MagicHome LED strip controller - RTurala/Sonoff-Tasmota GitHub Wiki
MagicHome LED controllers (aka Flux-Led, aka Arilux AL-LC01)
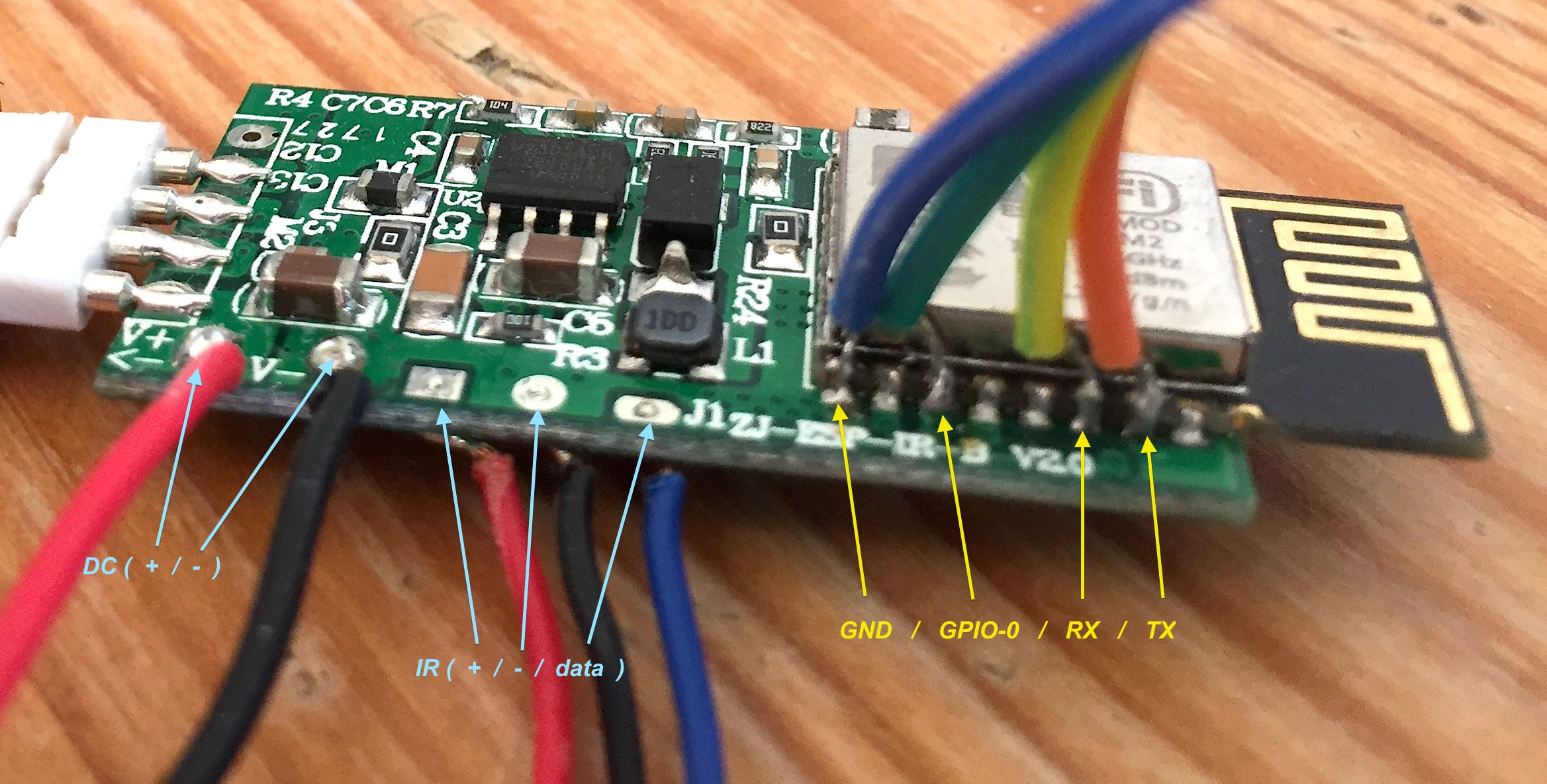
Board is essentially a ESP-12S (or ESP-2M) with necessary voltage converters, little bit of flash, 3 or 4 MOSFETs to drive LED strip (depending on the model), connector for LED strip and optional IR receiver.
Module is powered by 12V that is used to power LED strip as well. RGB models are declared as 144W, RGBW models as 192W.
Module comes in (at least) 3 variants:
- RGB,
- RGBW and
- RGBW with IR receiver.
A different version of this controller with an ESP8285 is documented here
Serial Connection
Board has RX, TX, GND and GPIO00 pads exposed on the bottom side of the PCB. You need to solder temporary wires those pads.
You need to power the board while keeping it connected to the programmer.
With all Sonoff boards that work with AC, this is a big no-no that will fry your programmer, your Sonoff and might even get you killed. In this case, you'd be dealing with 12V, so the only thing that matters is to connect the GND of your programmer to GND of the board before you supply the 12V. Not doing so might fry your board and/or programmer, but would definitely not hurt you.
Steps used:
- Connect your programmer to a breadboard and notice the locations of GND, TX and RX columns.
- Open the MagicHome controller box and expose bottom side of PCB
- Solder 4 jumper wires to 4 exposed pads.
- FIRST connect GND to your programmer (and make sure they are connected well!)
- Connect RX from the MagicHome to TX on the programmer. TX from the board goes to RX on the programmer.
- Connect GPIO00 to GND (best to use same column on the breadboard)
- Connect the 12V power supply to MagicHome. As GPIO00 is connected to GND, board will go into flash mode. I usually disconnect GPIO00 after few seconds, but not sure if this is mandatory or optional.
- Upload Sonoff-Tasmota like it would be any other board.
- Once upload is complete, disconnect power from the MagicHome controller
- Disconnect RX and TX and then only then GND. GND gets disconnected LAST.
You can then connect the power back to the board and Sonoff-Tasmota should be running on it. Once you verify that board is up and you can access it over the Web, you can unsolder temporary wires and update subsequent firmware versions using OTA.
Configuration
Some GPIO are preconfigured with the board:
- GPIO05 - (PWM2) Green color on the led strip, first pin from the GND
- GPIO14 - (PWM1) Red color on the LED strip, second pin from the GND
- GPIO12 - (PWM3) Blue color on the LED strip, third pin from the GND
Check this for Board Version 2.3 : #1867
Due to variants, you can configure:
- GPIO04 - on non-IR boards, it's an open pin you can use for Onewire, button or something else. It might have pull-down resistor and/or bypass capacitor, so please take that into consideration. On IR-enabled boards, IR receiver is connected to this pin, so you can use IRRecv as functionality.
- GPIO13 - This pin is not used on RGB board (so you'll leave it as "None"), but on RGBW, it's driving another channel (cold white or warm white) for LED strip.
Variant without Rx/Tx pads:
-
Using the IRrecv (IR Remote) feature
If you have a variant with an IR Remote (as per the opening picture), you can use the new rule command to make the remote buttons change the light levels. For example, this rule allows me to turn it on and off, change the brightness, and turn it on to full white:
mosquitto_pub -t 'cmnd/light/rule1' -m 'on IrReceived#Data=FFF807 do power OFF endon on IrReceived#Data=FFB04F do WAKEUP endon on IrReceived#Data=FF906F do dimmer + endon on IrReceived#Data=FFB847 do dimmer - endon on IrReceived#Data=FFA857 do color #000000ff endon'
The hex codes for the "Data" value come from the data tag when looking at the JSON sent via MQTT. From here you can program it to do what ever you want. See here for more details: https://github.com/arendst/Sonoff-Tasmota/wiki/Rules
