DEFINITION 4: CLASS VARIABLES - PRATMG/2143-OOP-Tamang GitHub Wiki
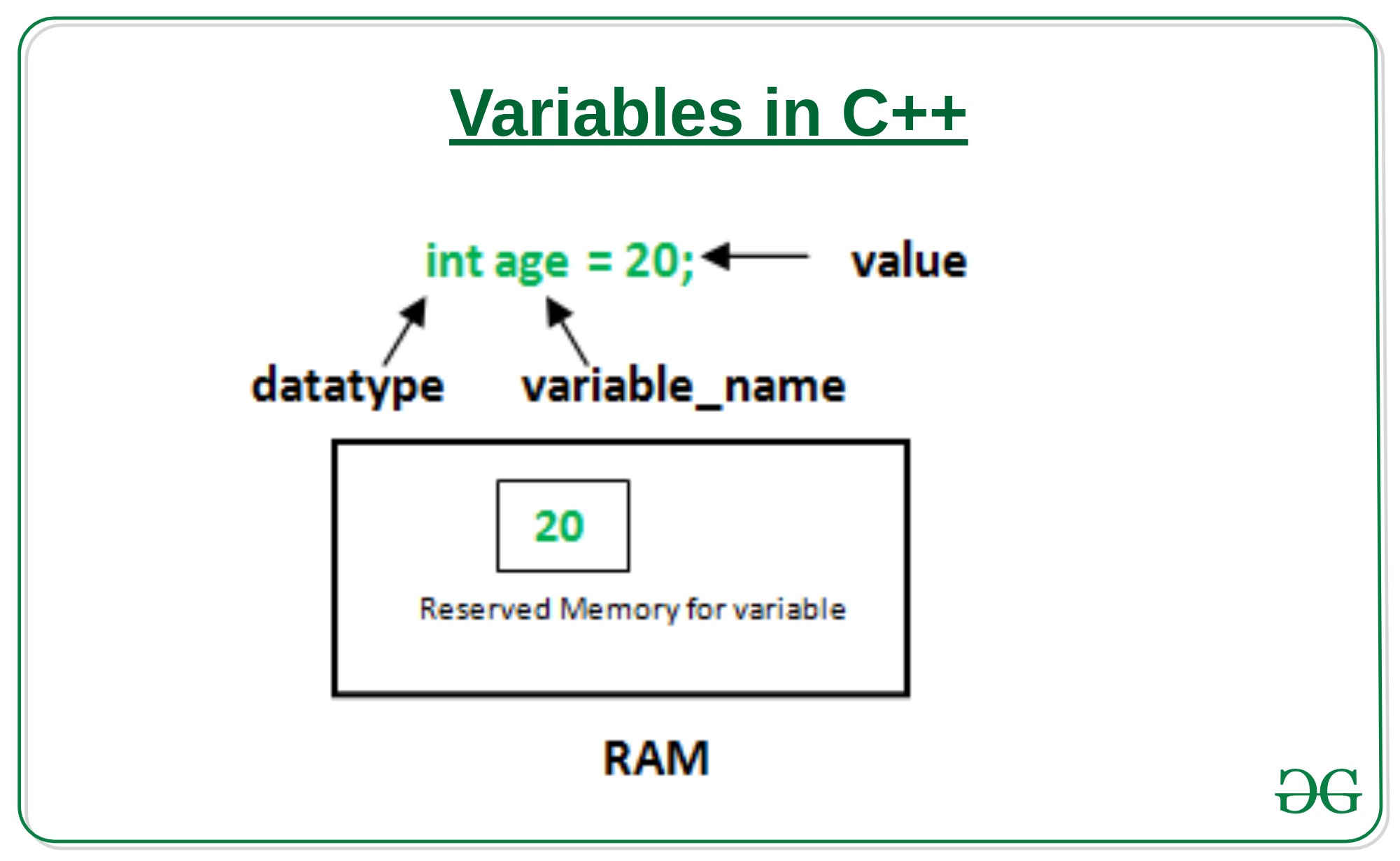
A variable is a name that is assigned to a memory location. It is the fundamental storage unit in a program.
During program execution, the value stored in a variable can be changed. A variable is simply the name given to a memory location; all operations performed on the variable have an effect on that memory location. All variables in C++ must be declared before they can be used.
There are three types of variables based on the scope of variables in C++:
- Local Variables
- Instance Variables
- Static Variables
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// declaration and definition
// of variable 'a123'
char a123 = 'a';
// This is also both declaration and definition
// as 'b' is allocated memory and
// assigned some garbage value.
float b;
// multiple declarations and definitions
int _c, _d45, e;
// Let us print a variable
cout << a123 << endl;
return 0;
}
My reference: