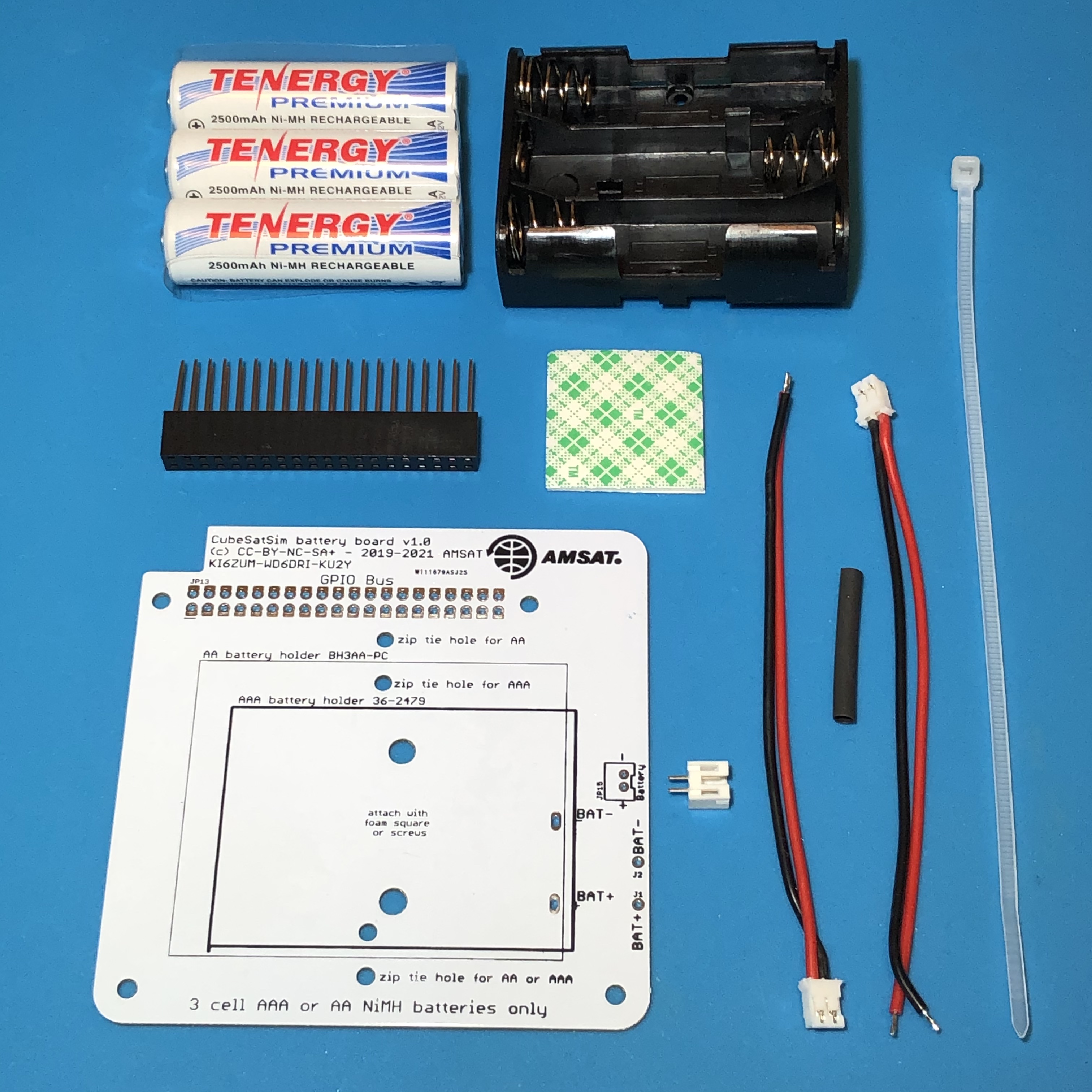
The battery holder can be mounted with screws and nuts, or with a foam square as shown here:
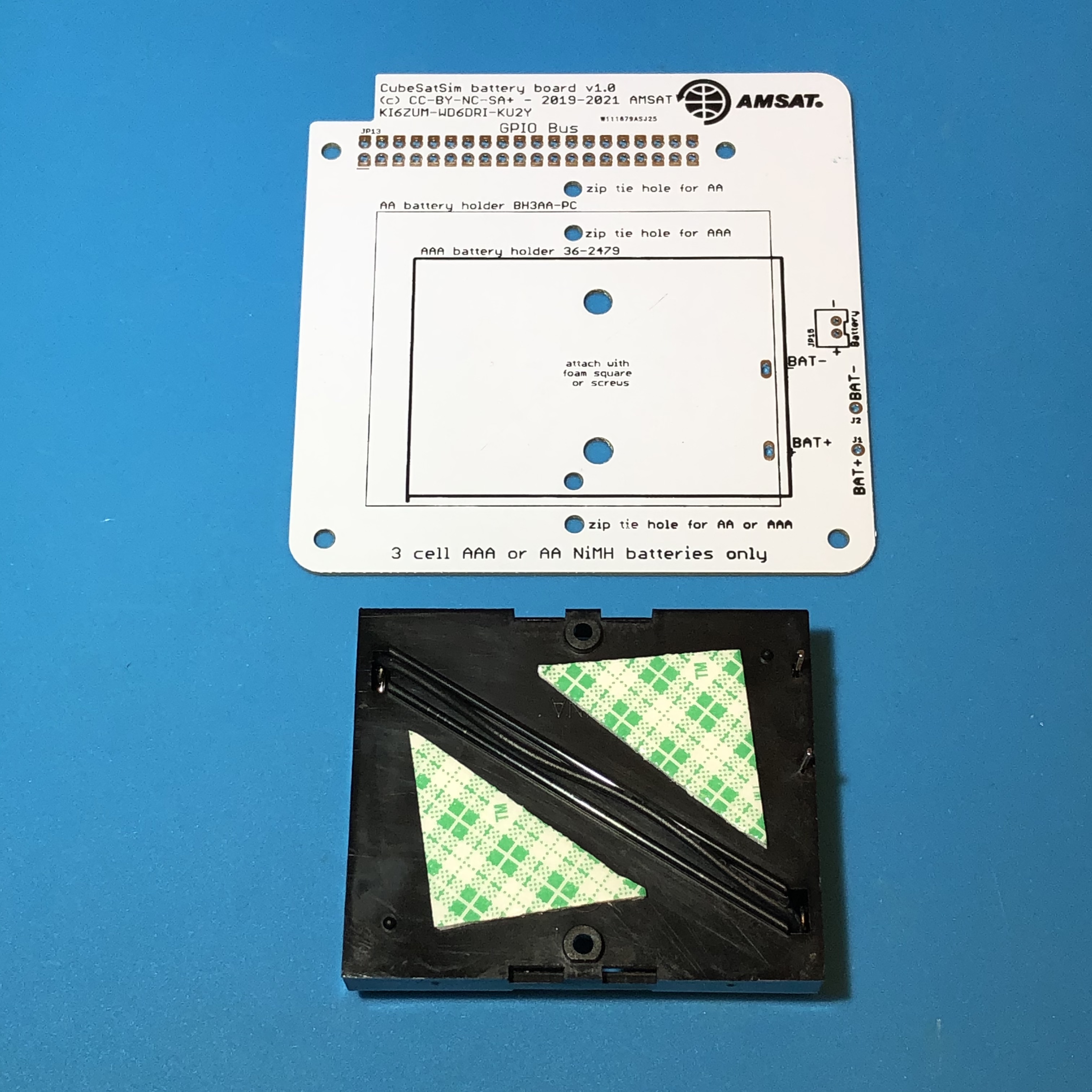

Insert the battery holder on the top of the PCB, then solder the two battery terminals on the bottom of the PCB. Next make up the micro JST cable (4"-6" long) by soldering the red to red and black to black of the JST 2.0 cables, and covering the connections with the cut in half heat shrink tubing, which you can shrink using the heat gun or hair dryer.
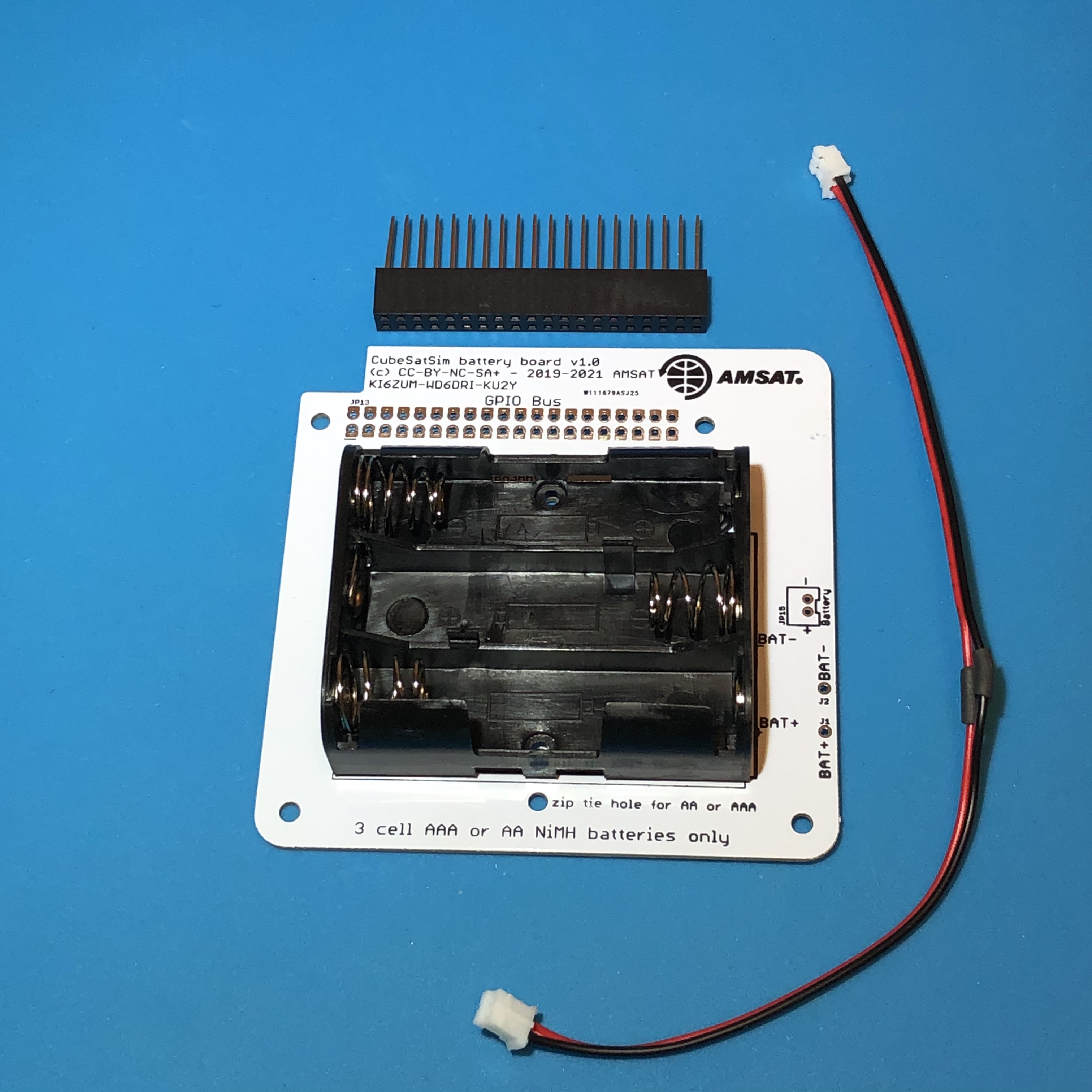
The stacking GPIO header is inserted on the bottom of the PCB as shown here:
Solder the GPIO header. If you just solder two pins on either side (4 pins in total), that will anchor it in place. Soldering all 40 pins doesn't do anything useful.
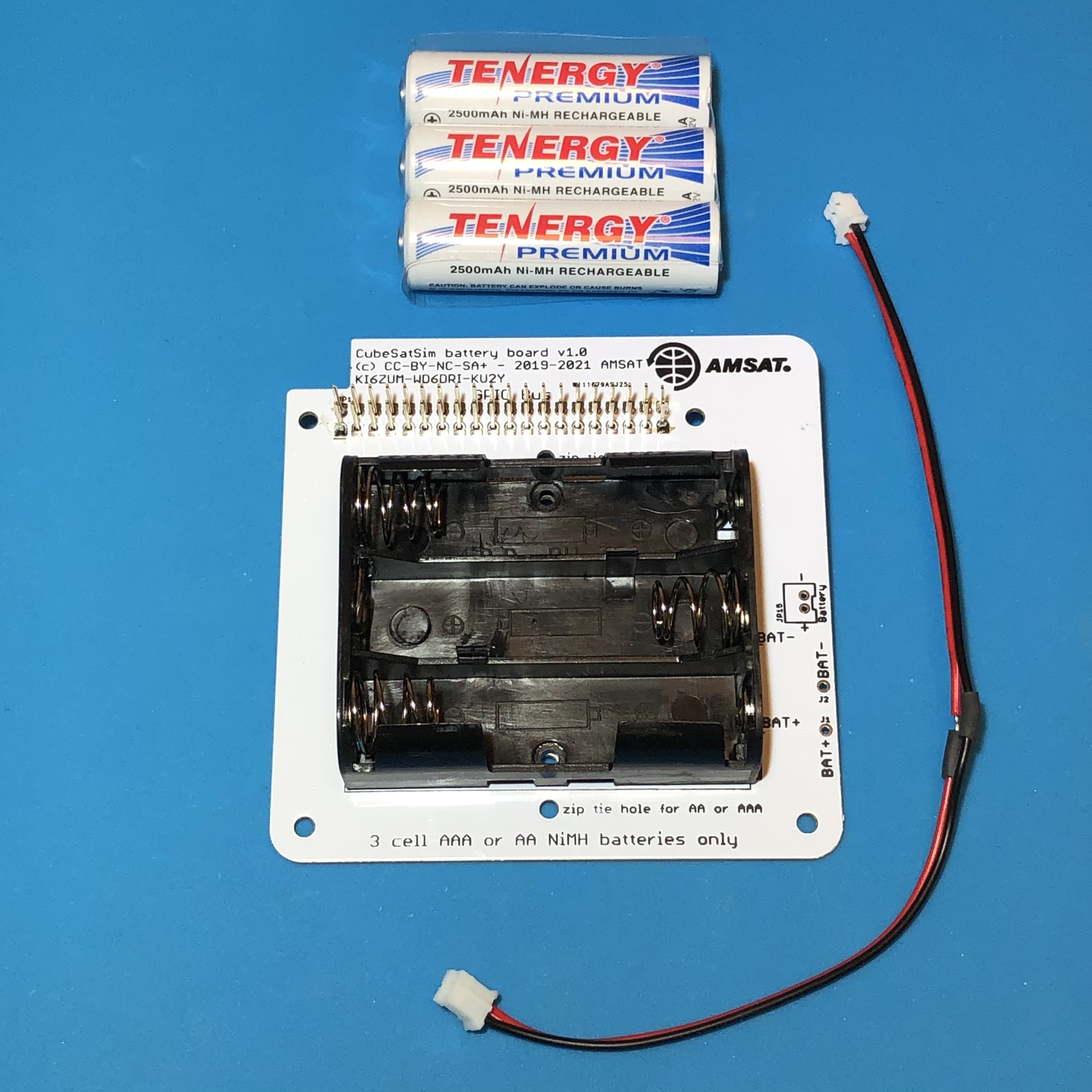
Next, insert a JST 2.0 connector onto the top of the PCB and solder. Pay attention to the polarity as indicated by the notch in the outline.
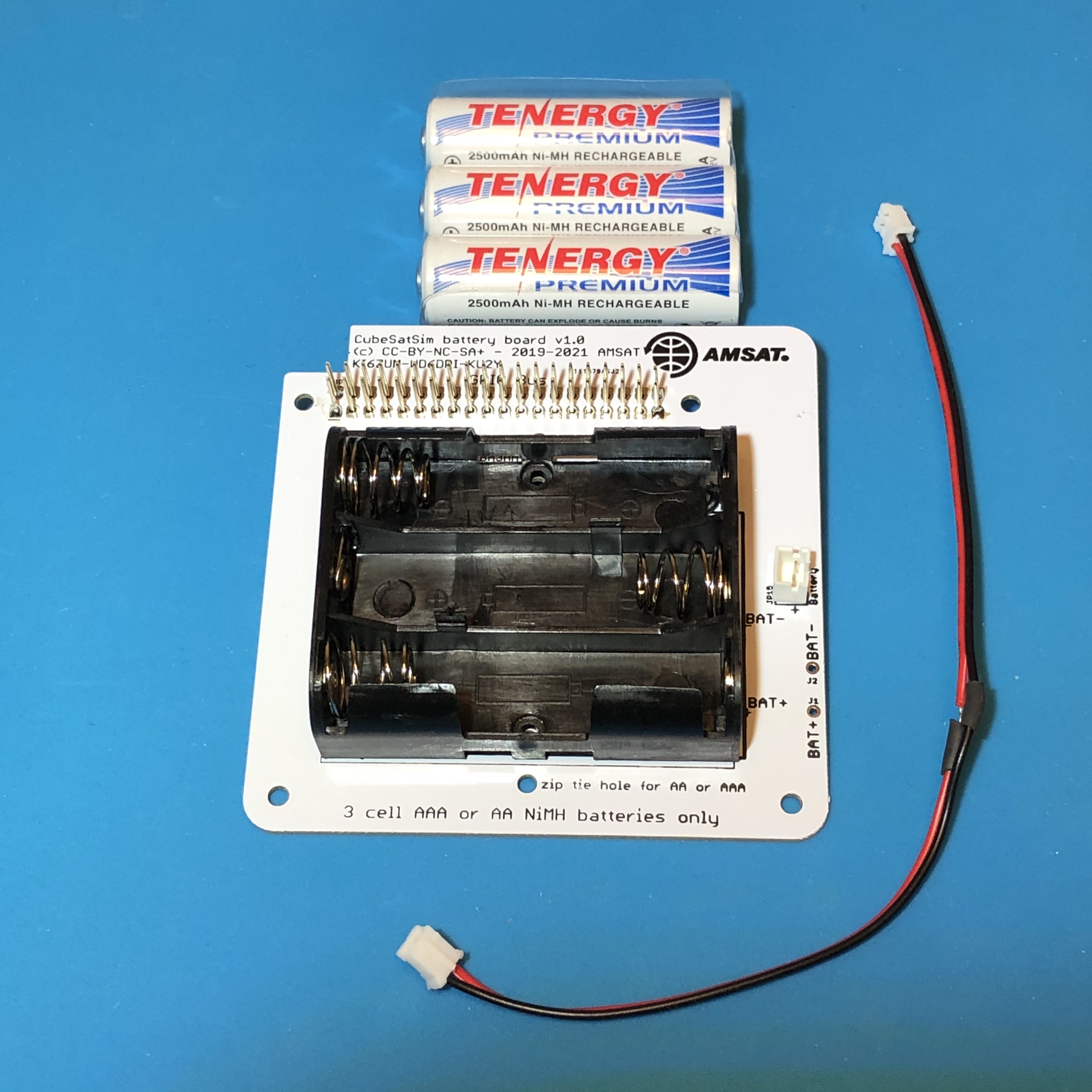

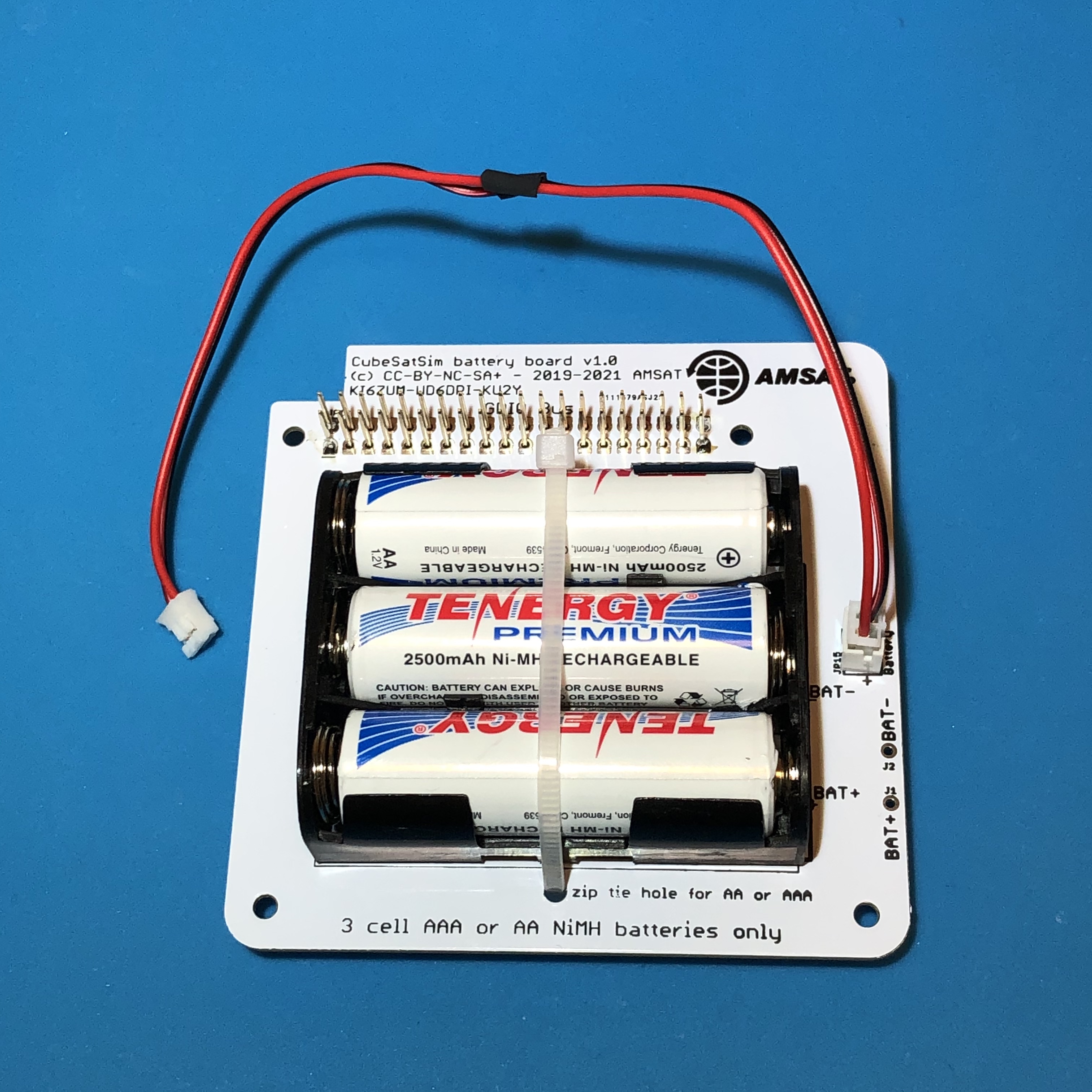
Insert the 3 batteries, paying attention to the polarity. Plug the JST cable into the JST connector on the board:
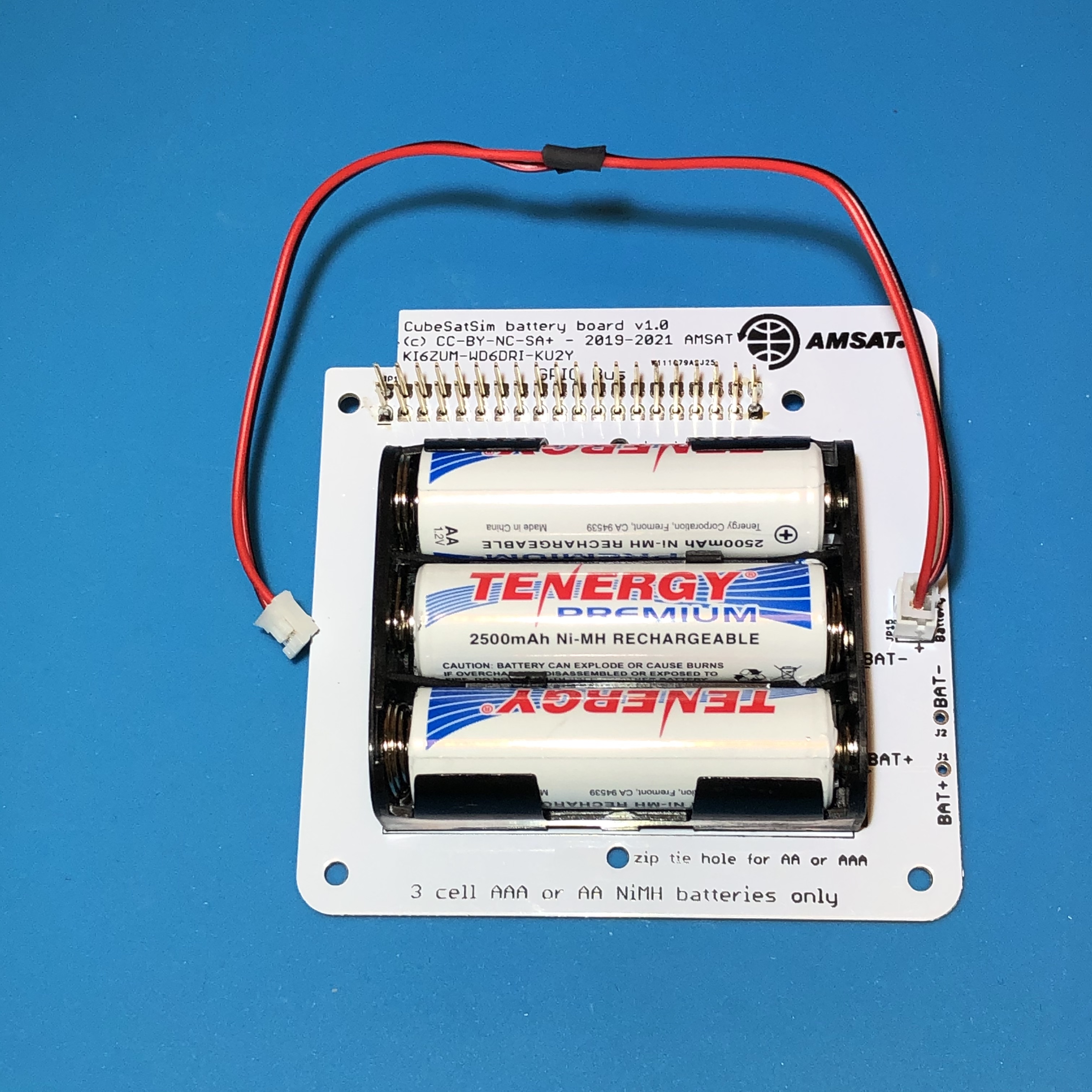
Finally, secure the batteries with two zip ties to ensure they can't pop out:

It is a good idea to test your battery polarity using a voltmeter. Use the BAT+ (J1) and BAT- (J2) test points on the board, being very careful not to short them together:
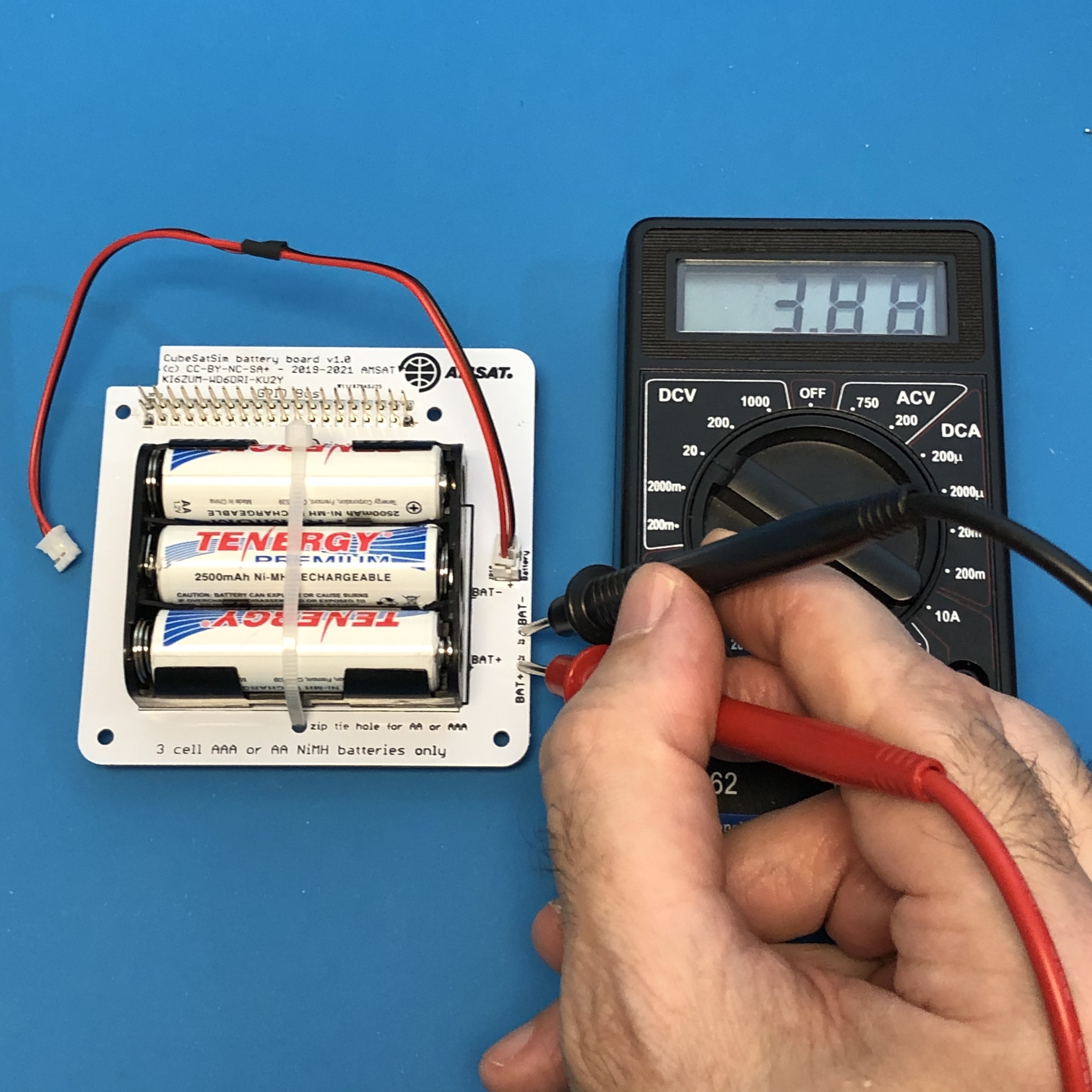
If you read a positive voltage in the range 3V - 4.5V, your Battery board is "nominal" and ready to be used. If you get a negative voltage, check that the red and black test leads are plugged into the positive and common inputs on your meter, or that your batteries aren't inserted backwards.
The next step is to assemble the Solar Panels.