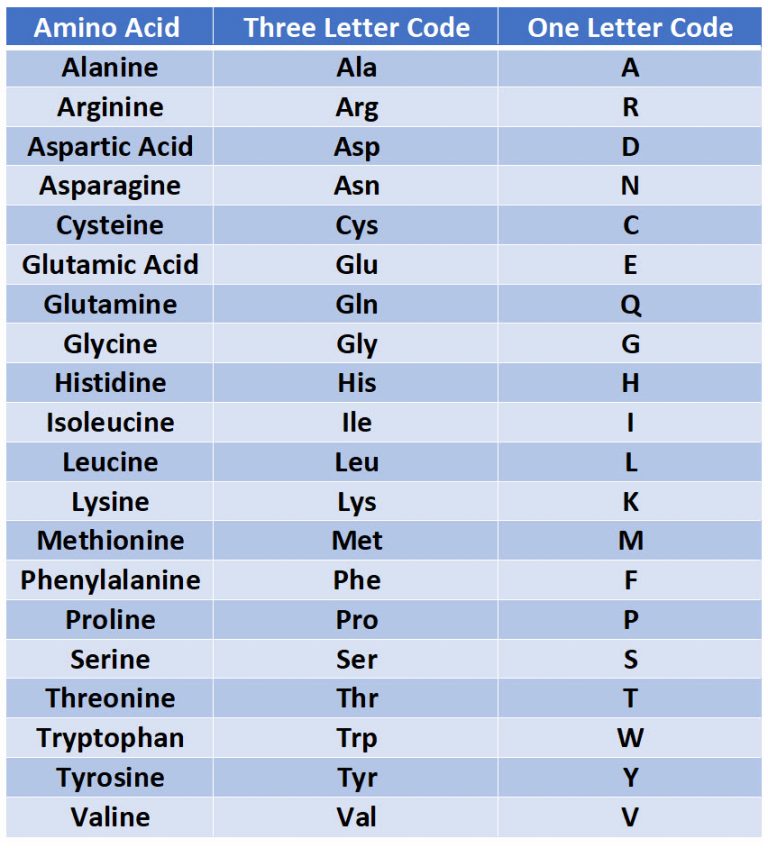
1.4 Amino acids in a table format - Oronda/Molecular_biology_concepts GitHub Wiki
Amino acids are monomers that make up proteins. These proteins are made up of amino acids each of which is called a polypeptide. The covalent bonds that attach one polypeptide to their neighbor are called peptide bonds. Each bond is formed in a dehydration synthesis.
There are 20 types of amino acids commonly known. They are mainly grouped into essential and no n-essential amino acids. Essential amino acids are those amino acids that humans and other vertebrates cannot synthesize from metabolic intermediates. They must come from a person's diet. They are 9 of them. Non-essential amino acids on the other hand are those that the human body is capable of synthesizing. They do not need to come from the diet. They are 11 of them.
Roles
Each of the amino acids do have various roles. They include;
-
Valine-Stimulate muscle growth. Also important in tissue repair and energy. Its codon is GUA GUC GUG GUU.
-
Tryptophan-Maintains proper nitrogen balance. Also a precursor to serotonin. Its codon is UAC UAU.
-
Phenylalanine-Plays a key part in the biosynthesis of other amino acids. Also a precursor for tyrosine and dopamine. Its codon is UUU UUC.
-
Threonine-Important in the nervous system. It helps in fat metabolism. It is also used to alleviate anxiety and mild depression. Its codon is ACA ACU ACG ACC.
-
Isoleucine-Wound healing, detoxify nitrogenous wastes, stimulates the immune system, regulates blood sugar and energy levels. Its coded by AUA AUC AUU.
-
Methionine-Growth and tissue repair, Helps in metabolism and detoxification, lipotropic agent. Coded by AUG.
-
Histidine-Immunity, gastric secretion and sexual functions. It protects tissue against damage caused by radiation and heavy metals. Coded by CAU CAC.
-
Leucine-Regulation of blood-sugar levels, wound healing. Its codon is CUU CUA CUC CUG.
-
Lysine-Protein synthesis, absorption of calcium, production of collagen and elastin. Coded by AAA AAG.
-
Alanine-Biosynthesis of proteins, strengthens the immune system. Coded by GCA GCG GCC GCU.
-
Arginine-Regulating blood flow, stimulates release of insulin. Is coded by AGA AGG.
-
Glutamate-Biosynthesis of proteins, excitatory neurotransmitter. Its codon is GAA GAG.
-
Asparagine-Development and function of the brain, protein modification. Coded by AAU AAC.
-
Aspartate-Increase absorption of minerals they are combined with, enhances athletic performance. is coded by GAC GAU.
-
Cysteine-Source of sulphide, making collagen, found in beta-keratin; important in nails, hair. Coded by UGU UGC.
-
Glutamine-Biosynthesis of proteins, can cross the blood-brain barrier, can reduce severe complications of sickle-cell disease. Its codon is CAA CAG.
-
Glycine-Inhibitory neurotransmitter, Helps in formation of proteins. Coded by GGA GGC GGU GGG.
-
Proline-Formation of collagen, general function of cells. Coded by CCU CCC CCG CCA.
-
Serine-Biosynthesis of purines and pyrimidines, improve sleeping, cognitive function. Coded by UCU UCA UCG UCC AGC AGU.
-
Tyrosine-Precursor to dopamine, cognitive function, athletic performance. Its coded by UAC UAU.