WireGuard Setup Guide - ajgillis04/GillisDockerDepot GitHub Wiki
WireGuard is a fast, modern, and secure VPN tunnel that provides ease of use and high performance. It is available for various platforms including Windows, Linux, macOS, iOS, and Android.
- Docker installed (optional, for containerized setup)
-
Docker: My preferred use case continue to
Step 2 - Windows: Download the installer from the official WireGuard website and follow the installation instructions.
-
Linux: Use your package manager to install WireGuard. For example, on Ubuntu:
sudo apt install wireguard
- Open
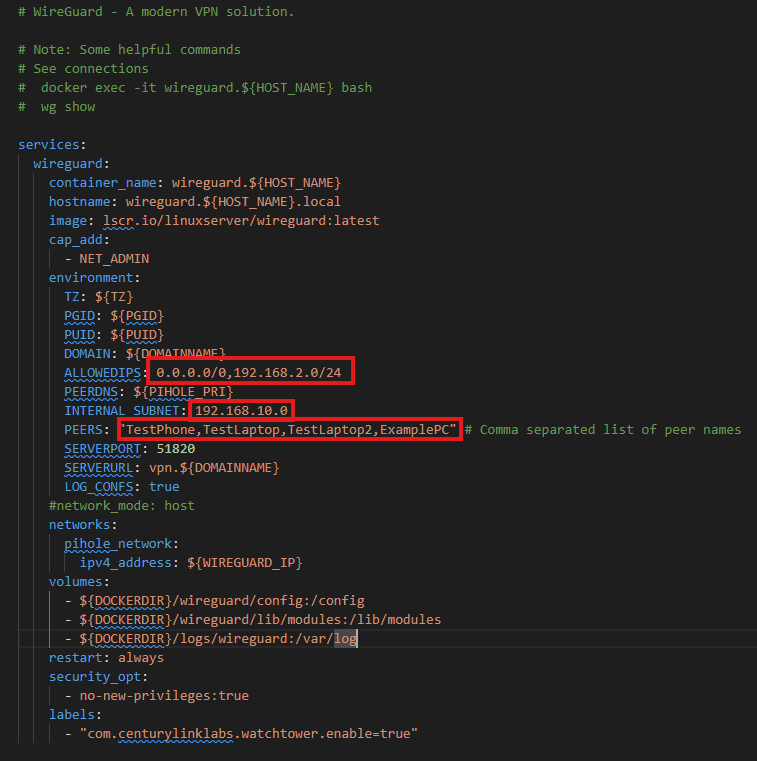
wireguard.yamland update the unique to you settings - ALLOWEDIPS: 0.0.0.0/0,<your networks IP range
- PEERDNS: ${PIHOLE_PRI} - This is optional, this will make sure everyone who connects to the VPN will use PIHole
- INTERNAL_SUBNET: <Choose an IP range for your VPN clients ie) 192.168.10.0
- PEERS: <Give each peer you intend to connect with a name here. You can add more later)
- Save
wireguard.yaml - Re-create the container
docker compose -p mediaserver -f docker-compose-server<num>.yaml up --detach
Follow these steps to reset the private and public keys for a WireGuard peer:
-
Generate New Private Key:
wg genkey | tee /path/to/new_private_key -
Generate New Public Key from Private Key:
- Note, if you get Permission denied set the permissions to write for the file.
wg pubkey < /path/to/new_private_key > /path/to/new_public_key
-
Update WireGuard Configuration File:
- Update your WireGuard configuration file (wg0.conf or similar) with the new keys.
-
Restart WireGuard Interface:
- Restart the WireGuard interface to apply the changes.
sudo wg-quick down wg0 sudo wg-quick up wg0
-
Update Peers:
- Inform the affected peer(s) to update their configuration with the new public key.
- Windows 10 or 11 (Pro or Home)
- Administrator access (for service registration, firewall, and ICS)
- WireGuard installed from https://www.wireguard.com/install
- Static IP or dynamic DNS (for remote peer access)
- Port forwarding enabled on your router (UDP 51820 to your Windows host)
To allow external clients to reach your WireGuard server, forward UDP port 51820 on your router:
- Protocol: UDP
- External Port: 51820
- Internal IP: IP of your Windows WireGuard server (e.g., 192.168.2.100)
- Internal Port: 51820
This ensures incoming VPN traffic is routed correctly to your WireGuard service.
If your public IP changes frequently, consider using a dynamic DNS service like DuckDNS or No-IP and set your client’s Endpoint to that hostname.
- Download the Windows installer from https://www.wireguard.com/install
- Run the installer and launch the WireGuard GUI
wg genkey | tee privatekey | wg pubkey > publickey-
privatekey→ used in[Interface]block -
publickey→ shared with peers in their[Peer]block
- Click “Add Tunnel” → “Add empty tunnel”
- The GUI will auto-generate a keypair
- You can copy the public key to share with peers
-
Open WireGuard GUI → Add Tunnel → Add empty tunnel
-
Set:
-
PrivateKey: use the key you generated -
Address:10.9.0.1/24(or your chosen VPN subnet) -
ListenPort:51820 -
DNS: optional, e.g.,192.168.2.12for Pi-hole
-
-
Add
[Peer]block for each client:
[Peer]
PublicKey = <client public key>
AllowedIPs = 10.9.0.2/32[Interface]
PrivateKey = <server private key>
Address = 10.9.0.1/24
ListenPort = 51820
DNS = 192.168.2.12
[Peer]
PublicKey = <client public key>
AllowedIPs = 10.9.0.2/32Use WireGuard mobile app or another Windows/Linux client
Set:
-
PrivateKey: generate on client -
Address:10.9.0.2/32 -
DNS: optional, e.g.,192.168.2.12 -
Endpoint:<your WAN IP or DNS>:51820- Use your public IP (e.g.,
142.x.x.x) or a dynamic DNS hostname (e.g.,myvpn.duckdns.org)
- Use your public IP (e.g.,
-
AllowedIPs:0.0.0.0/0, ::/0for full tunnel -
PersistentKeepalive = 25(optional for NAT traversal)
[Interface]
PrivateKey = <client private key>
Address = 10.9.0.2/32
DNS = 192.168.2.12
[Peer]
PublicKey = <server public key>
Endpoint = myvpn.duckdns.org:51820
AllowedIPs = 0.0.0.0/0, ::/0
PersistentKeepalive = 25From PowerShell (Admin), run:
"C:\Program Files\WireGuard\wireguard.exe" /installtunnelservice "C:\Program Files\WireGuard\Data\Configurations\wg-server.conf.dpapi"Confirm service appears in services.msc as:
WireGuard Tunnel: wg-server
Set to Automatic startup
Allow inbound UDP traffic on port 51820:
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "WireGuard UDP 51820" `
-Direction Inbound `
-Protocol UDP `
-LocalPort 51820 `
-Action Allow `
-Profile Any- Open
ncpa.cpl(Network Connections) - Right-click your main internet adapter → Properties → Sharing tab
- Enable “Allow other network users to connect…”
- Select the WireGuard adapter (e.g.,
wg_server)
To prevent routing issues and handshake failures, disable IPv6 system-wide and unbind it from all active adapters:
# Disable IPv6 system-wide and unbind from adapters
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip6\Parameters" -Name "DisabledComponents" -Value 0xFF
Get-NetAdapter | Where-Object { $_.Status -eq "Up" } | ForEach-Object {
Disable-NetAdapterBinding -Name $_.Name -ComponentID ms_tcpip6 -Confirm:$false
}Reboot after running to finalize changes.
From the client (e.g., phone):
ping 192.168.2.1 # Router
ping 192.168.2.12 # Pi-hole
nslookup google.com 192.168.2.12
curl https://icanhazip.comYou should see:
- Successful pings to LAN devices
- DNS resolution via Pi-hole
- Public IP matching your home WAN
.\wg.exe showShows:
- Latest handshake
- RX/TX stats
- Peer endpoint and status
### Troubleshooting
**Common Issues**:⚠️ July 2025, Note for Docker/Alpine Users
If you're using the linuxserver/wireguard container image and encountered issues around July 2025 (like WireGuard tunnels not passing traffic), it may be due to changes in Alpine base image or iptables configuration.
The image tagged 1.0.20250521-r0-ls81 introduced breaking changes — rolling back to 1.0.20210914-r4-ls80 resolved it for many.
To avoid future breakage, consider pinning your WireGuard image tag explicitly in docker-compose.yaml, and monitor the [GitHub repo](https://github.com/linuxserver/docker-wireguard) for updates or changelogs.
**Logs**: Check container logs (docker logs <container_name>) for error messages related to iptables, interfaces, or peer connections.
✘ wireguard Error manifest unknown Error response from daemon: manifest unknown
**Support**: Monitor the [GitHub repo](https://github.com/linuxserver/docker-wireguard) for updates or changelogs.