github commands - Omkar9089/Omkar1 GitHub Wiki
Introduction to GitHub Commands
GitHub is very much popular web-based application in current industry for hosting variety services targeting version control using GIT commands. It offers various distributed version controlling as well as source code management properly.
- git config
- git init
- git clone
- git add
- git commit
- git diff
- git reset
- git status
- git rm
- git log
- git show
- git tag
- git branch
- git checkout
- git merge
- git remote
- git push
- git pull
- git stash
git config
Usage: git config –global user.name “[name]”
Usage: git config –global user.email “[email address]”
This command sets the author name and email address respectively to be used with your commits.

git init
Usage: git init [repository name] This command is used to start a new repository.

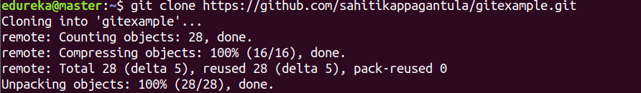
git clone
Usage: git clone [url]
This command is used to obtain a repository from an existing URL.
git add
Usage: git add [file]
This command adds a file to the staging area.
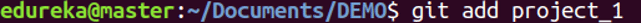
Usage: git add *
This command adds one or more to the staging area.

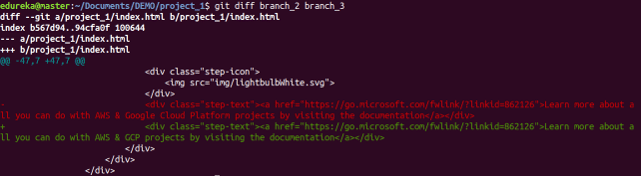
git diff
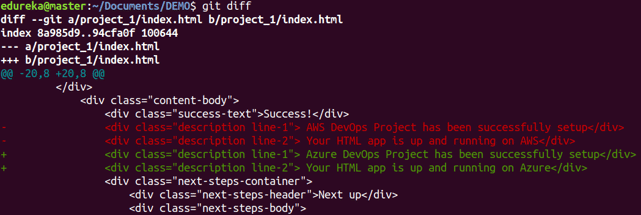
Usage: git diff
This command shows the file differences which are not yet staged.
 \
\
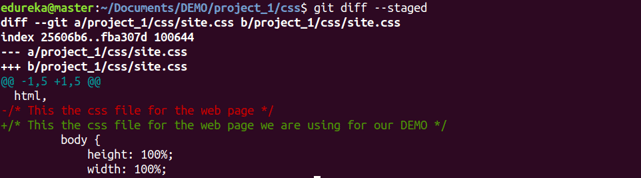
Usage: git diff –staged This command shows the differences between the files in the staging area and the latest version present.
Usage: git diff [first branch] [second branch]
This command shows the differences between the two branches mentioned.
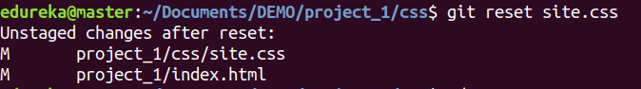
git reset
Usage: git reset [file]
This command unstages the file, but it preserves the file contents.
Usage: git reset [commit]
This command undoes all the commits after the specified commit and preserves the changes locally.

Usage: git reset –hard [commit] This command discards all history and goes back to the specified commit.

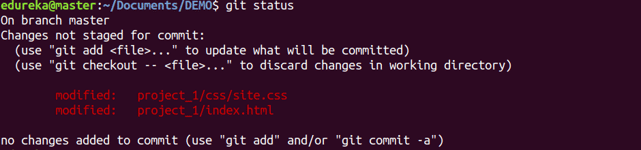
git status
Usage: git status
This command lists all the files that have to be committed.
git rm
Usage: git rm [file]
This command deletes the file from your working directory and stages the deletion.

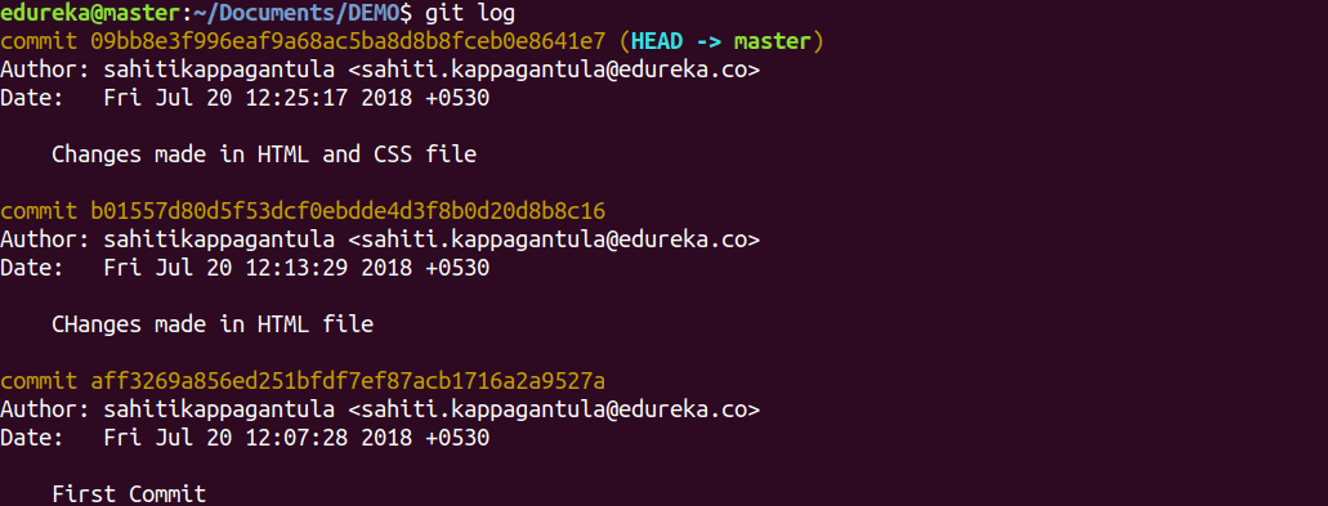
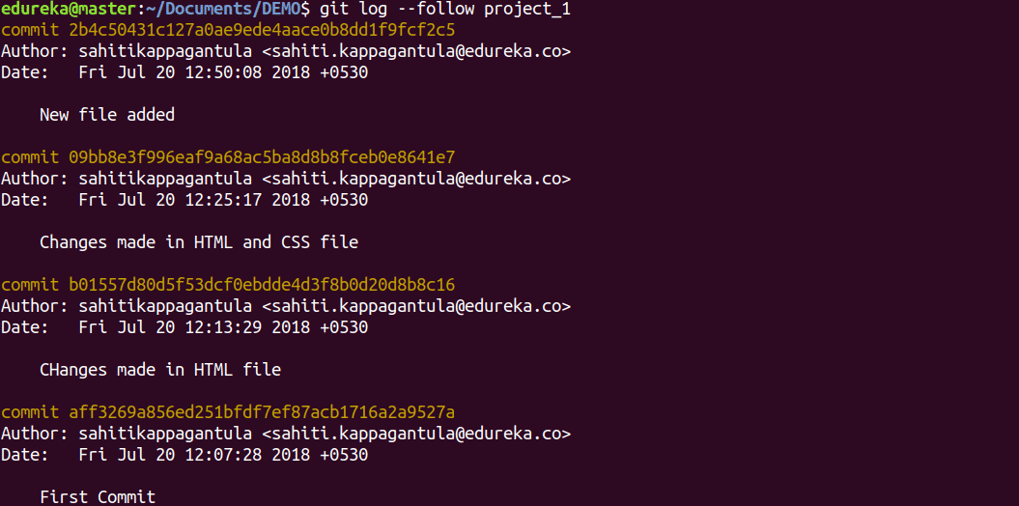
git log
Usage: git log
This command is used to list the version history for the current branch.
Usage: git log –follow[file]
This command lists version history for a file, including the renaming of files also.
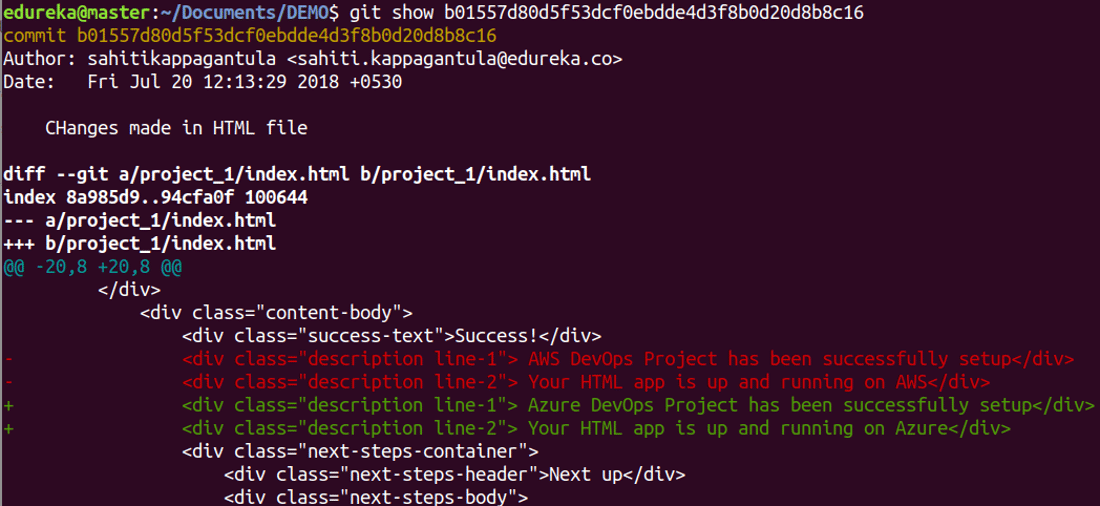
git show
Usage: git show [commit]
This command shows the metadata and content changes of the specified commit.
git tag
Usage: git tag [commitID]
This command is used to giv
e tags to the specified commit.

git branch
Usage: git branch
This command lists all the local branches in the current repository.

Usage: git branch [branch name]
This command creates a new branch.
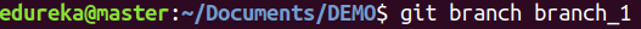
Usage: git branch -d [branch name]
This command deletes the feature branch.

git checkout
Usage: git checkout [branch name]
This command is used to switch from one branch to another.

Usage: git checkout -b [branch name]
This command creates a new branch and also switches to it.
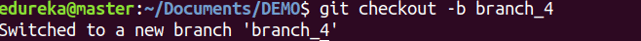
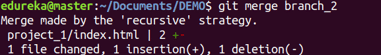
git merge
Usage: git merge [branch name]
This command merges the specified branch’s history into the current branch.
git remote
Usage: git remote add [variable name] [Remote Server Link]
This command is used to connect your local repository to the remote server.
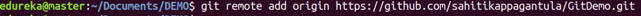
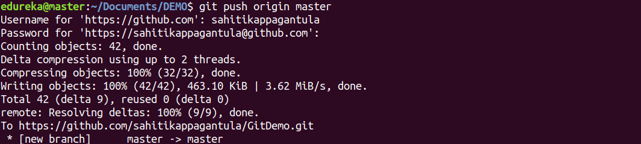
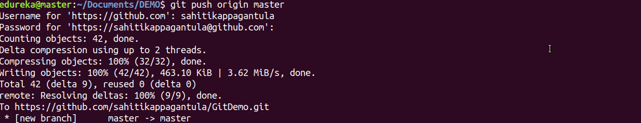
git push
Usage: git push [variable name] master
This command sends the committed changes of master branch to your remote repository.
Usage: git push [variable name] [branch]
This command sends the branch commits to your remote repository.
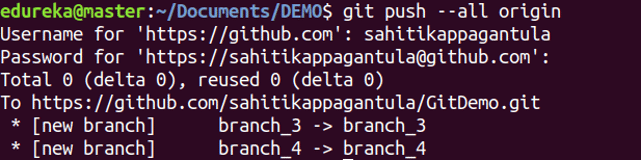
Usage: git push –all [variable name]
This command pushes all branches to your remote repository.
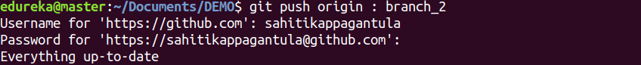
Usage: git push [variable name] :[branch name]
This command deletes a branch on your remote repository.
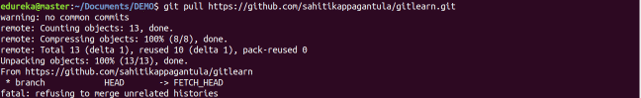
git pull
Usage: git pull [Repository Link]
This command fetches and merges changes on the remote server to your working directory.
git stash
Usage: git stash save
This command temporarily stores all the modified tracked files.

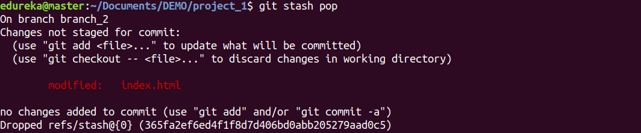
Usage: git stash pop
This command restores the most recently stashed files.
Usage: git stash list
This command lists all stashed changesets.
Usage: git stash drop
This command discards the most recently stashed changeset.
