uMesh Security - Shaofa/AliOS-Things-Certification-Manual GitHub Wiki
EN | 中文
AliOS Things is a light-weight embedded operating system for Internet of Things (IoT). It contains plenty of components with good capability and is convenient for further development. It supports devices to connect to Alibaba Cloud Link, integrating the cloud, and can be applied to smart homes and smart cities.
The large number of terminal devices involved in IoT challenges the regular way of maintaining cyber security. Operation in cloud side makes the physical border of devices no longer exist. With more and more cyber attacks reported these years, security is of vital importance for IoT developers.
In order to overcome this tough task, the core component of AliOS Things, uMesh, has paid great attention to ensure the safe connection of devices and maintain the security and confidentiality of data in cloud. uMesh is characterized as self-organized, self-repairing and multi-hop. It is suitable for scenarios that need large-scale deployment and with high security demands, such as intelligent homes, smart lighting and commercial buildings. The main capabilities and features of uMesh include:
-
seamlessly support IPv4 IPv6
-
support various communication media, such as Wi-Fi, BLE, IEEE 802.15.4
-
support heterogeneous networking among different communication media
-
support tree topology and mesh topology
-
support low energy-consumption
-
support ID² platform to authenticate and authorize the access devices
-
support AES-128 to encrypt and decrypt data
-
compatibly support Port-based Netwok Access Control IEEE802.1x and Extended Authentication Protocol(RFC3748)
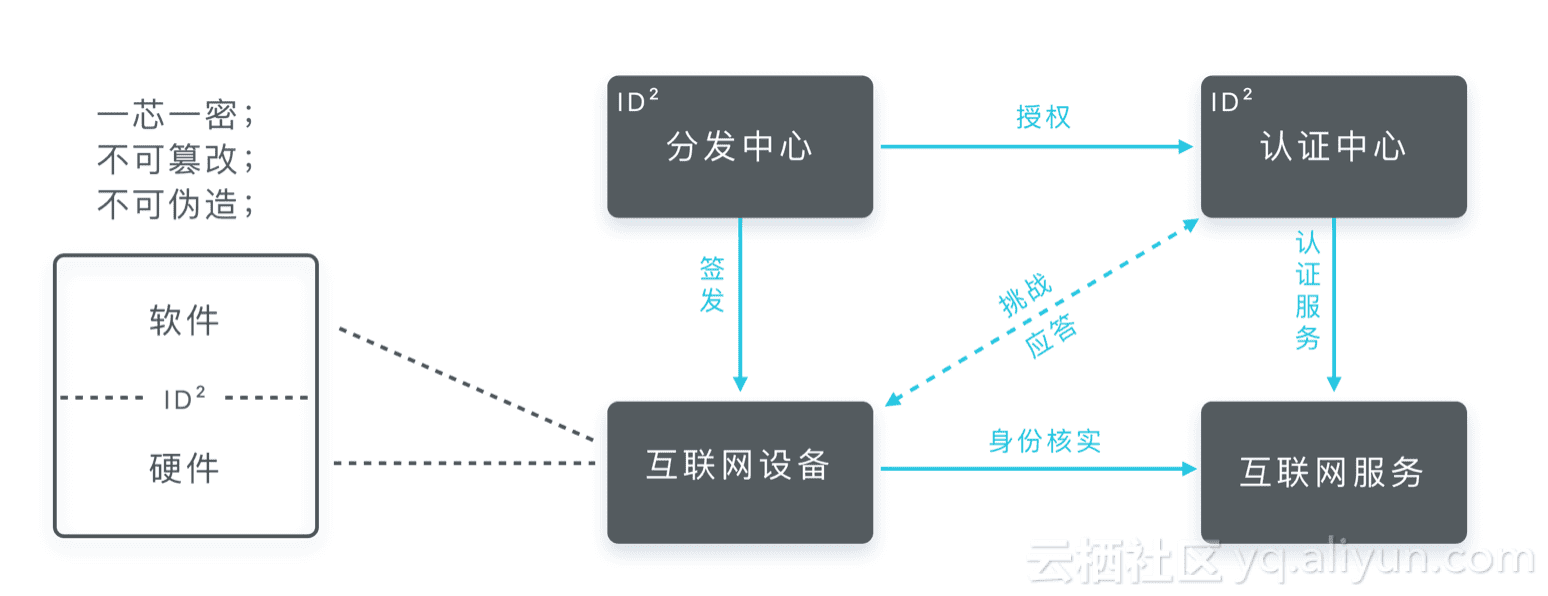
ID²(Internet Device ID) is an identification for IoT devices. It's unique, and can't be changed or counterfeited. It's the key foundation in achieving interconnection among things.
ID² platform is composed of Internet devices, ID² distribution center, ID² authentication center and Internet service. Chips manufactures can request, get and program ID² through SDK. After programing process, API can be called to confirm whether the chips have been successfully programed. Detailed process can be viewed at https://iot.aliyun.com/docs/security/ID2_license_application.html
When programing ID², the corresponding private key will be programed into the chip, while the public key uploaded to ID² authentication center. The private key can latter be used to decrypt the encrypted data sent by authentication center. In this case, channel authentication and key agreement in application layer can be achieved. The combination of ID² with various connecting protocols (such as MQTT and CoAP) further guarantees the safety of the whole IoT system. The framework of ID² platform is shown as followed:
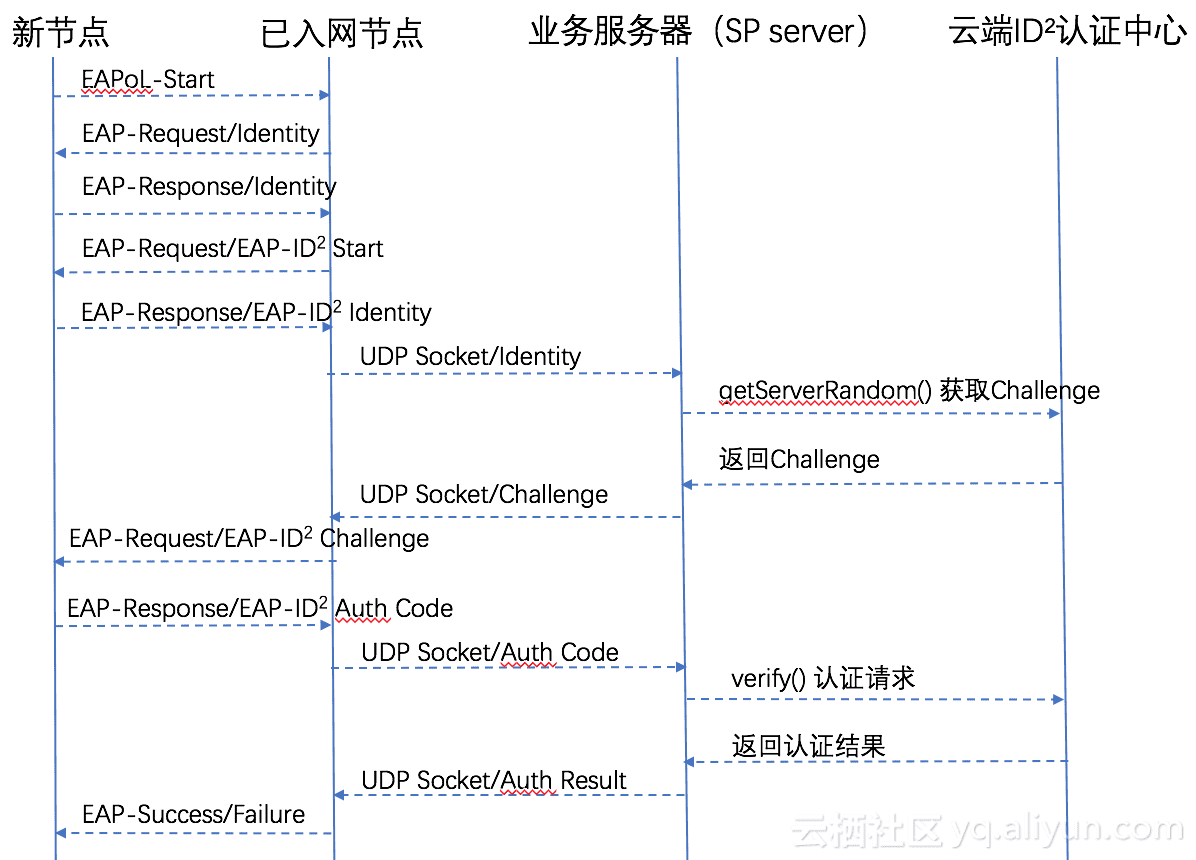
ID² platform offers two authentication modes: challenge-response based mode and timestamp-based mode, which can prevent replay attack. Take challenge-response based mode as an example, the sp server can work as proxy, to transmit message between devices and authentication center (devices are presupposed to programed with ID². The following is the flow chart about interaction of authentication message.
- devices send authentication request to sp server, applying for challenge to ID² authentication center
- the sp server calls POP SDK Java API:getServerRandom(), getting challenge from authentication center and returning it to devices
- devices receive challenge, and call TFS API:tfs_id2_get_challenge_auth_code() to generate auth code, with ID², challenge and extra data (optional) as parameters
- devices send auth code to sp server, which then forwards it to authentication center
- sp server calls POP SDK Java API:VerifyRequest() to complete authentication
- process transaction in sp server based on the result of authentication
In addition, for devices that have access to the SP server, ID² ensures the mutual authentication between devices and server. That is, on the one hand, SP server needs to decide whether or not the device with that identity information is allowed to access; on the other hand, the device needs to confirm whether the SP server has the legitimacy to provide certification service. Through this mutual authentication, devices that have legitimate identity information, but do not belong to SP server's services scope will be filtered out. Besides, different vendors can define their specific way of access to sp server, though this part will be out of scope of this article.
Sp server's use of POP SDK API in authentication process can be seen in sample code: get challenge; requirement for authentication; authentication and encryption. How to call TFS API in devices can refer to API declaration. Path to tfs is AliOS-Things/security/tfs/lib.
Traditional AAA(Authentication, Authorization and Accounting)service needs IT experts to create every certificate manually. In addition, x.509 certificate will consume many preset flash resources and extra MCU resources when analyzing and authenticating ASN.1 ( some may be larger than 1KBytes). Therefore, authentication based on certificates is not a best choice for resources-limited devices.
ID² is a light-weight platform based on identity. There is no need for IT experts to manually repeat the same process of deployment and configuration. Instead, they can just call the corresponding SDK to contact with ID² authentication center. The authentication process of devices in uMesh is set according to challenge-response-based mode. It compatibly support Port-based Netwok Access Control (IEEE802.1x) and Extended Authentication Protocol (EAP); IEEE802.11 is used in data transmission. EAP also provides a basic protocol framework for further expansion and compatibility of other authentication measures, such as MD5, OTP and TLS.
The security authentication process in uMesh based on ID² platform is shown as followed:
RPi 3, as is directly linked to AP, plays the role of leader in the framework. It generates a new uMesh and distributes 16 bits address for subsequently-joined devices, which is used in communication in this uMesh. Meanwhile, RPi 3 uses iptable to set up NAT to transmit the ip data packet between tun0 and eth0, which enables devices in uMesh to communicate with sp server in external network, and thus completing authentication process in ID² platform.
The security authentication process of devices in uMesh is shown as followed:
EAP defines the standard type of authentication ( such as MD5, OTP, GTC, TLS) as well as some expanded types ( type=254) to accommodate the existing process in different vendors. EAP-ID² is one of them used in uMesh based on ID² system. The detailed header format for extension type is shown as followed:
The authentication system in uMesh based on ID² platform has been verified in test environment, and its compatible support for IEEE802.1x and EAP gives it more flexibility to meet different vendors' need, which provides a strong support for its further deployment in business scenarios.
More details about AliOS Things can be see in AliOS Things Github。