Controllable Text Generation using Transformer based Pre trained Language Models - Songwooseok123/Study_Space GitHub Wiki
-
ctg 연구를 해야하는 이유 :
- "chatgpt가 원하는 대로 생성 잘 해주지 않나?"
- chatgpt 이용시 "쉬운단어로 친절하게 해줘" 이런 식으로 매번 prompt를 주면 텍스트 생성을 제어할 수 있음. 하지만, 내가 정확하게 원하는 스타일의 결과물을 만드려면 prompt를 잘 찾아내야 되고 안되는것들도 있음. (prompt 입력의 까다로움?)
-
후처리(조건부 언어 모델링)을 해야하는 이유 : 학습으로 해결하기에는 parameter가 너무 많음.
CTG survey 논문(링크)
1. Introduction 2. Concept of CTG & PLM 3. Summarized the approaches to PLM-based CTG 4. Evaluation metrics 5. CHALLENGES AND FUTURE DIRECTIONS
Introduction
CTG(Controllable Text Generation) 연구 동기
CTG란 NLG의 실제 application에서의 실용성을 위해 떠오르고 있는 분야입니다.
-
NLG(Generation) : 자연어 문장을 생성하는 기술
- NLG Application : Dialogue systems, Story generation, Data augmentation, Summarization, Question Answering 등
-
실용성 : 성능, 자연스러움, 사람이 원하는 특정 조건을 만족시키는가 등
NLP
- NLU(Understanding) : 자연어 형태의 문장을 이해하는 기술, 자연어를 컴퓨터가 이해할 수 있는 값으로 바꾸는 과정
- NLG(Generation) : 자연어 문장을 생성하는 기술 , 컴퓨터가 이해한 값을 사람이 이해할 수 있도록 바꾸는 과정
NLG using PLM
- 최근 Large-scale pre-trained language models (PLM) , 특히 Transformer-based PLM을 사용해서 text를 생성하는 방법이 더욱 다양하고 자연스러운 text를 생성하게 하면서 NLG 분야에서 각광 받고 있음.
PLM을 사용한 Method의 문제점
- NLG 시스템이 더 다양하고 자연스러운 text를 안정적으로 생성하기 위해선 task별로 control condition들을 충족시켜야함
- Control condition : task별로 사람이 원하는 특정 조건
- ex) story generation(왼쪽그림) : story 순서 등
- AI Chatbot(오른쪽 그림) : toxic한 내용 피하기, 감정, 관계 고려 등
- data augmentation : ensure data distribution balance in different domains
- Application의 윤리적인 측면? : 성, 인종, 등 차별적인 text 생성 피하기 등
- Controllability : 위의 condition을 만족시키는 text를 만드는 능력
- Control condition : task별로 사람이 원하는 특정 조건
낮은 interpretability와 controllability
- PLM은 neural network (black box 모델)
- latent representation으로부터 text 생성 -> 사람이 원하는대로 text 생성을 controll하기 어렵고 interpretability가 떨어짐
- 여전히 웹 상에 존재하는 거대한 양의 텍스트를 통해 학습된 PLM은 toxic한 표현(욕설, 차별 등)을 여과없이 생성하여 실용적이지 못할 수도 있음(오른쪽 그림)
"real application에서의 실용적인 텍스트 생성을 위해 plm based 모델의 interpretability와 controllability가 보장되어야 한다."
2. Concept of CTG & PLM
2.1 Controllable Text Generation
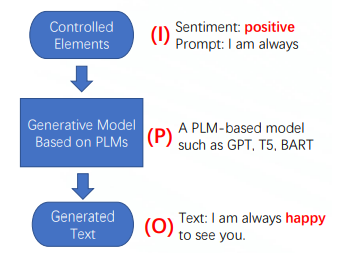
- Input : Controlled elements
- Process: Generative model (PLM-based model)
- Output: Generated text(satisfying the input control condition)
Goal of CTG
Given a vocabulary $V$ , Generate a target text $Y$ = { $𝑦_1, 𝑦_2, . . . , 𝑦_𝑛$ } - where $𝑦_𝑛 ∈ V$, Control element $C$
$$P(𝑌 |𝐶) = p(𝑦_1, 𝑦_2, . . . , 𝑦_𝑛 |C)$$
- 생성된 text $Y$ 는 constraint condition도 만족하고 또, general natural languate 특성도 만족해야한다.(유창함. 합리적, 가독성 )
Taxonomy of control condition

- (1) Semantic: content control at the semantic level
- emotion, topic 등 의미나 내용적인 control
- (2)Structural: control over the structure level of the generated text
- data-to text, information extraction 등 구조적인 level을 control
- (3)Lexical: control at the vocabulary level
- keyword inclusion 등 such as making the generated text contain certain keywords.
2.1.1 Relevant Tasks Involving CTG

-
Attribute-based Generation
- generate natural language sentences that satisfy specific attributes
- topic, emotion, and keywords 같은 특정한 attribute를 만족시키는 문장을 생성하는 task
- generate natural language sentences that satisfy specific attributes
-
Dialogue Generation
- Input: dialogue content, additional structural information(eg: persona, emotion, dialogue intent, template, etc.)
- Output: Dialogue Response
-
Storytelling
- Input: Story elements (Storylines , story endings)
- Output: Story paragraph
-
Data to Text
- to convert non-linguistic structured data (e.g., a table or a graph) into natural language text
- can be applied in tasks like weather forecast
- to convert non-linguistic structured data (e.g., a table or a graph) into natural language text
-
Data Augmentation
- CTG를 통해 주어진 attibute에 맞게 새로운 text를 생성한다.
- 동의어를 포함하도록 등
- CTG를 통해 주어진 attibute에 맞게 새로운 text를 생성한다.
-
Debiasing
- Rewriting biased text to unbiased text or changing the data distribution of the CTG-generated text
- 성별,인종 등 편견을 반영하는 text나 모델을 완화시키는 task
- Format Control
- 라임을 맞춰야하는 전통 시 등
2.2 Transformer-based Pre-trained Language Models(PLM)

- AR : 순차적으로 다음 토큰을 예측하는 LM모델, 이전 출력이 다음의 입력이 되는 모델
- AE : 노이즈가 섞인 입력(예를 들어 MASK)에서 원 데이터를 복원하는 과정을 거치는 모델
3. Approaches to PLM-based CTG(into three categories)
PLM-based CTG 의 핵심 아이디어
- control condition을 만족하는 text를 생성하도록 모델한테 control signal 을 주는 것.
Standard language model:
$$P(x_n|X_{1:n-1}) = p(x_n|x_1, x_2, . . . , x_{𝑛-1})$$
the goal of conditional text generation
$$P(X|C) = \displaystyle \prod_{i=1}^n p(x_i|x_{< i},C)$$
control signal의 작동방식에 따라 크게 3가지로
3.1. Fine-tuning
- PLM 파라미터의 일부를 finetuning 하는 방법
- The most direct way at a lower cost
3.2. Retraining/Refactoring
- PLM의 architecture를 바꾸거나 재학습시키는 방법
- fine-tuning보다는 좋은 결과를 낼 수 있지만 computing resource가 많이 소모되고 , labeled data 부족 문제에 직면할 수 있음.
3.3. Post-Processing
- PLM의 파라미터 사이즈가 증가하면, 위의 방법들은 resource-intensive(requires significant system resources or time, or requires exclusive access to large amounts of data) 이것을 피하기 위한 방법으로
- PLM의 파라미터들이 fixed 되고, control signal이 디코더에서 작동함.
- require fewer computation resources for training ,can guarantee a better quality of the generated text
- 대부분 이 방법을 씀.
3.1 Fine-tuning
3.1.1. Adapted Module
PLM에 'task-related adapted network module'을 추가하는 방법 추가된 adapted network는 일반 fine-tuning 방법처럼 target dataset에 대해서 PLM과 같이 train된다.
-
- Training 방법 : PLM의 logit과 Auxiliary model의 logits을 더하고 target task output의 likelihood를 최대화한다.
- PLM의 logit : Learning to generate fluent, natural language learn a distribution $p(x_t|x_{< t})$ that assigns high probability to fluent sequences.
- Auxiliary model의 logits : Learning to shift the probability distribution $p(x_t|x_{< t})$ as a function of α to obtain $p(x_t|x_{< t} ,α)$ we would like the resulting distribution to assign high probability to a subset of fluent sequences that also adhere to the desired attribute.
- Training 방법 : PLM의 logit과 Auxiliary model의 logits을 더하고 target task output의 likelihood를 최대화한다.

- STRUCTADAPT
-
AMR-to-text task AMR:문장의 의미 구조를 그래프로 표현한 것
-
Adapter module을 PLM의 encoder와 decoder 각각의 feed-forward layer 후에 더하는 방법
-
참고로 layer normalization and residual connections은 그림에서 생략되어있음.
Adapter
-
- which can encode the graph structure into the PLMs without contaminating its original distributional knowledge
- 학습시, the PLM’s parameters are frozen, and only the injected adapter is trainable
3.1.2. Prompted-based approaches
어떤 task의 Finetuning 단계의 training 목표를 원래 PLM의 task와 같게 한다.
Sentiment classification 예시
("I am always happy to see you") 감성 분석
Traditional approach : encode the sentence into a set of vectors, and then classify their sentiment through a fully connected layer
Prompted-base : 위의 traditional 방법과는 다르게, 밑의 그림처럼 templete을 만들어서 , mask 토큰을 예측하도록 하는 것


semtiment-control text generation 예시
현재 시점까지 생성되거나 입력된 토큰을 통해 다음 토큰을 예측하는 생성 모델의 특징을 이용하여 주어진 문장인 prompt로 다음 이어질 문장을 사용자에 의도에 맞게 생성하도록 하는 방법

PLM의 input에 어떤 prompt를 추가해서 text 생성을 control 한다.
prompt를 어떻게 구성하냐에 따라서 방법이 나뉜다.
- Prefix tuning
- PLM의 파라미터는 freeze시키고
- prefix(일종의 설명을 나타내는 가상토큰)라고 하는 연속적 task-specific 벡터를 추가하여 해당 prefix와 관련된 파라미터만 튜닝하는 방법

- P-tuning
- PLM에 입력할 Prompt를 생성하는 간단한 모델 (eg. LSTM, MLP, etc.)을 학습하여 원하는 task를 수행하도록 만드는 방법입니다.
PLM으로 들어가는 입력 벡터(prompt)를 학습한다. p-tuning 설명 한글 블로그

3.1.3. Reinforcement Learning (RL) inspired Approaches
3.2 Retraining/Refactoring
- CTRL
- 입력 시 control code인 토큰 하나를 문장 맨 앞에 추가해줌으로 원하는 문장을 생성할 수 있도록 모델의 목적 함수와 구조를 변경하여 transformer를 처음부터 학습시키는 것.
- POINTER : lexical constraints를 만족시킬 수 있는 방법
- 초기 입력된 단어들(lexical condition) 사이에 모델이 적절한 단어를 생성해서 매끄러운 문장이 완성될 수 있도록 모델을 수정한 방법
- CBART
- CoCon
3.3 Post-Processing
다음 토큰을 예측할 때, 생성된 text가 condition을 충족시킬 수 있도록 예측 분포를 바꿔주는 방법

-

- 후처리 방법 중 대표적인 논문
- LM 모델 아키텍처나 파라미터 아예 안건드림.
- 추론 할 때 attribute model 이용함 -> attribute 모델 정하고 loss함수 정의하면 끝남.
- 추론할 때 다음 단어 고를 때 확률 분포를 attribute 맞게 바꿔줌.
- pplm 보완 논문:
- Change or Not: A Simple Approach for Plug and Play Language Models on Sentiment Control
- 지금까지 생성된 부분적인 텍스트로만 감성을 예측하기 어렵, 과도한 수정으로 인한 fluency가 떨어지는 것을 보완

- Valance 차이 계산으로 change 할지 말지 정하고 , loss도 다시 정의.
- Diffusion-LM Improves Controllable Text Generation
- diffusion lm 모델 사용해서 pplm 성능 개선
- Attribute Alignment: Controlling Text Generation from Pre-trained Language Models
- Change or Not: A Simple Approach for Plug and Play Language Models on Sentiment Control
-
FAIR
-
MEGATRON-CNTR
-
Adversarial Search
-
GeDi
-
Mix and Match
-
EBM
4. EVALUATION METHODS
General NLG Evaluation Metrics(quality of the generated text) + CTG-specific Evaluation (fulfilling the controlled elements)
4.1 General NLG Evaluation Metrics
4.1.1 Human-Centric Evaluation Metrics.
- 생성된 문장에 대해서 사람이 직접 Score를 주는 방법.
4.1.2 Automatic Evaluation Metrics
생성된 문장 $G$ 와 Reference(정답) text $R$ 을 비교하는 방법
Lexical-based Metrics
- BLEU : Generated Sentence의 단어가 Reference Sentence에 포함되는 정도
- ROUGE : Reference Setence의 단어가 Generated Sentence에 포함되는 정도
- Perplexity (PPL)

-
- Generation probability의 역수의 기하평균 (문장 생성 확률의 역수를 단어의 수 N으로 정규화 함 )
- '헷갈리는 정도'로 낮을 수록 좋은거
Semantic-based Metrics
Semantic-based metrics aim to handle the evaluation of texts that are lexically different but have a similar semantic meaning
- PLM based 모델로 평가
- BERT의 embedding을 사용해서 capture the semantic similarity between the generated text and its reference.
4.1.3 Semi-automatic Evaluation Metrics.
- Human-Centric Evaluation와 Automatic Evaluation를 함께 쓰는 평가 방법
4.2 CTG-specific Evaluation
4.2.1. Semantic consistency metric(for semantic control conditions)
-
training set을 postive(control conditions을 만족하는 sample들)와 negative(만족하지 않는) 로 나눈다.
-
classifier가 생성된 문장이 condition을 만족하는 문장인지 아닌지 (pos/neg classificaiton) 구분하도록 학습시킨다.
- Accuracy : condition 만족시킨 문장 비율
- CTRLEVAL : 생성된 문장의 coherence, consistency, and attribute relevance를 평가함
4.2.2. Rule-based metric(for structural and lexical-based controll conditions)
- Coverage : calculate the average percentage of input keywords that are present in the generated text of the CTG model
- Success Rate : measure the matching degree between the generated text and the given structural control elements
4.2.3. Human evaluation metric
5. CHALLENGES AND FUTURE DIRECTIONS
5.1 Challenges
-
- catastrophic forgetting problem in PLM : First, pre-trained language models have learned rich knowledge from large-scale corpus used for pre-training. However, an NLG model needs to learn control constraints on its own training corpus. It is often difficult for the existing PLM-based models to ensure the domain diversity of the generated text while pursuing controllability. This is indeed the well-known catastrophic forgetting problem in PLM. In the field of text generation, it is still a challenge to overcome this problem and make the PLM-based NLG model generate multi-domain text that satisfies specific control conditions with few or zero domain-specific samples.
-
- controlling the generation of text in the decoding stage of a generative mode 의 문제점 :
- distribution gap between the discriminator and the generator, leading to a coarser granularity in the guidance process and decreased quality of the generated text.
- hard to be directly applied to fine-grained control scenarios such as date-to-text or multi-attribute control tasks.
-
- GPT-like models $p(x_n|x_1, x_2, . . . , x_{𝑛-1})$
- this local normalization format has certain limitations in paragraph/document-level
modeling
- For example, it is hard to keep long-range coherency in both semantic logic and controlled condition. It calls for further research to establish global normalization based on PLMs to ensure that text generation can be controlled locally and globally at the same time.
-
- Fourth, the construction of large-scale pre-trained language models is typically data-driven, which allows the models to learn the primary logic and common sense contained in the training corpus. However, the knowledge captured in those models is rather superficial. The PLMs will lose generalization ability when the training data does not contain relevant common sense and domain-specific knowledge. Therefore, purely relying on PLMs could be difficult to control the generated texts faithfully to common sense and rich knowledge specific to the target domain
-
- Fifth, a reasonable and reliable evaluation has always been a bottleneck restricting the development of more advanced text generation technologies
5.2 Future Directions
- Prompt-based Learning
- Based on the well-designed prompting function, a PLM is able to perform few-shot or even zero-shot learning, adapting to new scenarios with few or no labeled data, thus overcoming the problem of catastrophic forgetting ->CTG 적용
- Fine-grained(잘게 쪼개는 것) Decoding Control
Integration with Classic Generative Theory and Linguistic Knowledge Incorporation of Knowledge Graphs:
Novel Evaluation Metrics and Methods
New CTG tasks [교수님]
- 노인친화적인 대화 유도
- 원더풀플랫폼 예시 : 여기저기 아파요 -> 어떤 약을 먹으세요 -> 불법행위임 (constraint 어케 주냐 , 어케 피하냐 )
- 욕을 우회하는 text control ex) 자음모음욕