Adb - YamamotoDesu/Yamamoto-Notes GitHub Wiki
ADB, Android Debug Bridge, is a command-line utility included with Google's Android SDK. ADB can control your device over USB from a computer, copy files back and forth, install and uninstall apps, run shell commands, and more.
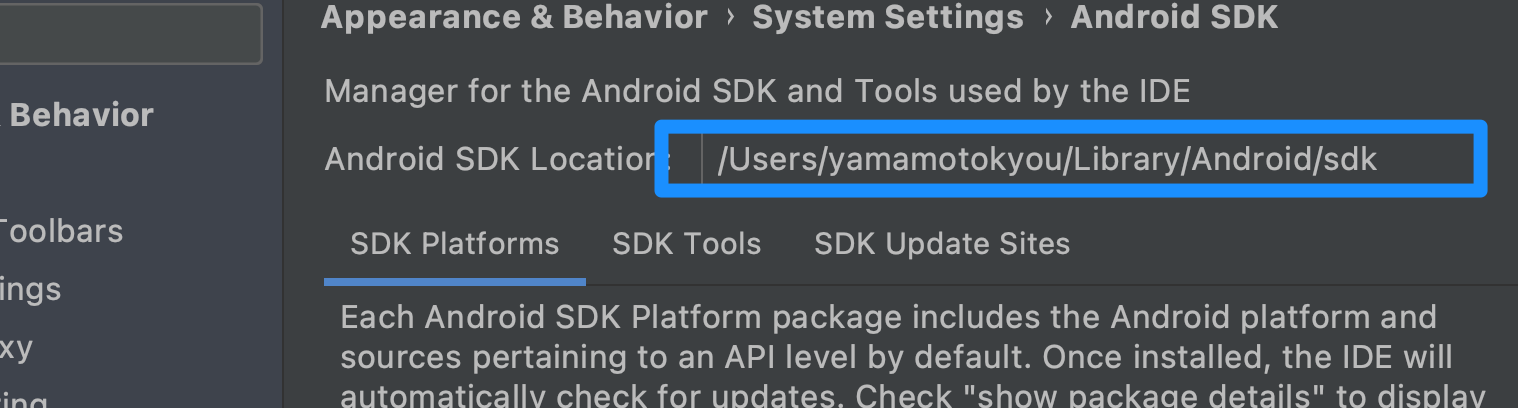
Ex.
export PATH=$PATH:/Users/yamamotokyou/Library/Android/sdk/platform-tools
- Open a Terminal
- Create a .bash_profile file if you don’t have one already.
- This is a configuration file for bash) - it’s executed when you start bash:
touch ~/.bash_profile
- Open up the ~/.bash_profile file in your preferred text editor:
open ~/.bash_profile
- Add the following to your .bash_profile file and save:
export PATH=<Path to platform-tools>:$PATH
- Either restart your terminal, or enter:
source ~/.bash_profile
- Ensure you can run adb by typing:
adb
adb devices (lists connected devices)
adb root (restarts adbd with root permissions)
adb start-server (starts the adb server)
adb kill-server (kills the adb server)
adb reboot (reboots the device)
adb devices -l (list of devices by product/model)
adb shell (starts the backround terminal)
exit (exits the background terminal)
adb help (list all commands)
adb -s <deviceName> <command> (redirect command to specific device)
adb –d <command> (directs command to only attached USB device)
adb –e <command> (directs command to only attached emulator)
adb shell am kill <package name>(terminating a process)