Classes and log levels - RobertoPrevato/rolog GitHub Wiki
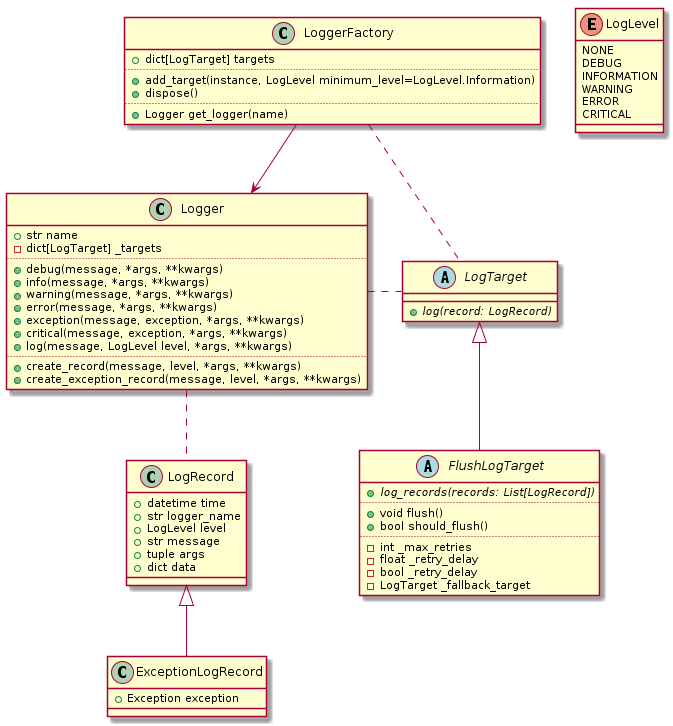
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| LogLevel | Int enum: NONE, DEBUG, INFORMATION, WARNING, ERROR, CRITICAL |
| LogTarget | base for classes that are able to send log records to a certain destination |
| Logger | class responsible for creating log records and sending them to appropriate targets, by level |
| LoggerFactory | configuration class, responsible for holding configuration of targets and providing instances of loggers |
| LogRecord | log record created by loggers, sent to configured targets by a logger |
| ExceptionLogRecord | log record created by loggers, including exception information |
| FlushLogTarget | abstract class, derived of LogTarget, handling records in groups, storing them in memory |
Basic use
As with the built-in logging module, Logger class is not meant to be instantiated directly, but rather obtained using a configured LoggerFactory.
Example:
import asyncio
from rolog import LoggerFactory, Logger, LogTarget
class PrintTarget(LogTarget):
async def log(self, record):
await asyncio.sleep(.1)
print(record.message, record.args, record.data)
factory = LoggerFactory()
factory.add_target(PrintTarget())
logger = factory.get_logger(__name__)
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
async def example():
await logger.info('Lorem ipsum')
# log methods support any argument and keyword argument:
# these are stored in the instances of LogRecord, it is responsibility of LogTarget(s)
# to handle these extra parameters as desired
await logger.info('Hello, World!', 1, 2, 3, cool=True)
loop.run_until_complete(example())