JavaScript Arrays - Yash-777/SeleniumDriverAutomation GitHub Wiki
Chrome Browser Snippets: Run Snippets Of Code From Any Page
The JavaScript Array object is a global object that is used in the construction of arrays; which are high-level, list-like objects.
Sorting
- Array.prototype.sort()
The sort() method sorts the elements of an array in place and returns the array. The sort is not necessarily stable. The default sort order is according to string Unicode code points.
var fruit = ['cherries', 'apples', 'bananas'];
fruit.sort(); // ['apples', 'bananas', 'cherries']
var scores = [38,27,43,3,9,82,10];
console.log('Array.prototype.sort() : ' ,scores.sort()); // [10, 27, 3, 38, 43, 82, 9]
function compareNumbers(a, b) {
return a - b;
}
console.log('Array.prototype.sort(compareFunction):', scores.sort(compareNumbers) ); // [3, 9, 10, 27, 38, 43, 82]
- Merge sort Wiki:
- If the list is of length 0 or 1, then it is already sorted. Otherwise:
- Divide the unsorted list into two sub-lists of about half the size.
- Sort each sub-list recursively by re-applying merge sort. Merge the two sub-lists back into one sorted list.
Merge sort animation. The elements to sort are represented by dots.
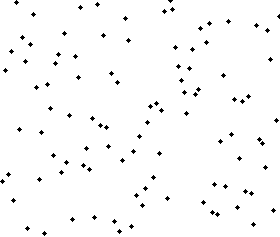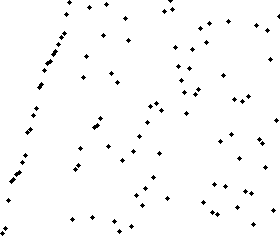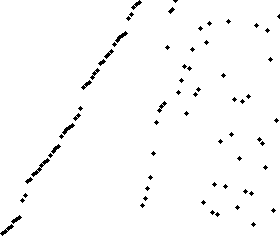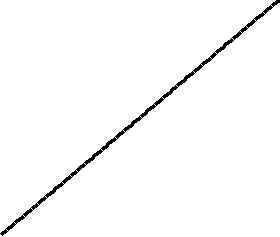
var unsortedArray = [38,27,43,3,9,82,10];
function mergeSort(arr){
if (arr.length < 2) return arr;
var middle = parseInt(arr.length / 2);
var left = arr.slice(0, middle);
var right = arr.slice(middle, arr.length);
return merge(mergeSort(left), mergeSort(right));
}
function merge(left, right) {
var result = [];
while (left.length && right.length) {
if (left[0] <= right[0]) {
result.push(left.shift());
} else {
result.push(right.shift());
}
}
while (left.length)
result.push(left.shift());
while (right.length)
result.push(right.shift());
return result;
}
console.log('Sorted Array : ', JSON.stringify(mergeSort(unsortedArray)) );
// Sorted Array : [3,9,10,27,38,43,82]
No of ways to empty an Array Using JavaScript
- To Empty a Current memory location of an array use:
'myArray.length = 0'or'myArray.pop() UN-till its length is 0'
length: Pops till length of an array is of Specified Size.pop(): The pop method removes the last element from a current memory address of an array.
var mainArr = new Array();
mainArr = ['1', '2', '3', '4'];
var refArr = mainArr;
console.log('Current', mainArr, 'Refered', refArr);
refArr.length = 3;
console.log('Length: ~ Current', mainArr, 'Refered', refArr);
mainArr.push('0');
console.log('Push to the End of Current Array Memory Location \n~ Current', mainArr, 'Refered', refArr);
mainArr.poptill_length(0);
console.log('Empty Array \n~ Current', mainArr, 'Refered', refArr);
Array.prototype.poptill_length = function (e) {
while (this.length) {
if( this.length == e ) break;
console.log('removed last element:', this.pop());
}
};
- Use
slice(): when you want to clone an array from given array with new memory address, So that any modification on cloneArr will not affect to an actual array.
Empty Array with new Memory address use : slice(0, 0)
var cloneArr = mainArr.slice(0, 3);
console.log('Main', mainArr, '\tCloned', cloneArr);
cloneArr.length = 0; // Clears current memory location of an array.
console.log('Main', mainArr, '\tCloned', cloneArr);
To assigning new empty array [] with a new memory location.
mainArr = []; // a new empty array is addressed to mainArr.
Merge two sorted arrays into single array
var a = [3, 9, 34, 198, 200, 203, 222, 777];
var b = [5, 6, 8,9,12, 34,78];
var arr = [];
var i = 0, j = 0, temp = 0, totalsize = a.length + b.length;
while(temp < totalsize) {
(j <= b.length)
if ( (i < a.length) && ( (a[i] < b[j]) || (a[i] == b[j]) || !(j < b.length) ) ) {
arr.push(a[i]); i++;
} else {
arr.push(b[j]); j++;
}
temp++;
}
console.log('final : '+ JSON.stringify(arr) );
Common Elements from Both Arrays
- Array of Numbers
var main = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,10,14,16,233,235,245,2,5,7,236,237];
var compare = [2,3,6,10,12,13,14,172,122,234];
function compareNumbers(a, b) {
return a - b;
}
console.log('Sorted Array :', main.sort(compareNumbers) );
// Sorted Array : [1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 5, 5, 6, 7, 7, 8, 10, 14, 16, 233, 235, 236, 237, 245]
Array.prototype.unique = function() {
var unique = [];
for (var i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
var current = this[i];
if (unique.indexOf(current) < 0) unique.push(current);
}
return unique;
}
console.log('Unique Array Elements:', main.unique() );
// Unique Array Elements: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, 14, 16, 233, 235, 236, 237, 245]
function commonElements(arr1, arr2) {
var common = [];
for (var i = 0; i < arr1.length; i++) {
for (var j = 0; j < arr2.length; j++) {
if (arr1[i] == arr2[j] ) {
common.push( arr1[i] );
j == arr2.length; // To break the loop;
}
}
}
return common;
}
console.log('Common Elements from Both Arrays : ', commonElements(main.unique(), compare.unique()) );
//Common Elements from Both Arrays : [2, 3, 6, 10, 14]
- Array of Objects
var objArray = [ { key1: 1, key2: 2}, { key1: 3, key2: 4}, { key1: 5, key2: 6} ];
var result = objArray.map( function(a) { return a.key1; } );
console.log('Array of KEYs coresponding Values', JSON.stringify(result) ); // result [ 1, 3, 5 ]
var objArray1 = [{key:1, value:10}, {key:2, value:20}, {key:3, value: 30}];
var objArray2 = [{key:1, value:10}, {value:20, key:2}, {key:4, value: 3}];
var reformattedArray = objArray1.map(
function(obj) {
var rObj = {};
rObj[obj.key] = obj.value;
return rObj;
}
);
console.log('reformattedArray', JSON.stringify(reformattedArray) ); // [{"1":10},{"2":20},{"3":30}]
var commonValues_ArrayOfMaps = [];
objArray1.forEach( function(obj1) {
// Sort Objects - http://stackoverflow.com/a/31102605/5081877
var map1 = {};
Object.keys(obj1).sort().forEach(function(key) {
map1[key] = obj1[key];
});
console.log('Sorted JSON : ', JSON.stringify(map1) );
// Break ForEach - http://stackoverflow.com/a/6260865/5081877
objArray2.every( function(obj2, index) {
var map2 = {};
Object.keys(obj2).sort().forEach(function(key) {
map2[key] = obj2[key];
});
console.log('Sorted JSON : ', JSON.stringify(map2) );
var isEqual = JSON.stringify(map1) === JSON.stringify(map2);
if( isEqual ){
commonValues_ArrayOfMaps.push( map1 ); return false;
}
return true;
});
});
console.log('commonValues_ArrayOfMaps', JSON.stringify(commonValues_ArrayOfMaps));
// commonValues_ArrayOfMaps [{"key":1,"value":10},{"key":2,"value":20}]