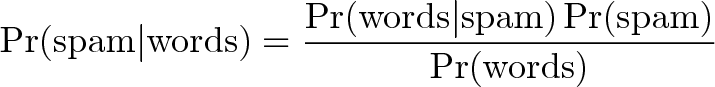Bayes Theorem - SoojungHong/MachineLearning GitHub Wiki
Bayes Theorem
describes the probability of an event, based on prior knowledge of conditions that might be related to the event. For example, if cancer is related to age, then, using Bayes’ theorem, a person’s age can be used to more accurately assess the probability that they have cancer, compared to the assessment of the probability of cancer made without knowledge of the person's age.

P ( A ∣ B ) is a conditional probability: the likelihood of event A occurring given that B is true. P ( B ∣ A ) is also a conditional probability: the likelihood of event B occurring given that A is true. P(A) and P(B) are the probabilities of observing A and B independently of each other; this is known as the marginal probability.
Example
Event A: The message is spam.
Test X: The message contains certain words (X)