networking concepts - TarisMajor/5143-OpSystems GitHub Wiki
Networking Concepts
This section explores fundamental concepts in networking, focusing on protocols, programming, file systems, memory access, and scheduling techniques.
Table of Contents
- Network Protocols (TCP/IP)
- Socket Programming
- Network File System (NFS)
- Remote Memory Access
- Packet Scheduling
- Fair Queuing
- Weighted Fair Queuing
Network Protocols (TCP/IP)
- Transmission Control Protocol (TCP):
- Reliable, connection-oriented protocol.
- Ensures ordered data delivery with error correction.
- Internet Protocol (IP):
- Connectionless protocol responsible for routing and addressing packets.
- Use Case: Commonly used for web browsing, email, and file transfer.
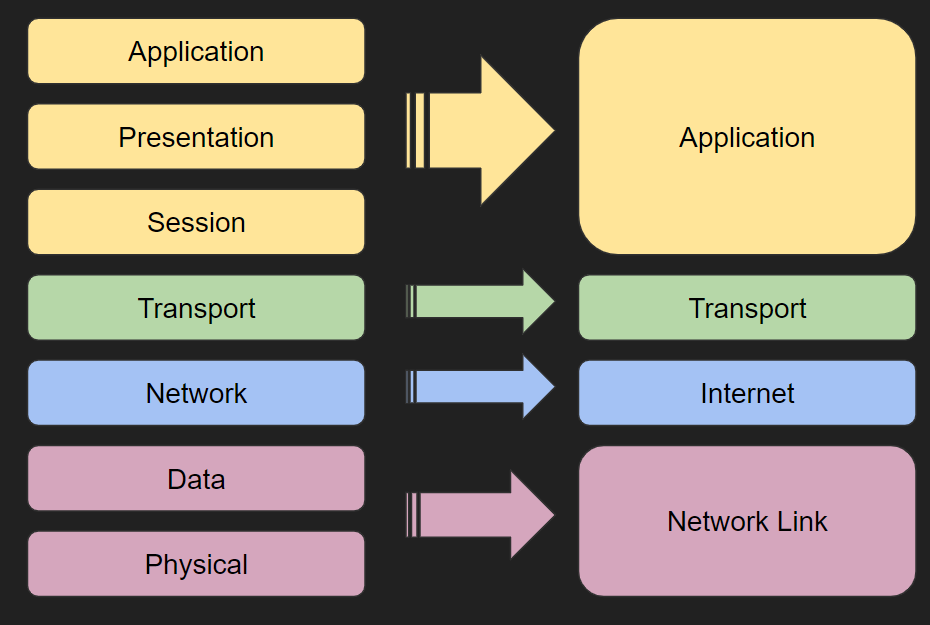
Figure 1: TCP/IP Protocol Stack.
Socket Programming
- Definition: Enables communication between two endpoints (client and server) over a network.
- Key Concepts:
- Sockets represent endpoints.
- TCP and UDP are common transport layer protocols.
- Applications:
- Web servers, chat applications, and networked games.
Figure 1. Socket Programming Example.
Network File System (NFS)
- Definition: Allows access to files on remote systems as if they were local.
- Features:
- Shared storage for distributed systems.
- Stateless protocol for efficient access.
- Use Case: Common in enterprise environments for centralized file management.
Remote Memory Access
- Definition: Direct memory access across a network, bypassing the CPU.
- Benefits:
- Reduces latency and CPU overhead.
- Improves performance for distributed systems.
- Use Case: High-performance computing (HPC).
Packet Scheduling
- Definition: Determines the order of packet transmission in a network.
- Techniques:
- Prioritizing packets based on size, source, or destination.
- Managing bandwidth usage.
Fair Queuing
- Definition: Allocates bandwidth fairly among competing flows.
- Mechanism:
- Uses separate queues for each flow.
- Ensures equal packet transmission over time.
- Use Case: Avoids bandwidth monopolization in shared networks.
Weighted Fair Queuing
- Definition: Extends fair queuing by assigning weights to different flows.
- Features:
- Provides proportional bandwidth allocation.
- Higher weights mean higher bandwidth priority.
- Use Case: Quality of Service (QoS) in multimedia streaming.
Conclusion
Networking concepts such as TCP/IP, socket programming, and advanced scheduling techniques form the backbone of modern distributed systems. These concepts are essential for building reliable, efficient, and scalable networks.
References
- Kurose, J. F., & Ross, K. W. (2024). Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (8th ed.). Pearson. ISBN: 978-0136681557.
- Edelman, J., Lowe, S. S., & Oswalt, M. (2023). Network Programmability and Automation (2nd ed.). O'Reilly Media. ISBN: 978-1492082104.
- Bashir, I. (2023). Mastering Blockchain: Unlocking the Power of Cryptocurrencies, Smart Contracts, and Decentralized Applications (3rd ed.). Packt Publishing. ISBN: 978-1803241067.