Architecture - RDR3/cx-flow GitHub Wiki
- Web Service
- Overview
- Load Balancing
- Workflow
- Network Architecture
- Software Components
- Execution
- Configuration
- Access Control
- Defect Trackers
- Checkmarx
- SCM Repository
- Secrets and Credentials
- CxFlow
- Data Elements
- Persistence
- Logging
- Development
- Backlog
- Build/Release
Web Service (WebHook)
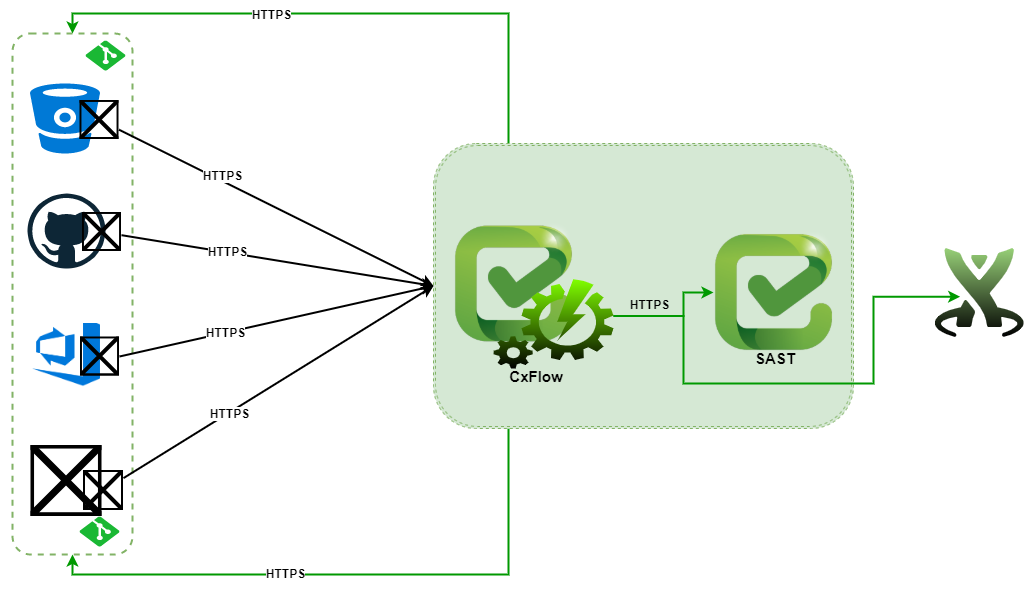
Overview
- CxFlow listens to HTTP/S requests matching specific payloads that represent pull/merge requests and push requests.
- Bitbucket (Server & Cloud)
- GitHub
- Azure DevOps / TFS
- GitLab
- CxFlow is configured to process events associated with branches considered important/protected across the enterprise based on the following:
- List of static values
- master
- develop
- release
- List of regular expressions
- External Groovy Script execution hooks
- List of static values
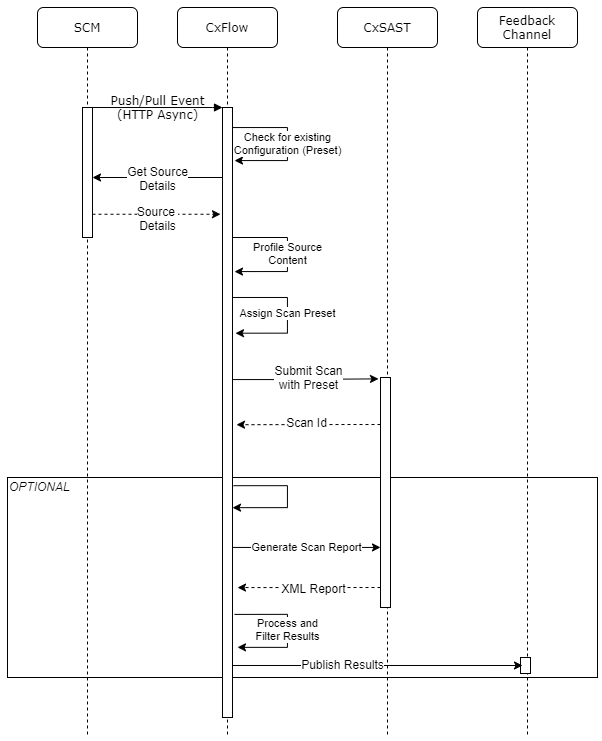
- Upon receiving an event, CxFlow will:
- A scan request for the repository will be initiated
- Scans will be attempted as incremental with the following rules (optional):
- A full scan was conducted within the last 7 days (configurable)
- A scan was conducted within the last 5 scans (configurable)
- Global file exclusion pattern(s) will be applied for every scan according to the CxFlow configuration
- Scans will be attempted as incremental with the following rules (optional):
- Optionally Result feedback can be configured
- CxFlow generates the XML report
- Results are filtered
- Results are published according to the configured feedback channel(s)
- File type, number of references, percentage of code base (reflected from post exclusions) are mapped
- CxFlow iterates through a rule set that attempts to match the fingerprint of the source code
- Rules are evaluated in the order they have been provided in the configuration file. Once a match is found, CxFlow stops checking further
- There is a default/catchall rule for those not matching a finger print
- Based on the fingerprint rule matching, an associated Checkmarx preset is assigned
- This information is saved to the local CxFlow cache. Note: If multiple instances of CxFlow are load-balanced, the cache is only available to the local instance performing the processing. This design can be enhanced if required.
- A scan request for the repository is initiated with the scan preset that has been assigned in the previous step(s)
- Scans are attempted as incremental with the following rules:
- A full scan has been conducted within the last 7 days
- A scan has been conducted within the last 5 scans
- Global file exclusion pattern(s) are applied for every scan according to the CxFlow configuration
- Scans are attempted as incremental with the following rules:
- In addition, result feedbacks can be configured as follows:
- CxFlow generates the XML report.
- Results are filtered
- Results are published according to the configured feedback channel(s)
- A scan request for the repository will be initiated
Load Balancing
CxFlow integrates easily with Load Balancing as it is stateless/RESTful and can run on any available port
Workflow
Refer to the following for additional information.
Network Architecture
The network architecture is divided into inbound and outbound traffic.
Inbound
CxFlow requires network connectivity from the SCM Repository to the specified port which it is listening on (8443 - HTTPS | 8080 - HTTP). CxFlow can filter access based on IP addresses.
NOTE: This functionality becomes available with the next release.
Outbound
CxFlows requires access to any of the desired feedback channels over HTTP/S:
- Jira
- Azure DevOps WorkItems
- GitLab Issues
- GitHub Issues
- Pull / Merge Request Markdown Comments Access is required for any Checkmarx Instances
Software Components
- Java Runtime 8 or 11
- Gradle 5.4 (Build)
- Spring Boot 2.1.9, Spring boot is regularly updated as part of ongoing 3rd party library maintenance
Execution
Refer to the detailed execution instructions
Configuration
Refer to the detailed configuration instructions
Access Control
This section outlines various access aspects.
Defect Trackers
Access to the various defect management systems is provided via a service account and leverages an API token or service account credentials. Access should be granted to the appropriate service account for the desired use cases (i.e. create/update/close issue)
Checkmarx
Access to Checkmarx is granted through OIDC JWT Token in the same fashion as any of the Checkmarx Plugins. Required access is to Create teams, projects, initiate scans, retrieve results.
SCM Repository
Access to the various defect SCM Repositories (Pull Request Feedback/Repo Issues) is provided via a service account and leverages an API token or service account credentials. Access must be granted as well to the appropriate service account for the desired use cases (i.e. read access to all relevant sources/read access to Pull events/access to comments on pull requests)
Secrets/Credentials
Credentials can be injected into CxFlow using several techniques according to the following resource: https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/2.1.9.RELEASE/reference/html/boot-features-external-config.html. These credentials can be encrypted leveraging Jasypt
CxFlow
SCM Repository events are authenticated by a shared key/token. Each SCM provides a different mechanism to authenticate the request. GitHub and Bitbucket Server use digital signature validation leveraging the shared key/token. Others use a basic auth or API token header. This is specific and relative to the SCM design.
Data Elements
Inputs
- CM Repository Event Details are associated with code management events. GitHub Example: https://developer.github.com/v3/activity/events/types/#pullrequestevent
- Checkmarx Results. When scans are completed, the results are generated and pulled from Checkmarx. Checkmarx scans are triggered using the GIT URL scan configuration with Auth token (GIT Clone). This means that the GIT must be configured in CxSAST.
Outputs
- SAST/OSA scan results
- HTTP API Payload with Vulnerability details. Refer to the feedback channels for details
Persistence
CxFlow has no persistence layer. It is stateless and can easily be scaled behind several LB and container orchestration technologies. Instead, it relies on the Checkmarx and Defect management system to store defects in a meaningful way to associate projects with existing issues and defects.
Logging
Logging details can be found under Troubleshooting. Logging elements contain unique identifiers to associate all events for a specific payload/event request. All events are logged for inbound SCM events and outbound feedback channel (defect management) events.
Development
Refer to the Development page
Backlog
Issues and feature requests are managed here.
Build/Release
Build and Release is managed via CircleCI using Gradle. Releases are published automatically (develop branch for TS version) to
- GitHub Release: https://github.com/checkmarx-ts/cx-flow/releases (compile JAR)
- DockerHub: https://hub.docker.com/r/checkmarxts/cxflow