Django Model Relationships - Sloathking/Foolish-Wizardz GitHub Wiki
Django Model Relationships
Author: By Josh E
Related assignments: GE03
Quick Resources on model relationships and inheritance
https://docs.google.com/document/d/1gJ_YCeBDj-pTFdk0GGaB_YFU_5fCsJe9TxH77VuucjI/edit
There are three types of relationships with models in Django: One-To-One, One-To-Many, Many-To-Many.
One-To-One (Django Docs)
In One-to-One relationship, one record of the first table will be linked to zero or one record of another table. For example, each employee in the Employee table will have a corresponding row in EmployeeDetails table that stores the current passport details for that particular employee. So, each employee will have zero or one record in the EmployeeDetails table. This is called zero or one-to-one relationship.
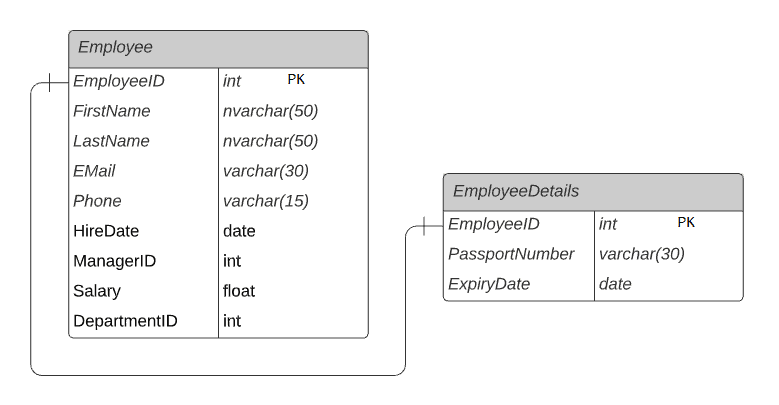
using a One-To-One relationship in code
from django.db import models
# inside Student model description, each Student has one portfolio associated with their profile
class Student(models.Model):
portfolio = models.OneToOneField(Portfolio, null=True, on_delete=models.CASCADE, unique=True)
One-To-Many
One-to-Many is the most commonly used relationship among tables. A single record from one table can be linked to zero or more rows in another table.
Let's take an example of the Employee and Address table in the HR database. The Employee table stores employee records where EmployeeID is the primary key. The Address table holds the addresses of employees where AddressID is a primary key and EmployeeID is a foreign key. Each employee will have one record in the Employee table. Each employee can have many addresses such as Home address, Office Address, Permanent address, etc.
The Employee and Address tables are linked by the key column EmployeeID. It is a foreign key in the Address table linking to the primary key EmployeeID in the Employee table. Thus, one record of the Employee table can point to multiple records in the Address table. This is a One-to-Many relationship.
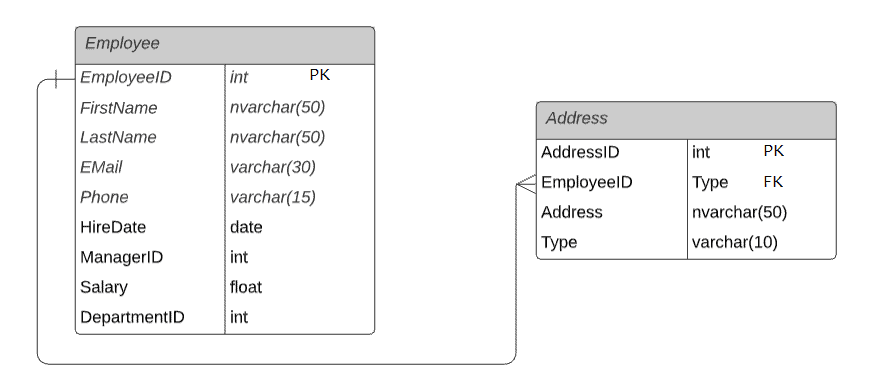
using a One-To-Many relationship in code
from django.db import models
# inside Project model description, each Project can be linked to a portfolio, multiple projects can link to one portfolio
class Project(models.Model):
portfolio = models.ForeignKey(Portfolio, on_delete=models.CASCADE, default=1)
Many-To-Many
Many-to-Many relationship lets you relate each row in one table to many rows in another table and vice versa. As an example, an employee in the Employee table can have many skills from the EmployeeSkill table and also, one skill can be associated with one or more employees.
The following figure demonstrates many-to-many relation between Employee and SkillDescription table using the junction table EmployeeSkill.
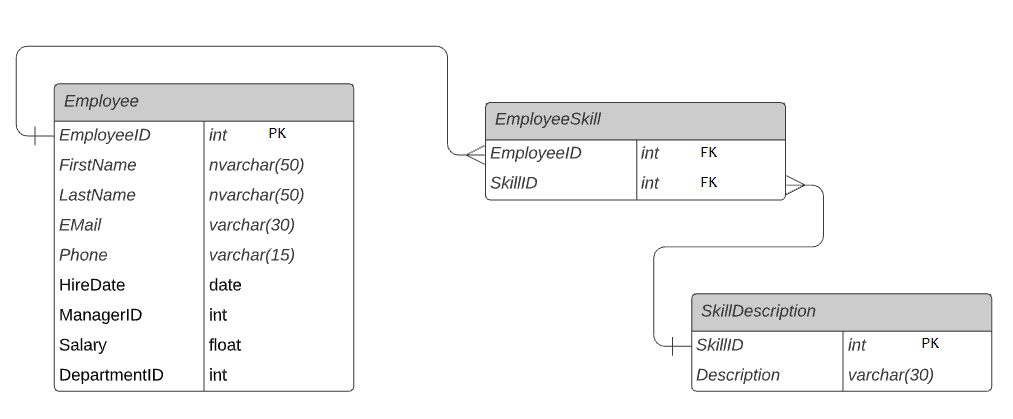 Every employee in the
Every employee in the Employee table can have one or many skills. Similarly, a skill in the SkillDescription table can be linked to many employees. This makes a many-to-many relationship.
In the example above, the EmployeeSkill is the junction table that contains EmployeeID and SkillID foreign key columns to form many-to-many relation between the Employee and SkillDescription table. Individually, the Employee and EmployeeSkill have a one-to-many relation and the SkillDescription and EmployeeSkill tables have one-to-many relation. But, they form many-to-many relation by using a junction table EmployeeSkill.
using a Many-To-Many relationship in code
from django.db import models
# inside Article model, an article can have many publications associated and a publication can be associated to many different articles
class Article(models.Model):
publications = models.ManyToManyField(Publication)