SHOW 'DATABASE'
- display information contained in the database and its tables.
SHOW 'TABLE'
- display all of the tables in the currently selected database.
SHOW 'COLUMNS' FROM 'TABLE'
- display information about the columns in a given table.
CREATE TABLE
CREATE TABLE 'TABLE'
(
'COLUMN1' 'DATATYPE(SIZE)',
'COLUMN2' 'DATAYPTE(SIZE)',
....
);
- If you want set primary key
CREATE TABLE 'TABLE'
(
'COLUMN1' 'DATATYPE(SIZE)',
'COLUMN2' 'DATAYPTE(SIZE)',
PRIMARY KEY('COLUMN1')
);
ALTER TABLE
- used to add, delete or modify columns in a existing table
- add column
ALTER TABLE 'TABLE' ADD 'COLUMN1' 'DATATYPE';
ALTER TABLE 'TABLE' DROP COLUMN 'COLUMN2';
- If you want drop whole table
DROP TABLE 'TABLE';
- column1 -> column2 renaming
ALTER TABLE 'TABLE' RENAME 'COLUMN1' TO 'COLUMN2'
RENAME TABLE 'TABLE1' TO 'TABLE2';
VIEW
- virtual table that is based on the result-set of an SQL statement
- contains rows and columns
- Summarize data from various tables and use it to generate report
CREATE VIEW 'VIEW' AS SELECT ....';
- When you want update view
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW 'VIEW' AS SELECT ...';
- When you want delete view
DROP VIEW 'VIEW';
SELECT 'COLUMN_LIST' FROM 'TABLE' (COLUMN_LIST include one or more columns)
- select data from a database.
- result is stored in a result table, which is called the result-set.
- when, selecting multiple columns using commas for separated column names.
SELECT 'COLUMN1', 'COLUMN2', ... FROM 'TABLE';
- if you want to selection all columns using asterisk(*)
SELECT * FROM 'TABLE';
DISTINCT is used in conjunction with SELECT to eliminate all duplicate records and return only unique ones.
SELECT DISTINCT 'COLUMN1', 'COLUMN2', ... FROM 'TABLE';
LIMIT is used to retrieve just a subset of records
SELECT 'COLUMN' FROM 'TABLE' LIMIT 'number of records';
OFFSET is used to pick up a set of records. Below statement means, pick up j records, starting from the i position.
SELECT 'COLUMN_LIST' FROM 'TABLE' OFFSET 'i' LIMIT 'j';
ORDER BY is used with SELECT to sort the returned data. If you want to multiple columns sort using commas. (When COLUMN1 value is same, compare COLUMN2 value)
SELECT * FROM 'TABLE' ORDER BY 'COLUMN';
SELECT * FROM 'TABLE' ORDER BY 'COLUMN1', 'COLUMN2' ...;
WHERE is used to extract only those records that fulfill a specified criterion.
SELECT 'COLUMN_LIST' FROM 'TABLE' WHERE 'CONDITION';
BETWEEN 'VALUE1' AND 'VALUE2' is selects values within a range
SELECT 'COLUMN_LIST' FROM 'TABLE' WHERE 'COLUMN' BETWEEN 'VALUE1' AND 'VALUE2';
CONCAT is used to concatenate two or more text values and returns the concatenation string. (return value is 'COLUMN1_VALUE', 'COLUMN2_VALUE')
SELECT CONCAT('COLUMN1', ',', 'COLUMN2') FROM 'TABLE';
AS, using a concatenation results in a new column
SELECT CONCAT('COLUMN1',',','COLUMN2') AS 'NEW_COLUMN' FROM 'TABLE';
LIKE
- useful when specifying a search condition within your WHERE clause. (For example, When 'PATTERN' is 'A%', return 'COLUMN1' value include 'A...'. 'Andrew', 'Anthony'...)
SELECT 'COLUMN' FROM 'TABLE' WHERE 'COLUMN1' LIKE 'PATTERN';
_ means set number of character, below means find two letter words starting with A
SELECT 'COLUMN' FROM 'TABLE' WHERE 'COLUMN1' LIKE 'A_';
% means no limit on the number of characters, below means all words starting with a
SELECT 'COLUMN' FROM 'TABLE' WHERE 'COLUMN1' LIKE 'A%';
- Any string whose first character is not A
SELECT 'COLUMN' FROM 'TABLE' WHERE 'COLUMN1' LIKE '[^A]';
- Any string whose first character is A, B or C
SELECT 'COLUMN' FROM 'TABLE' WHERE 'COLUMN1' LIKE '[ABC]' | '[A-C]';
JOIN
- Create a temporary table with the joined tables' data(TABLE1.COLUMN1, TABLE1.COLUMN2, TABLE2.COLUMN1, TABLE2.COLUMN2...)
SELECT 'TABLE1.COLUMN1', 'TABLE1.COLUMN2'... 'TABLE2.COLUMN1', 'TABLE2.COLUMN2'... FROM 'TABLE1', 'TABLE2' WHERE 'CONDITION' ...;
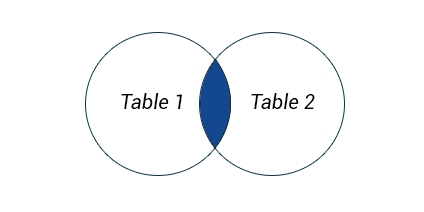
INNER JOIN is equivalent to JOIN. It returns rows when there is a match between the tables.
SELECT 'COLUMNS' FROM 'TABLE1' INNER JOIN 'TABLE2' ON 'CONDITION';
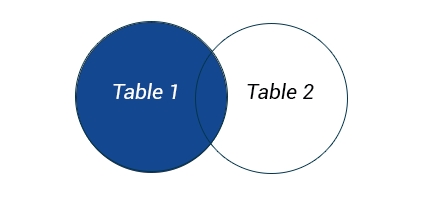
LEFT JOIN returns all rows from the left table, even if there are no matches in the right table
SELECT 'COLUMNS' FROM 'TABLE1' LEFT OUTER JOIN 'TABLE2';
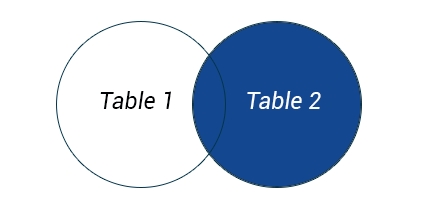
RIGHT JOIN returns all rows from the right table, even if there are no matches in the left table
SELECT 'COLUMNS' FROM 'TABLE1' RIGHT OUTER JOIN 'TABLE2';
AS
- used for custom names to table
SELECT 'NICKNAME.COLUMN1', 'NICKNAME_COLUMN2' FROM 'TABLE' AS 'NICKNAME' WHERE 'CONDITION'...
UNION
- used to combine the result-sets of two or more SELECT statements
- must have the same number of columns
- must have the same data type
UNION will return removing the duplicates.
SELECT 'COLUMNS' FROM 'TABLE' UNION SELECT 'COLUMNS' FROM 'TABLE2';
- If columns don't match exactly across all queries, you can use a NULL value
SELECT 'COLUMNS1', 'COLUMNS2' FROM 'TABLE' UNION SELECT 'COLUMNS1', NULL FROM 'TABLE2';
UNION ALL selects all rows from each table and combines them into a single table.(include duplicate data)
SELECT 'COLUMNS' FROM 'TABLE' UNION ALL SELECT 'COLUMNS' FROM 'TABLE2';
INSERT INTO
- used to add new rows of data to a table in the database
INSERT INTO 'TABLE' VALUES ('VALUE_LIST');
INSERT INTO 'TABLE('COLUMN_LIST')' VALUES ('VALUE_LIST');
UPDATE
- allows us to alter data in the table
- basic syntax of an UPDATE query with a WHERE clause is as follows
UPDATE 'TABLE' SET 'COLUMN1=VALUE1', 'COLUMN2=VALUE2'... WHERE 'CONDITION';
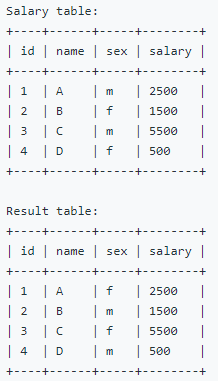
- when using case when statement, can process multiple update
UPDATE 'TABLE' SET CASE ... WHEN 'COLUMN1'='COMPAREVAL1' THEN 'RETURNVAL1' ELSE 'RETURNVAL2' END;
- ex) UPDATE Salary SET sex = CASE sex WHEN 'm' THEN 'f' ELSE 'm' END;
DELETE
DELETE FROM 'TABLE' WHERE 'CONDITION';
GROUP BY - HAVING
- By
GROUP BY, set the values for a specific column, Use the HAVING to apply conditions to the record group.
SELECT 'COLUMN' FROM 'TABLE' GROUP BY 'COLUMN2' HAVING 'CONDITION';


