Home - abhi0751/Blogimages GitHub Wiki
You can use a network security group to filter network traffic inbound and outbound from a virtual network subnet.
Network security groups contain security rules that filter network traffic by IP address, port, and protocol. Security rules are applied to resources deployed in a subnet.
In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Create a network security group and security rules
- Create a virtual network and associate a network security group to a subnet
- Deploy virtual machines (VM) into a subnet
- Test traffic filters
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you begin.
- An Azure subscription.
Sign in to the Azure portal at https://portal.azure.com.
- Select Create a resource in the upper left-hand corner of the portal.
- In the search box, enter Virtual Network. Select Virtual Network in the search results.
- In the Virtual Network page, select Create.
- In Create virtual network, enter or select this information in the Basics tab:
TABLE 1 Setting Value Project details Subscription Select your subscription. Resource group Select Create new.
Enter myResourceGroup.
Select OK.Instance details Name Enter myVNet. Region Select (US) East US. - Select the Review + create tab, or select the blue Review + create button at the bottom of the page.
- Select Create.
An application security group enables you to group together servers with similar functions, such as web servers.
- Select Create a resource in the upper left-hand corner of the portal.
- In the search box, enter Application security group. Select Application security group in the search results.
- In the Application security group page, select Create.
- In Create an application security group, enter or select this information in the Basics tab:
TABLE 2 Setting Value Project details Subscription Select your subscription. Resource group Select myResourceGroup. Instance details Name Enter myAsgWebServers. Region Select (US) East US. - Select the Review + create tab, or select the blue Review + create button at the bottom of the page.
- Select Create.
- Repeat step 4 again, specifying the following values:
TABLE 3 Setting Value Project details Subscription Select your subscription. Resource group Select myResourceGroup. Instance details Name Enter myAsgMgmtServers. Region Select (US) East US. - Select the Review + create tab, or select the blue Review + create button at the bottom of the page.
- Select Create.
A network security group secures network traffic in your virtual network.
- Select Create a resource in the upper left-hand corner of the portal.
- In the search box, enter Network security group. Select Network security group in the search results.
- In the Network security group page, select Create.
- In Create network security group, enter or select this information in the Basics tab:
TABLE 4 Setting Value Project details Subscription Select your subscription. Resource group Select myResourceGroup. Instance details Name Enter myNSG. Location Select (US) East US. - Select the Review + create tab, or select the blue Review + create button at the bottom of the page.
- Select Create.
In this section, we'll associate the network security group with the subnet of the virtual network we created earlier.
- In the Search resources, services, and docs box at the top of the portal, begin typing myNsg. When myNsg appears in the search results, select it.
- In the overview page of myNSG, select Subnets in Settings.
- In the Settings page, select Associate:
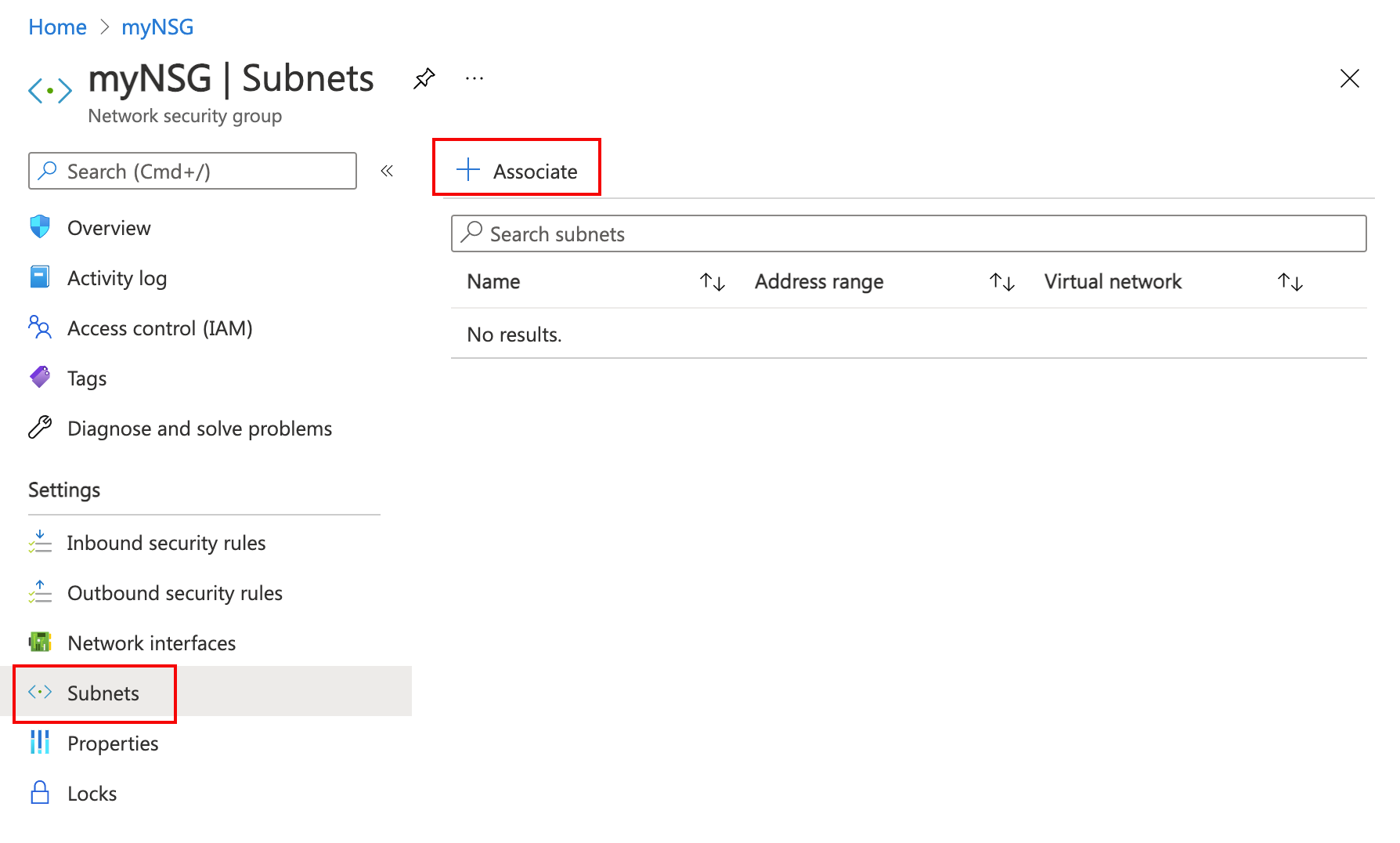
- Under Associate subnet, select Virtual network and then select myVNet.
- Select Subnet, select default, and then select OK.
- In Settings of myNSG, select Inbound security rules.
- In Inbound security rules, select + Add:
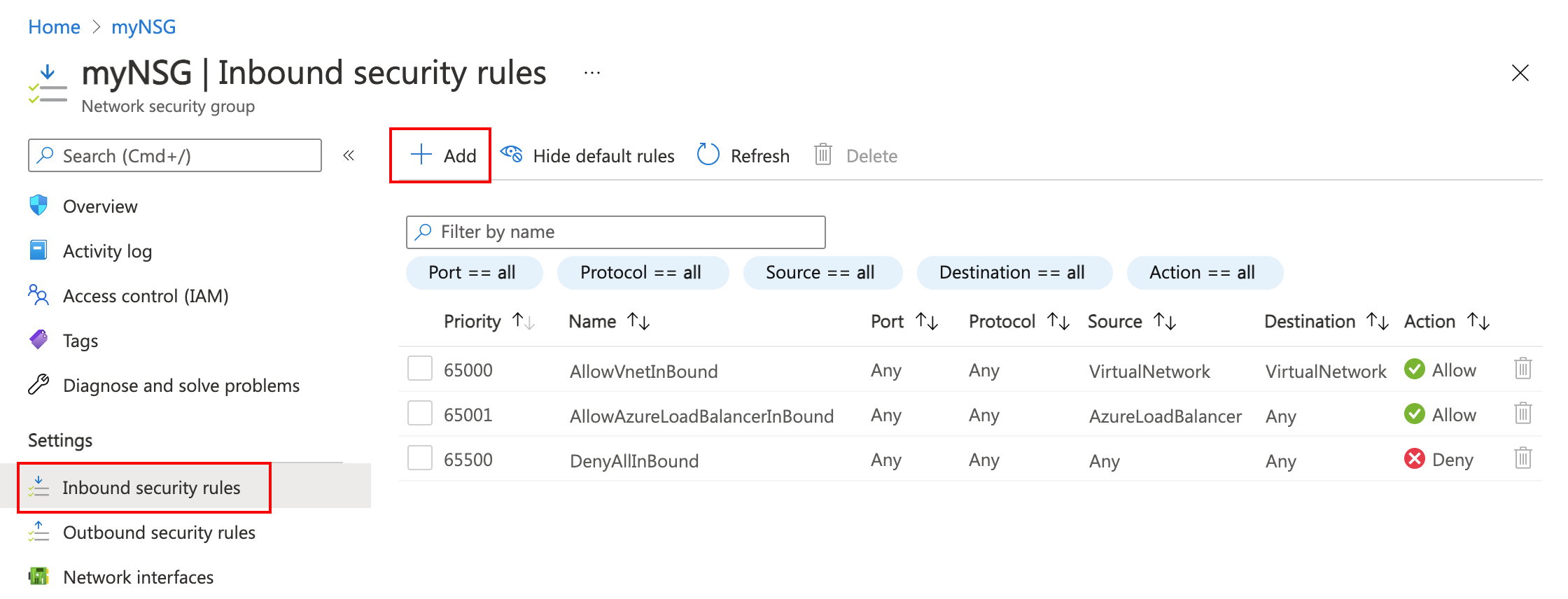
- Create a security rule that allows ports 80 and 443 to the myAsgWebServers application security group. In Add inbound security rule, enter or select the following information:
TABLE 5 Setting Value Source Leave the default of Any. Source port ranges Leave the default of (*) Destination Select Application security group. Destination application security group Select myAsgWebServers. Service Leave the default of Custom. Destination port ranges Enter 80,443. Protocol Select TCP. Action Leave the default of Allow. Priority Leave the default of 100. Name Enter Allow-Web-All. 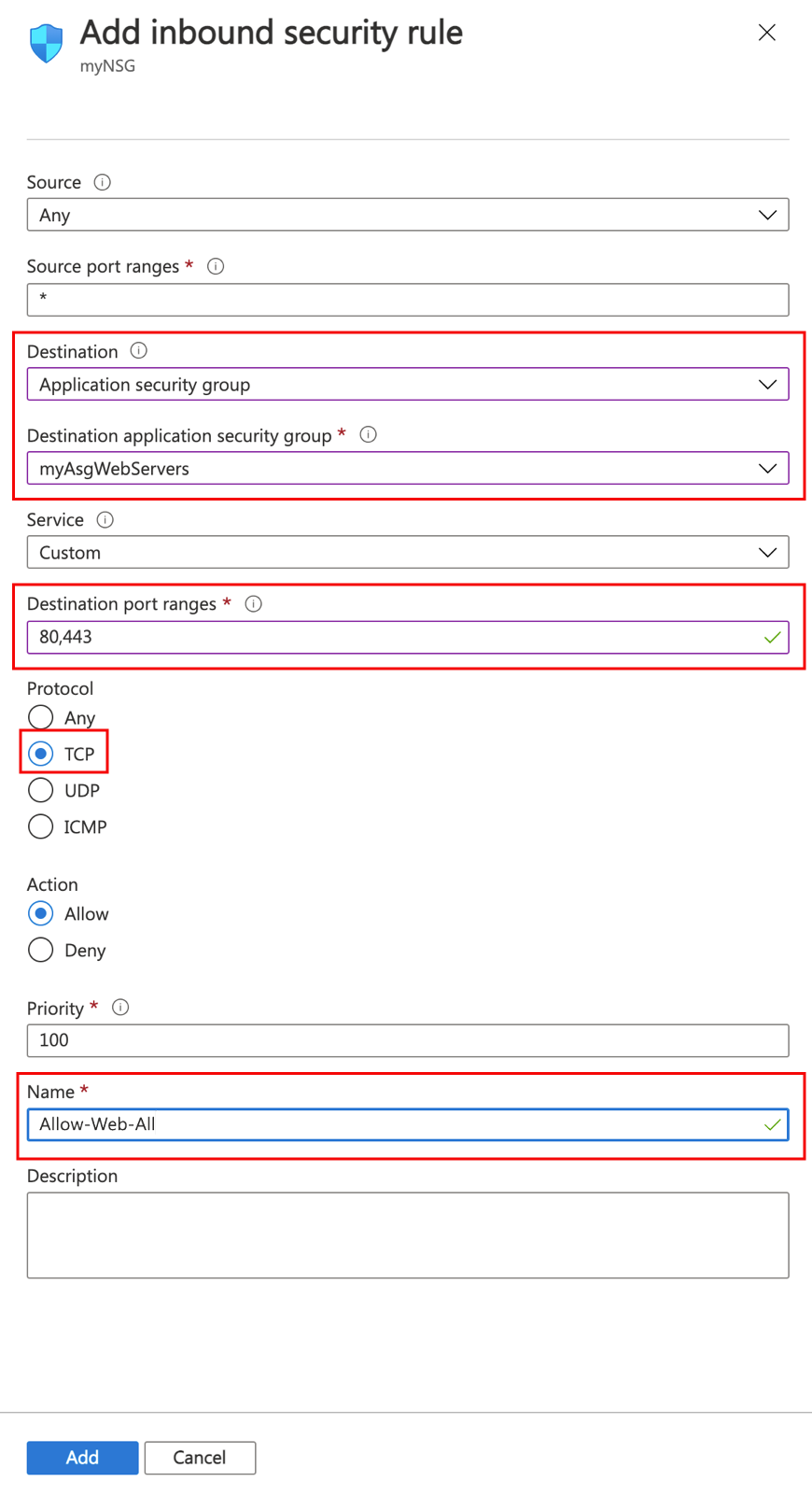
- Complete step 2 again, using the following values:
TABLE 6 Setting Value Source Leave the default of Any. Source port ranges Leave the default of (*) Destination Select Application security group. Destination application security group Select myAsgMgmtServers. Service Leave the default of Custom. Destination port ranges Enter 3389. Protocol Select TCP. Action Leave the default of Allow. Priority Leave the default of 110. Name Enter Allow-RDP-All. Caution
In this article, RDP (port 3389) is exposed to the internet for the VM that is assigned to the myAsgMgmtServers application security group.
For production environments, instead of exposing port 3389 to the internet, it's recommended that you connect to Azure resources that you want to manage using a VPN, private network connection, or Azure Bastion.
For more information on Azure Bastion, see What is Azure Bastion?.
Once you've completed steps 1-3, review the rules you created. Your list should look like the list in the following example:
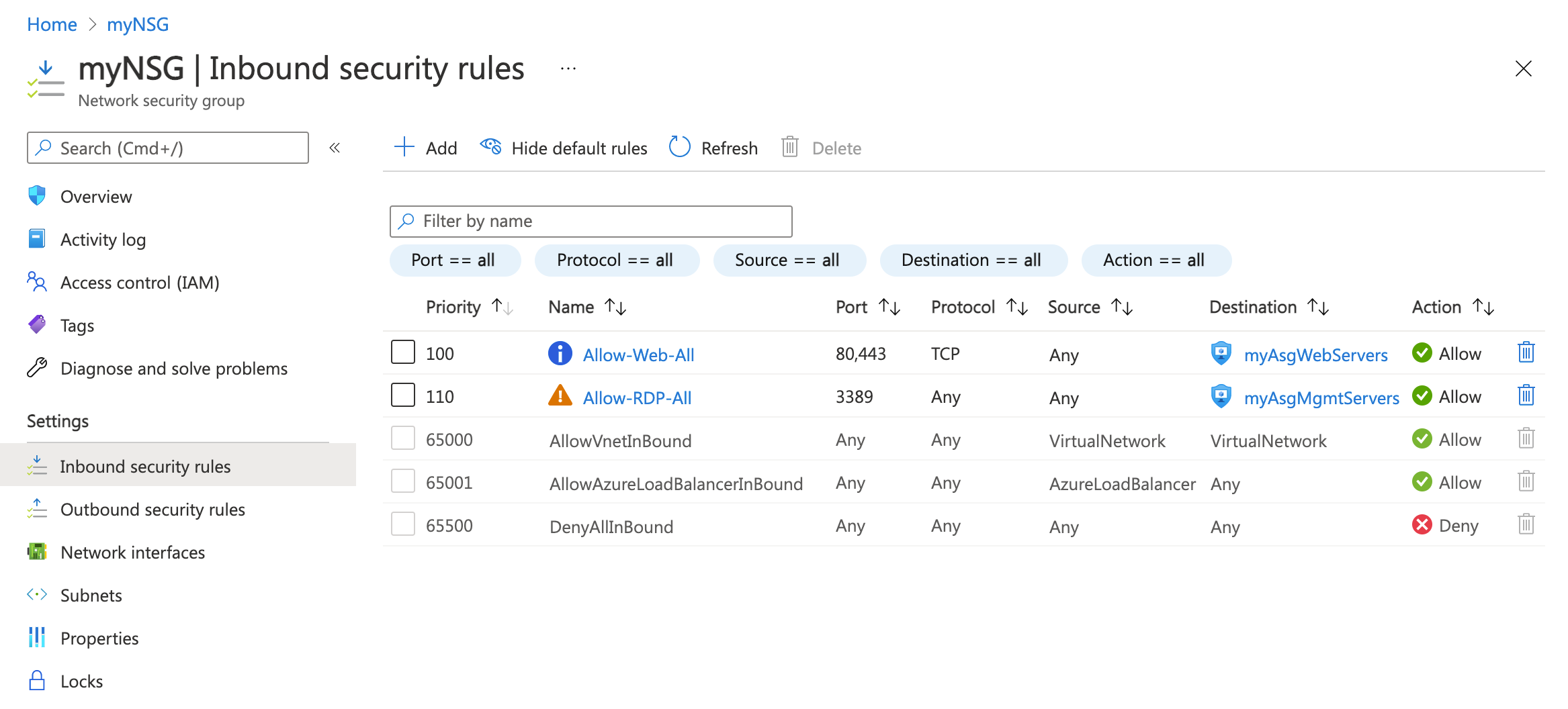
Create two VMs in the virtual network.
- Select Create a resource in the upper left-hand corner of the portal.
- Select Compute, then select Virtual machine.
- In Create a virtual machine, enter or select this information in the Basics tab:
TABLE 7 Setting Value Project details Subscription Select your subscription. Resource group Select myResourceGroup. Instance details Virtual machine name Enter myVMWeb. Region Select (US) East US. Availability options Leave the default of no redundancy required. Image Select Windows Server 2019 Datacenter - Gen1. Azure Spot instance Leave the default of unchecked. Size Select Standard_D2s_V3. Administrator account Username Enter a username. Password Enter a password. Confirm password Reenter password. Inbound port rules Public inbound ports Select None. - Select the Networking tab.
- In the Networking tab, enter or select the following information:
TABLE 8 Setting Value Network interface Virtual network Select myVNet. Subnet Select default (10.0.0.0/24). Public IP Leave the default of a new public IP. NIC network security group Select None. - Select the Review + create tab, or select the blue Review + create button at the bottom of the page.
- Select Create.
Complete steps 1-7 again, but in step 3, name the VM myVMMgmt. The VM takes a few minutes to deploy.
Don't continue to the next step until the VM is deployed.
When the portal created the VMs, it created a network interface for each VM, and attached the network interface to the VM.
Add the network interface for each VM to one of the application security groups you created previously:
- In the Search resources, services, and docs box at the top of the portal, begin typing myVMWeb. When the myVMWeb virtual machine appears in the search results, select it.
- In Settings, select Networking.
- Select the Application security groups tab, then select Configure the application security groups.
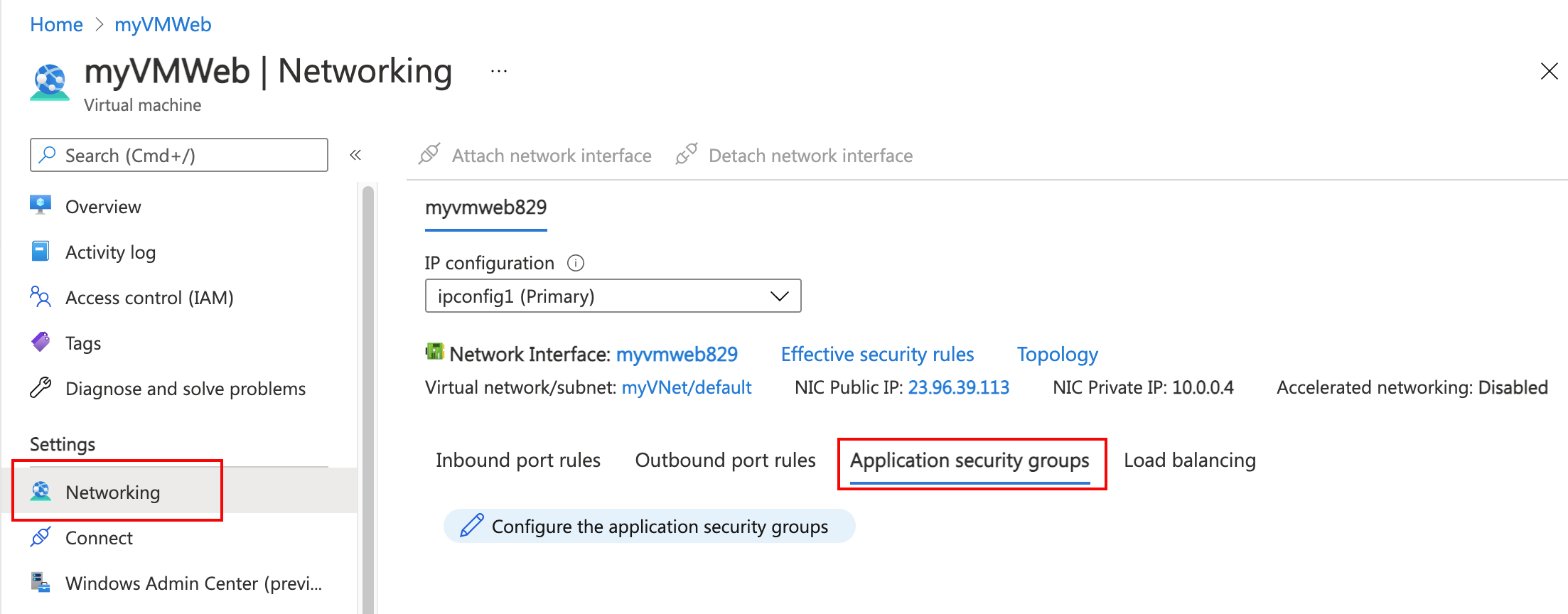
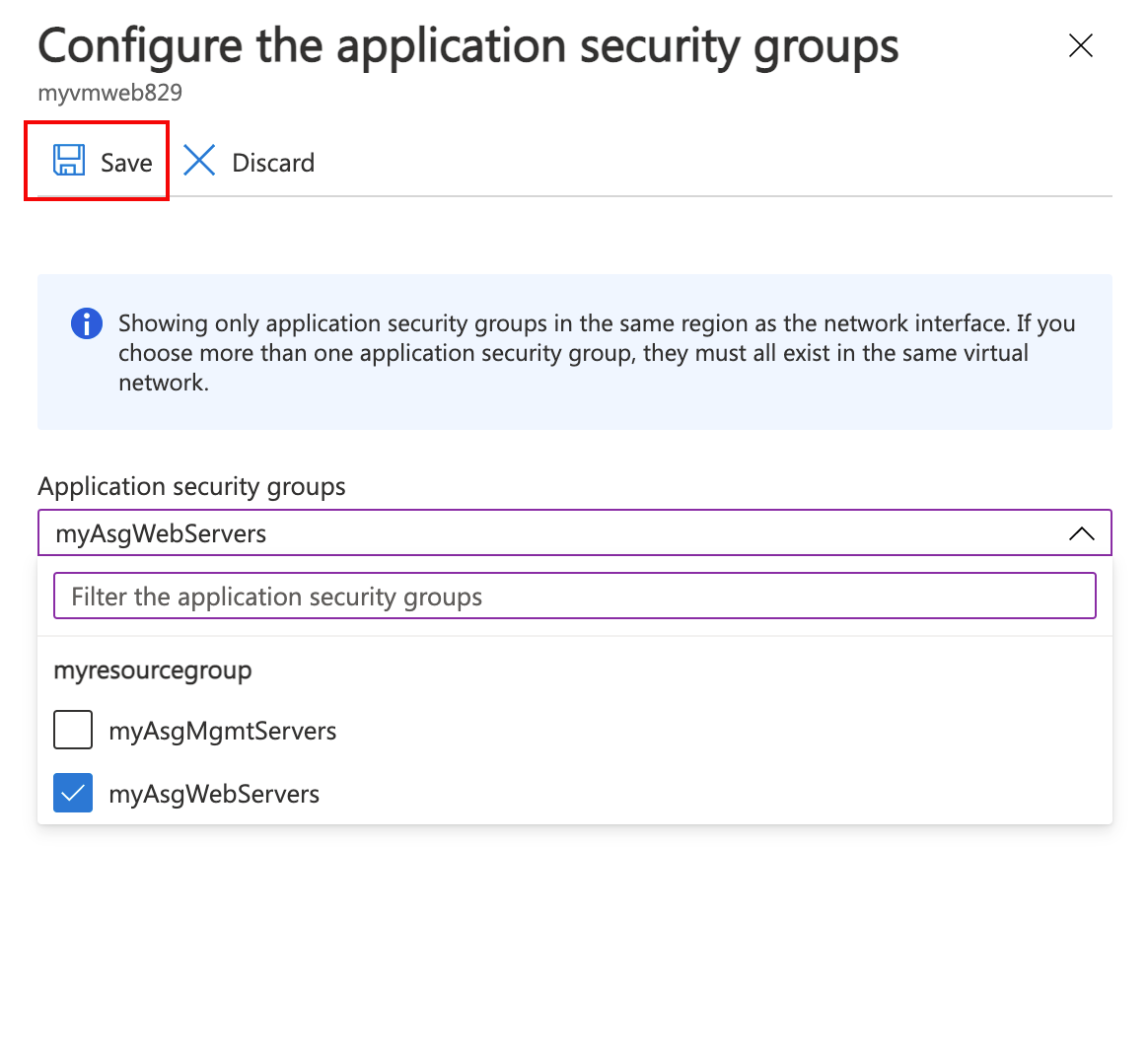
- In Configure the application security groups, select myAsgWebServers. Select Save.
- Complete steps 1 and 2 again, searching for the myVMMgmt virtual machine and selecting the myAsgMgmtServers ASG.
- Connect to the myVMMgmt VM. Enter myVMMgmt in the search box at the top of the portal. When myVMMgmt appears in the search results, select it. Select the Connect button.
- Select Download RDP file.
- Open the downloaded rdp file and select Connect. Enter the user name and password you specified when creating the VM.
- Select OK.
- You may receive a certificate warning during the connection process. If you receive the warning, select Yes or Continue, to continue with the connection.The connection succeeds, because port 3389 is allowed inbound from the internet to the myAsgMgmtServers application security group.
The network interface for myVMMgmt is associated with the myAsgMgmtServers application security group and allows the connection.
- Open a PowerShell session on myVMMgmt. Connect to myVMWeb using the following example:
PowerShellCopy
mstsc /v:myVmWebThe RDP connection from myVMMgmt to myVMWeb succeeds because virtual machines in the same network can communicate with each over any port by default.
You can't create an RDP connection to the myVMWeb virtual machine from the internet. The security rule for the myAsgWebServers prevents connections to port 3389 inbound from the internet. Inbound traffic from the Internet is denied to all resources by default.
- To install Microsoft IIS on the myVMWeb virtual machine, enter the following command from a PowerShell session on the myVMWeb virtual machine:
Install-WindowsFeature -name Web-Server -IncludeManagementTools - After the IIS installation is complete, disconnect from the myVMWeb virtual machine, which leaves you in the myVMMgmt virtual machine remote desktop connection.
- Disconnect from the myVMMgmt VM.
- In the Search resources, services, and docs box at the top of the Azure portal, begin typing myVMWeb from your computer. When myVMWeb appears in the search results, select it. Note the Public IP address for your VM. The address shown in the following example is 23.96.39.113, but your address is different:

- To confirm that you can access the myVMWeb web server from the internet, open an internet browser on your computer and browse to
http://<public-ip-address-from-previous-step>.
You see the IIS welcome screen, because port 80 is allowed inbound from the internet to the myAsgWebServers application security group.
The network interface attached for myVMWeb is associated with the myAsgWebServers application security group and allows the connection.
When no longer needed, delete the resource group and all of the resources it contains:
- Enter myResourceGroup in the Search box at the top of the portal. When you see myResourceGroup in the search results, select it.
- Select Delete resource group.
- Enter myResourceGroup for TYPE THE RESOURCE GROUP NAME: and select Delete.