Restart the nodes using an automated script - SkycoinProject/skywire GitHub Wiki

Restart the nodes using an automated script
This guide assumes that you have read and understood the readme.md, downloaded the official images or installed Skywire from source and do every step exactly the way it is described. Misconduct will lead to an inability to connect and to potential reflashing. It is very important that there is no IP collision with your existing home router subnet. The default settings of the official images, as well as the router of the Skyminer, are using the 192.168.0.0/24 subnet.
Table of Contents
Introduction
This guide will provide you with a script that restarts the secondary pi's + the manager all at once. All the steps are designed for usage with the official images but can be adjusted to work with any other startup scripts as well.
Requirements
- official images/multiple pi's with static ip's
- SSH/Putty to access the manager pi or access to the manager's web interface
Usage
Create the script
Login to your manager pi via SSH/using putty or open a terminal inside the manager's web interface.
Change to home directory via cd ~.
Now we need to create the script that will take care of the changes we want to apply.
Execute nano restart.sh to open an editor:
This is the content of the script that we are going to use. Copy and paste it into the editor you just opened.
#!/bin/bash
#This script schedules a reboot for the secondary pi's after 2 minutes
#It assumes that you previously changed the rebuild.sh scripts to start with a time delay that
#is individual to each node (10 seconds rest in between nodes is sufficient)
#username
USERNAME=root
#reboot the secondary pi
HOSTS="192.168.0.3 192.168.0.4 192.168.0.5 192.168.0.6 192.168.0.7 192.168.0.8 192.168.0.9"
for HOSTNAME in ${HOSTS} ; do
if ping -W5 -i0.5 -c 1 &> /dev/null
then
echo 1
echo "no connection to host" ${HOSTNAME}
else
echo "ping received from" ${HOSTNAME}
ssh ${USERNAME}@${HOSTNAME} "shutdown -r 2"
fi
done
#reboot the manager itself
echo "Rebooting the manager now"
reboot
Save the file via ctrl+x and yes.
After that make the script executable via chmod +x restart.sh
Execute the script
Execute the script via ./restart.sh, you will be queried to enter the passwords for the root user one after another. The output should look like this:
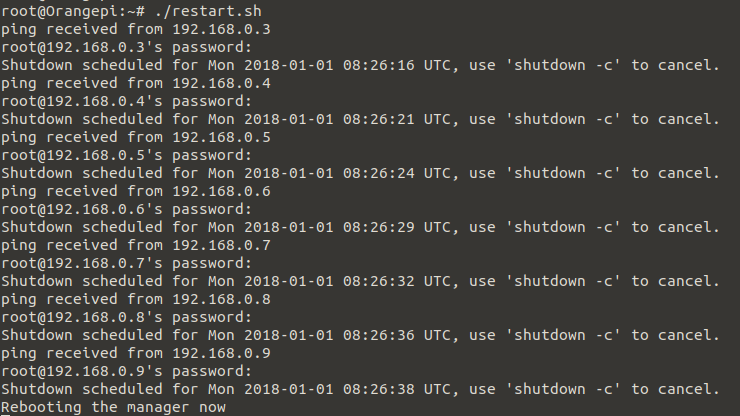
All the secondary pi's will now reboot after 2 minutes, the manager will reboot immediately. This will result in temporary unresponsive nodes connected to the manager, you need to wait a total of 3.5 minutes (210 seconds) until all pi's should be up again and connected to the manager.
Troubleshooting
Unable to connect to pi
If you happen to encounter the error message Read from socket failed: connection reset by peer
then you need need to apply the steps describe here
Adjustments
Adjust the script to work with other IPs
Change the following line
HOSTS="192.168.0.3 192.168.0.4 192.168.0.5 192.168.0.6 192.168.0.7 192.168.0.8 192.168.0.9"
to
HOSTS="IP_NODE_1 IP_NODE_2 IP_NODE_3 IP_NODE_4 IP_NODE_5 IP_NODE_6 IP_NODE_7 IP_NODE_8 IP_NODE_9"
where you have to replace IP_NODE_1 IP_NODE_2 etc. with the IPs of your nodes.
Keep in mind that the IPs are starting with your first node and not with the IP of the manager!
Adjust the script to work with a different user than root
Change the following line:
USERNAME = your_username
to the user you are using on the pi's. For raspberry pi that would be USERNAME=pi
Adjust the script to work on a raspberry pi with user pi
IP range of 192.168.0.3-9 is assumed.
#!/bin/bash
#This script schedules a reboot for the secondary pi's after 2 minutes
#It assumes that you previously changed the rebuild.sh scripts to start with a time delay that
#is individual to each node (10 seconds rest in between nodes is sufficient)
#username
USERNAME=pi
#reboot the secondary pi
HOSTS="192.168.0.3 192.168.0.4 192.168.0.5 192.168.0.6 192.168.0.7 192.168.0.8 192.168.0.9"
for HOSTNAME in ${HOSTS} ; do
if ping -W5 -i0.5 -c 1 &> /dev/null
then
echo 1
echo "no connection to host" ${HOSTNAME}
else
echo "ping received from" ${HOSTNAME}
ssh ${USERNAME}@${HOSTNAME} "sudo shutdown -r 2"
fi
done
#reboot the manager itself
echo "Rebooting the manager now"
sudo reboot
The rest of the steps in the guide stay the same.