Git Tools client and Commands - Yash-777/LearnJava GitHub Wiki
To manage branches in SVN and Git based on Jira tickets, you can use a simple naming convention that includes the Jira issue key. This helps keep track of the work related to specific Jira tasks.
Here’s a simple naming pattern for branches:
Feature Branch: feature/<Jira-issue-key>-<short-description>
Bugfix Branch: bugfix/<Jira-issue-key>-<short-description>
Hotfix Branch: hotfix/<Jira-issue-key>-<short-description>
For example: This keeps it clear and organized.
Jira issue key: PROJ-1234
Task: Adding a login feature
The branch name would be: feature/PROJ-1234-login
Important
In a .gitignore file, you can add comments by starting a line with a # character. Git ignores any line that begins with #, considering it as a comment. Here's an example:
# Ignore compiled files
*.exe
*.class
# Ignore log files
*.log
Distributed SCM GIT CHEAT SHEET
One of the nicest features of any Distributed SCM, Git included, is that it's distributed. This means that instead of doing a "checkout" of the current tip of the source code, you do a "clone" of the entire repository.
Feature Based Workflow. Create new branches for each new feature you're working on so you can seamlessly switch back and forth between them, then delete each branch when that feature gets merged into your main line.
| Feature Based Workflow | Bug Fix Workflow |
|---|---|
Configuration - Git Commands GIT CHEAT SHEET
To start using Git from your computer, you must enter your credentials to identify yourself as the author of your work. The username and email address should match the ones you use in GitLab.
- In your shell, add your user name:
git config --global user.name "your_username" - Add your email address:
git config --global user.email "[email protected]" - To check the configuration, run:
git config --global --list - To add SSL cert: `git config --global http.sslCAInfo "Self signed SSL cert *.crt"
To unset user/password of Git/Bitbucket use following commands referred form stackoverflow
-
Open Git Bash.
-
Set a Git username:
$ git config --global user.name "Mona Lisa" -
Confirm that you have set the Git username correctly:
$ git config --global user.name > Mona Lisa
# Set
git config --global user.name "your_username"
# Unset
git config --global --unset user.name
git config --global user.name "your_username2"
# Set and Reset
git config --global --unset user.password
git push (will prompt you for the password)
git status (will not prompt for password again)
# Git GUI
git config --global credential.helper wincred$ git remote add origin https://github.com/Yash-777/SpringBoot_MicroService.git
error: remote origin already exists.
$ git branch -M main
$ git push -u origin main
remote: Permission to Yash-777/SpringBoot_MicroService.git denied to gitAdminSri.
fatal: unable to access 'https://github.com/Yash-777/SpringBoot_MicroService.git/': The requested URL returned error: 403
Pushing to https://github.com/Yash-777/SpringBoot_MicroService.git
$ git push https://Yash-777:**%40***@github.com/Yash-777/SpringBoot_MicroService.git --all
remote: Support for password authentication was removed on August 13, 2021.
remote: Please see https://docs.github.com/en/get-started/getting-started-with-git/about-remote-repositories#cloning-with-https-urls for information on currently recommended modes of authentication.
fatal: Authentication failed for 'https://github.com/Yash-777/SpringBoot_MicroService.git/'For anyone having issues with passwords with special chars just omit the password and it will prompt you for it: Username and password in command for git push
$ git push https://Yash-777@github.com/Yash-777/SpringBoot_MicroService.git --all
Enumerating objects: 168, done.
Counting objects: 100% (168/168), done.
Delta compression using up to 8 threads
Compressing objects: 100% (132/132), done.
Writing objects: 100% (168/168), 107.50 KiB | 4.67 MiB/s, done.
Total 168 (delta 23), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0
remote: Resolving deltas: 100% (23/23), done.
To https://github.com/Yash-777/SpringBoot_MicroService.git
* [new branch] main -> mainFor Windows 10 it is:
Control Panel > User Accounts > Manage your Credentials > Windows Credentials > Generic Credentials, search for the git credentials and edit
When you clone a repository, the files from the remote repository are downloaded to your computer, and a connection is created.
This connection requires you to add credentials. You can either use SSH or HTTPS. SSH is recommended.
Clone with SSH/HTTPS:
SSH: git clone [email protected]:gitlab-tests/sample-project.git
HTTPS: git clone https://gitlab.com/gitlab-tests/sample-project.git
Clone to Specific Branch
git clone -b <feature-branch-Name> https://gitlab.com/gitlab-tests/sample-project.git
# With user as `Yash-777`
git clone -b <feature-branch-Name> https://[email protected]/gitlab-tests/sample-project.git
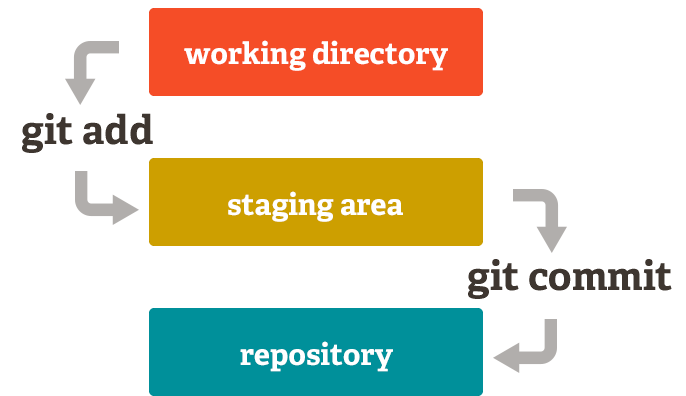
Unlike the other systems, Git has something called the "staging area" or "index". This is an intermediate area where commits can be formatted and reviewed before completing the commit.
One thing that sets Git apart from other tools is that it's possible to quickly stage some of your files and commit them without committing all of the other modified files in your working directory or having to list them on the command line during the commit.
Git Status: Inspecting a repository
List the files you've changed and those you still need to add or commit
The git status command displays the state of the working directory and the staging area. It lets you see which changes have been staged, which haven’t, and which files aren’t being tracked by Git. Status output does not show you any information regarding the committed project history. For this, you need to use git log.
The git log command displays committed snapshots. It lets you list the project history, filter it, and search for specific changes. While git status lets you inspect the working directory and the staging area, git log only operates on the committed history.
$ git log
commit 0000011111222223333344444555556666677777
Merge: 88888999999 aaaaabbbbbb
Author: [email protected]
Date: Tue Aug 31 21:19:41 2021 +0000
| Stage | Commit | Stage + Commit |
|---|---|---|
Add one or more files to staging (index)
git add <file-name OR folder-name>
- The
git addcommand adds a change in the working directory to the staging area. It tells Git that you want to include updates to a particular file in the next commit. However, git add doesn't really affect the repository in any significant way—changes are not actually recorded until you rungit commit.
git add <file> git add hello.py
git add <directory> git add .
The git add command is used to promote or 'stage' changes to the project that will be stored in a commit. These two commands git commit and git add are two of the most frequently used.
Commit changes to head (but not yet to the remote repository)
git commit -m "Commit message of Staged files"
- The
git commitcommand captures a snapshot of the project's currently staged changes.
Unstage all changes that have been added to the staging area. The
git resetcommand is used to undo a commit or staged snapshotgit add.
-
git resetTo unstage (remove) all files that have not been committed -
git reset HEAD~1To undo the most recent commit
For example, to push your local commits to the main branch of the origin remote:
git push
git push origin feature-branch-main git push <remote> <name-of-branch>
- BitBucket/GitHub Create a pull request form
feature-branchtodevelop-branch. This generates a Merge request by clicking on Merge changes get updatedFeature to Develop branch.
Before merging you can view the differences by using the command git diff [source branch] [target branch]
- Use Rebase when updating your branch with main
- Use Merge when bringing changes from feature to main
When you rebase:
Git imports all the commits submitted to main after the moment you created your feature branch until the present moment. Git puts the commits you have in your feature branch on top of all the commits imported from main:
git stash
git pull --rebase origin develop-branch
git push -f origin feature-branch
git stash pop

Force-push
When you perform more complex operations, for example, squash commits, reset or rebase your branch, you must force an update to the remote branch. These operations imply rewriting the commit history of the branch. To force an update, pass the flag --force or -f to the push command. For example:
git push --force origin my-feature-branch
Forcing an update is not recommended when you’re working on shared branches.
Alternatively, you can pass the flag --force-with-lease instead, as it is safer. This flag preserves any new commits added to the remote branch by other people: git push --force-with-lease origin my-feature-branch
project/
│
├── src/
│ ├── main/
│ │ ├── java/
│ │ │ └── com/
│ │ │ └── example/
│ │ │ └── MyClass.java
│ │ └── resources/
│ │ └── config/
│ │ └── config.properties
│
└── docs/
└── README.md
Checkout changes made to specific files from the current branch or specified branch.
| couple of common methods | commands |
|---|---|
| Checkout specific files from another branch |
git checkout <branch_name> -- <file_path>git checkout MyWorld -- src/main/java/com/example/MyClass.java
|
| Reset specific files to the state in the last commit |
git checkout -- <file_path>git checkout -- src/main/java/com/example/MyClass.java
|
Important
# To check out a specific file from a stash in Git. Replace <stash_index>with the index of the stash you want to access (e.g., 0 for the most recent stash, 1 for the second most recent, and so on). Replace<file_path> with the path to the file you want to retrieve from the stash.
git checkout stash@{<stash_index>} -- <file_path>
git checkout stash@{0} -- src/main/java/com/example/MyClass.java
git checkout stash@{4} -- src/main/java/com/example/MyClass.java
We use git stash to store our changes when they are not ready to be committed, but we must change to a different branch.
# Use any Stash command.
git stash
git stash save
git stash save "this is a message to display on the list"
# Apply stash to keep working on it:
git stash apply
# To clean our stack, manually remove them
git stash drop
# Apply and drop on one command:
git stash pop
🧩 Git Actions in SourceTree
🔁 Rebase git rebase <target-branch>
- Purpose: Move your commits to start from another base (e.g. update from develop)
- Effect: Rewrites history (new commit hashes)
- Use When: Cleaning up commit history or syncing with upstream
-
SourceTree:
- Checkout your branch
- Right-click target branch (e.g., develop) → Rebase current changes onto...
- Safe on Shared Branches? ❌ No
🔄 Reset
- Purpose: Move the branch pointer to a previous commit
-
Types:
-
Soft: Keeps all changes staged
git reset --soft <commit> -
Mixed: Keeps changes, unstaged (default)
git reset <commit> -
Hard: Discards all changes
git reset --hard <commit>
-
Soft: Keeps all changes staged
- Use When: Undo commits locally
-
SourceTree:
- Right-click target commit → Reset current branch to this commit
- Safe on Shared Branches? ❌ No (unless local only)
Important
Discard Local Changes: Use git reset --hard HEAD to discard all local changes and revert your working directory to the state of the last commit. This command will move the HEAD pointer of your current branch back two commits, effectively resetting your working directory to the state it was in at the second last commit. It will also discard any local changes you have made since that commit.
Ensure Clean State: Use git clean -fd to remove untracked files and directories from the working tree. This will ensure that your working directory is clean and matches the HEAD revision of the branch.
git reset HEAD --hard # To remove all not committed changes!
git clean -fd # To remove all untracked (non-git) files and folders!
// To reset your working directory to the state of the second last commit (HEAD~2)
git reset --hard HEAD~2🔙 Revert git revert <commit>
- Purpose: Create a new commit that undoes a previous commit (without deleting history)
- Effect: Keeps commit history intact
- Use When: Safely undo changes, especially on shared branches
-
SourceTree:
- Right-click the commit → Reverse commit
- Safe on Shared Branches? ✅ Yes
✅ Summary Table
| Action | Rewrites History | Keeps Changes | Safe on Shared Branches | Use For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rebase | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | Reordering / syncing |
| Reset | ✅ Yes | ✅/❌ (type-based) | ❌ No | Undo commits (local only) |
| Revert | ❌ No | ✅ Yes (via new commit) | ✅ Yes | Undo commit (safe/remote) |
git -c diff.mnemonicprefix=false -c core.quotepath=false --no-optional-locks checkout -- myworld-*/.classpathImportant
🐞 Error: Untracked working tree file would be overwritten by merge
📌 Problem : When switching branches or pulling changes, you might see:
error: Untracked working tree file 'src/example.js' would be overwritten by merge🛠 Cause : Git sees an untracked file in your working directory that would be overwritten by a file in the branch you're trying to check out or pull.
✅ Solution : Clean Untracked Files
- Check the untracked files:
git status- Remove or stash them:
# Be careful—this deletes all untracked files
$ git clean -f
# Or to delete untracked directories too
$ git clean -fd # WARNING: This deletes all untracked files and directories!Important
🐞 Error: Filename too long in Git
📌 Problem : When cloning a repository or checking out a branch, you might encounter:
fatal: cannot create directory at 'some/very/long/path/to/file': Filename too long
error: cannot stat 'some/very/long/path/to/file': Filename too long🛠 Cause Windows has a maximum file path length of 260 characters by default, and Git may fail when a file path exceeds that limit.
✅ Solution : Enable Long Paths in Git
If you are using Windows and Git >= 2.10, you can enable long paths:
$ git config --system core.longpaths true
(or)
$ git config --global core.longpaths truegit checkout feature-branch
git cherry-pick commit-id-of-repository [get particular commit changes to the branch]
git commit -amend --reset-author [change the identity of this commit to your name and current date]
git push [push changes to current branch]
In Git, you can cherry-pick a commit (a set of changes) from an existing branch, and apply those changes to another branch. Cherry-picks can help you
git cherry-pick commitId123
git cherry-pick -m 2 7a39eb0Important
Cherry picking is the act of picking a commit from a branch and applying it to another. git cherry-pick can be useful for undoing changes. For example, say a commit is accidently made to the wrong branch. You can switch to the correct branch and cherry-pick the commit to where it should belong.
- Git Clone vs Check out stackoverflow
- Git Fetch vs Pull vs Push
Notes:
- If you're cherry-picking a commit across different branches, make sure that the changes in the commit are not heavily dependent on other changes in the branch, as this could lead to merge conflicts or inconsistencies.
- Cherry-picking only applies the changes made in a single commit, so it doesn't bring over any history or other commits from oldBranch.
Discard the Cherry-Pick Changes:
Abort the Cherry-Pick: Git provides a simple way to abort the cherry-pick operation if you're in the middle of a conflict. This will revert the changes and bring the repository back to the state it was in before you started the cherry-pick.
git cherry-pick --abortHandling Merge Conflicts: Cherry-picking a merge commit can lead to conflicts, especially if there are changes in both parents that affect the same parts of the code. You'll need to manually resolve these conflicts and then commit the result.
Git Tutorial: git status vs. git log
- create a new branch from the current one (
git switch -c rebase-to-<new-version>) - rebase the patches (
git rebase -i --onto <component>-<new-version> <component>-<version>)
🧹 1. git prune
- Purpose: Remove unreachable (dangling) Git objects.
- Command:
git pruneUse With: Typically used after repack or reflog expire.
🔧 2. Remove Stale Remote Branch Info
- Purpose: Clean up deleted remote branches from local tracking.
- Command:
git remote prune origin
🗑️ 3. Delete Local Branches
- Purpose: Remove unused or outdated local branches.
- Command:
git branch -D <branch-name>
🔹 4. Empty .git/objects/pack Trash Files
- Sometimes Git leaves behind temp files.
- Run this from your repo root:
rm -f .git/objects/pack/tmp_pack_*
🔍 Dangling/Unreachable Objects Not Removed
If .git/objects is massive (like >10 GB), run:
$ git fsck --unreachable
Checking object directories: 100% (256/256), done.
Checking objects: 0% (216064/127797252)
The output confirms a massive number of objects (over 127 million!) in your Git repository. That's extremely abnormal unless:
- You've imported a huge monorepo,
- Accidentally committed a massive build artifact or log directory repeatedly over time,
- Or have deep history with frequent, large changes.
Even without large media files, this level of object count is enough to bloat the .git directory to 100+ GB. The issue is clearly not just file size — it’s object count and history complexity.
🧼 5. Shrink git folder, Full Deep Cleanup, You Must Free Up Significant Disk Space:
- Purpose: Optimize and shrink the repository.
🔥 "out of disk space" errors during Git's background cleanup process:
$ git fetch --all --prune
remote: Enumerating objects: 198978, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (198959/198959), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (40422/40422), done.
fatal: write error: No space left on device
fatal: fetch-pack: invalid index-pack output
Shrink a Git Repository by removing some files log history from the .git Folder based on their last updated time.
$ git remote prune origin && git repack && git prune-packed && git reflog expire --expire=1.month.ago && git gc --aggressive
$ git reflog expire --expire-unreachable=now --all && git repack -Ad && git prune && git gc --aggressive --prune=now🔥 "out of disk space" errors during Git's background cleanup process:
$ git fetch --all --prune
remote: Enumerating objects: 198978, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (198959/198959), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (40422/40422), done.
remote: Total 198978 (delta 99069), reused 197305 (delta 98028), pack-reused 19 (from 1)
Receiving objects: 100% (198978/198978), 251.27 MiB | 1.64 MiB/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (99069/99069), completed with 2182 local objects.
From gitlab.myComp.net:vorward/commissionengine/myworld
...
Auto packing the repository for optimum performance.
See "git help gc" for manual housekeeping.
Enumerating objects: 733171, done.
Counting objects: 100% (109658/109658), done.
Delta compression using up to 12 threads
Compressing objects: 100% (27855/27855), done.
fatal: sha1 file '.git/objects/pack/tmp_pack_vMihHz' write error. Out of diskspace
fatal: failed to run repack
error: task 'gc' failed🧼 6. Remove the Broken Remote Reference
Error: means that Git is trying to access a broken or corrupt reference (refs/remotes/origin/ES/SNOW/INC1208213), and it’s halting the entire process.
$ git reflog expire --expire-unreachable=now --all && git repack -Ad && git prune && git gc --aggressive --prune=now
fatal: bad object refs/remotes/origin/ES/SNOW/INC1208213
Fix: manually delete the broken reference so Git can continue.
rm -f .git/refs/remotes/origin/ES/SNOW/INC1208213
💣 7. Force-Delete .git Folder (Unversion Entire Project)
- Purpose: Remove Git tracking completely.
- Command (run from repo root):
rm -rf .git - Effect: Deletes all version history. Project remains, but is no longer a Git repo.
- This removes all Git tracking, history, branches, remotes, reflogs, etc.
- Your code will remain, but it will no longer be a Git repository.
- This is irreversible unless you backed up or cloned it elsewhere.
-
At its core, Git is a set of command line utility programs that are designed to execute on a Unix style command-line environment. Modern operating systems like Linux and macOS both include built-in Unix command line terminals. This makes Linux and macOS complementary operating systems when working with Git. Microsoft Windows instead uses Windows command prompt, a non-Unix terminal environment.
- To Stage only selected files use
Ctrl + Tform Git GUI. - If the password is saved and want to change password of your user-Repository the use
git config --global credential.helper wincred
- To Stage only selected files use
| The File Status tab shows all changes as observed by Git. Additionally, you can filter this tab & check your current filter. |
 |
Change The Maximum Lines And Size In Options:Tools > Options > Diff - Change Max Diff Line Count And Change Size Limit (Text)
|
 |