Log JDBC Calls (Payara 4.1.1.161) - Pandrex247/Payara GitHub Wiki
Payara Server and Micro 161 (4.1.1.161) onwards
From Payara 161 (4.1.1.161) tracing of all SQL calls through a Payara Server connection pool is possible, with the time taken to execute the call also recorded. SQL Tracing is ideal fo debugging those hard to pin down performance issues during the development phase and as all SQL is visible SQL tracing is also a great way to see the SQL generated out of your JPA code. With "Log JDBC Calls" configured on the connection call each call into the Connection pool is timed and logged to the server log at FINE level. A typical log message with Log JDBC Enabled is shown below;
[#|2016-02-04T18:51:01.467+0000|FINE|Payara 4.1|javax.enterprise.resource.sqltrace.com.sun.gjc.util|_ThreadID=35;_ThreadName=http-listener-1(5);_TimeMillis=1454611861467;_LevelValue=500;ClassName=com.sun.gjc.util.SQLTraceLogger;MethodName=sqlTrace;|
PoolName=DerbyPool | ExecutionTime=1ms | ClassName=org.apache.derby.client.net.NetConnection40 | MethodName=prepareStatement | arg[0]=SELECT ID, AGE, BIO, BIRTHDATE, BIRTHDAY, DATEFORMAT, DATEOFBIRTH, DATEOFHIRE, EMAIL, HIREDATE, HIREDAY, MEMBERAGE, NAME, TODAYSDATE FROM MEMBERENTITY WHERE (NAME = ?) | arg[1]=1003 | arg[2]=1007 | |#]
[#|2016-02-04T18:51:01.467+0000|FINE|Payara 4.1|javax.enterprise.resource.sqltrace.com.sun.gjc.util|_ThreadID=35;_ThreadName=http-listener-1(5);_TimeMillis=1454611861467;_LevelValue=500;ClassName=com.sun.gjc.util.SQLTraceLogger;MethodName=sqlTrace;|
PoolName=DerbyPool | ExecutionTime=0ms | ClassName=com.sun.gjc.spi.jdbc40.PreparedStatementWrapper40 | MethodName=setString | arg[0]=1 | arg[1]=test | |#]
[#|2016-02-04T18:51:01.468+0000|FINE|Payara 4.1|javax.enterprise.resource.sqltrace.com.sun.gjc.util|_ThreadID=35;_ThreadName=http-listener-1(5);_TimeMillis=1454611861468;_LevelValue=500;ClassName=com.sun.gjc.util.SQLTraceLogger;MethodName=sqlTrace;|
PoolName=DerbyPool | ExecutionTime=1ms | ClassName=com.sun.gjc.spi.jdbc40.PreparedStatementWrapper40 | MethodName=executeQuery | |#]
[#|2016-02-04T18:51:01.483+0000|FINE|Payara 4.1|javax.enterprise.resource.sqltrace.com.sun.gjc.util|_ThreadID=35;_ThreadName=http-listener-1(5);_TimeMillis=1454611861483;_LevelValue=500;ClassName=com.sun.gjc.util.SQLTraceLogger;MethodName=sqlTrace;|
PoolName=DerbyPool | ExecutionTime=0ms | ClassName=com.sun.gjc.spi.jdbc40.PreparedStatementWrapper40 | MethodName=close | |#]
You can see in the log messages that the prepareStatement, setString, executeQuery and close methods are all logged along with their execution times and their parameters. This gives exceptional debugging capabilites for tracking down database connection related issues.
WARNING: This is a feature best used for development due to the volume of trace that is produced.
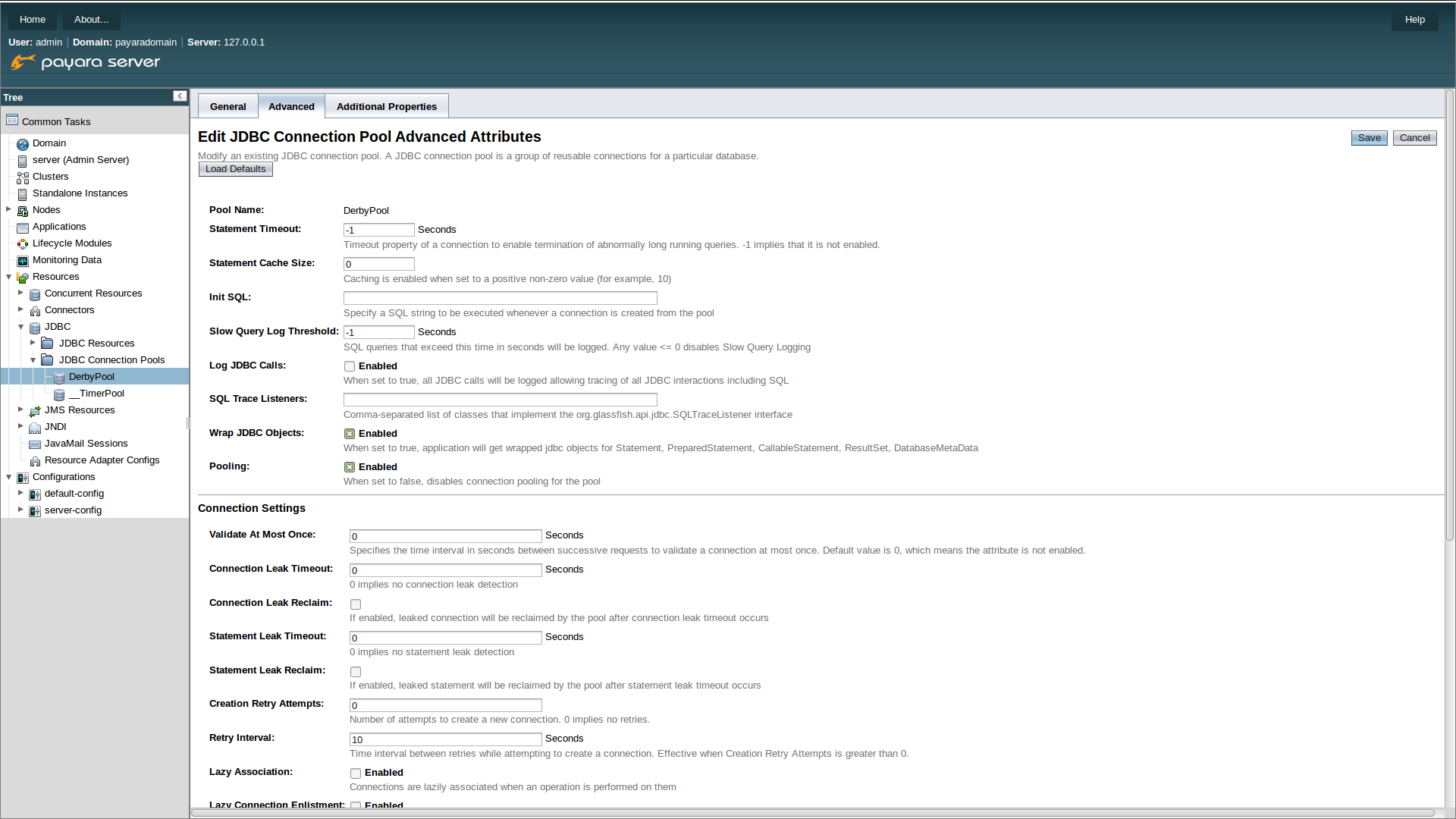
SQL Tracing caan be enabled through the Payara Server administration console. Navigate to the advanced tabl of your connection pool. Using the left hand tree view selecte JDBC->JDBC Connection pools->Your Connection pool. then select the Advanced Tab in the main window of the administration console. Then select the checkbox next to Log JDBC Calls to enable logging of all SQL call.
The Log JDBC Calls setting for a connection pool can also be configured via asadmin using the set command to set the fish.payara.log-jdbc-calls property of your connection pool to true. For example the command enables JDBC call logging.
asadmin set domain.resources.jdbc-connection-pool.__TimerPool.log-jdbc-calls=trueIn Java EE 7 a JDBC datasource can be deployed by adding annotations to a JavaEE component. The Log JDBC Calls setting can be configured via these annotations. Using annotations is the best way to enable SQL Tracing through logging of the JDBC calls.
@DataSourceDefinition(
name = "java:app/MyApp/MyDS",
className = "org.h2.jdbcx.JdbcDataSource",
url = "jdbc:h2:mem:test",
properties = {"fish.payara.log-jdbc-calls=true"})or the Datasource definition can be added to a deployment descriptor of an application for example in the web.xml
<data-source>
<name>java:global/ExampleDataSource</name>
<class-name>com.mysql.jdbc.jdbc2.optional.MysqlXADataSource</class-name>
<server-name>localhost</server-name>
<port-number>3306</port-number>
<database-name>mysql</database-name>
<user>test</user>
<password>test</password>
<!-- Example of how to use a Payara specific custom connection pool setting -->
<property>
<name>fish.payara.log-jdbc-calls</name>
<value>true</value>
</property>
</data-source>Payara Micro also supports SQL Tracing which brings powerful operational diagnostics to your micro-services platform. To enable SQL Tracing of JDBC calls your datasource must be deployed using the annotations described above.