An Introduction to FreeSWITCH Configuration folders and files. - Omid-Mohajerani/freeswitch GitHub Wiki
Introduction
When we install FreeSWITCH from source by default it will be installed in /usr/local/freeswitch
FreeSWITCH ships with a large number of configuration files. Today I will help to explain the various configuration files and their default contents. Most of the FreeSWITCH configuration files are formatted in XML. We will learn about XML in the late videos. When FreeSWITCH starts or when the reloadxml command is issued to the API, FreeSWITCH compiles all configuration files into one huge file that is kept in memory.
log/freeswitch.xml.fsxml contains all the individual configuration files concatenated together into one huge file. When FreeSWITCH reports a configuration file error, the line number in the error message refers to this file, which can have more than 10 thousand lines.
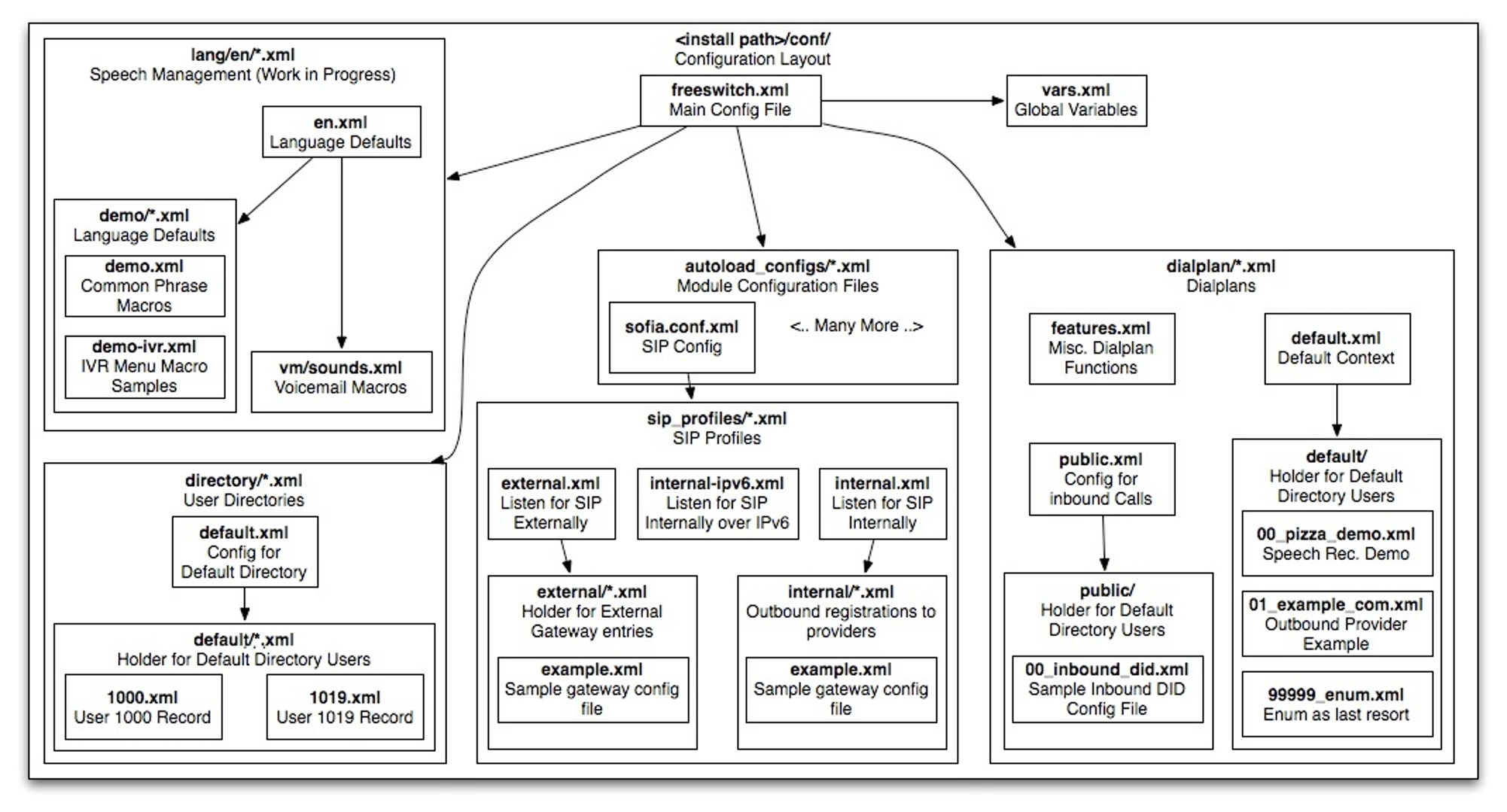
FreeSWITCH Folder Structure
The table below describes the Configuration Folders in the FreeSWITCH.
| Configuration Folder | Description |
|---|---|
| autoload_configs | It contains configuration information for all the core modules and these configuration files will automatically load into FreeSWITCH. |
| dialplan | The dialplan section is where you setup all your call-routing rules. |
| Directory | It will hold all of the users allowed access to make calls via FreeSWITCH. |
| jingle_profiles | This is a module that handles XMPP |
| lang | It tells FreeSWITCH in which language to say the like currency, etc. |
| mrcp_profiles | MRCP is used to allow FreeSWITCH to use speech recognition and TTS. |
| sip_profile | Tells FreeSWITCH how to talk sip. Each profile has its own port. |
| chatplan | Here you setup routing rules for SMS and other chatting platforms. |
| ivr_menus | IVR menu config directory. |
FreeSWITCH main configuration files
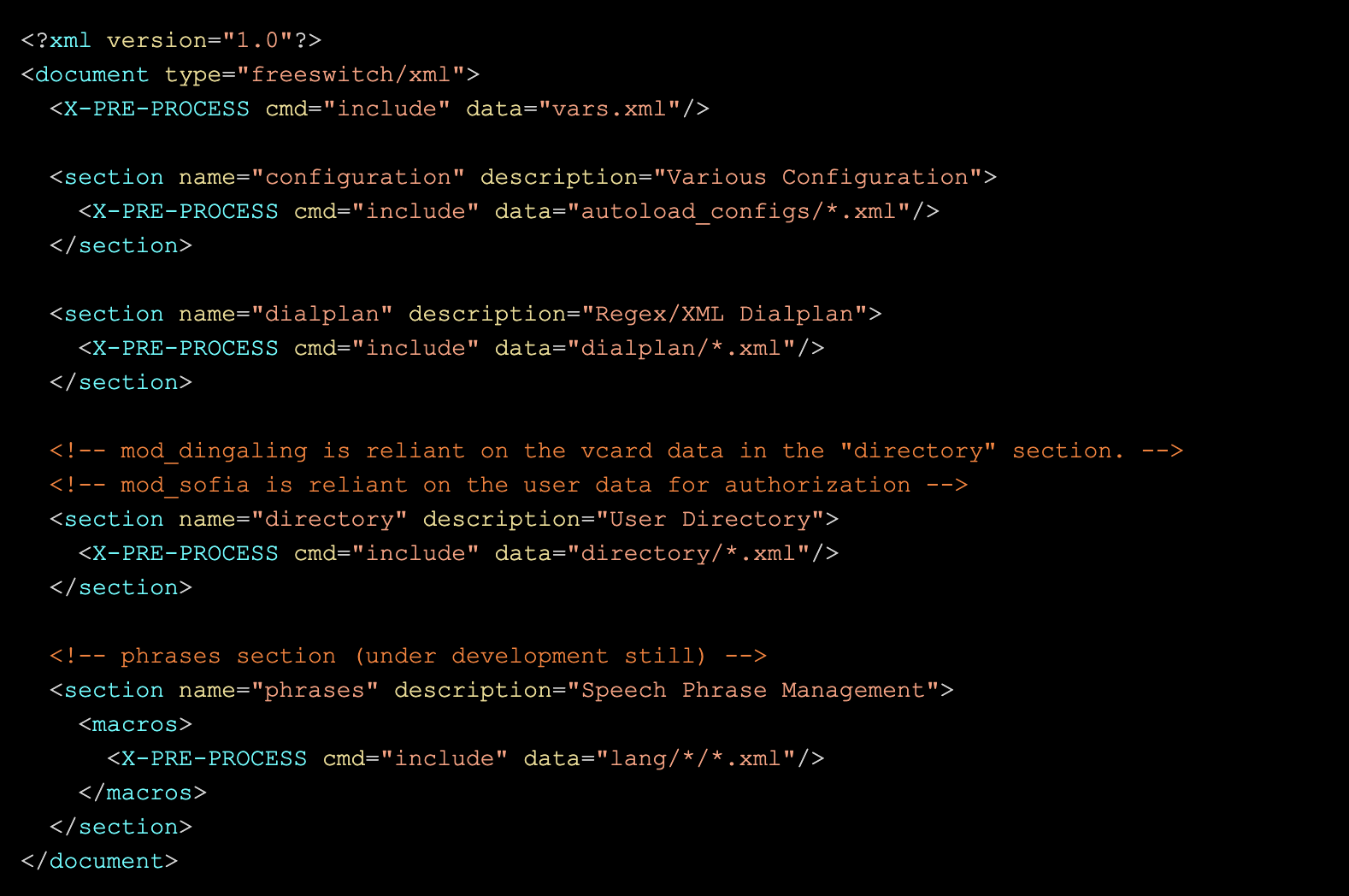
freeswitch.xml
This is the main configuration file and the only one that has a fixed name. When you start FreeSWITCH it will locate this file and process it. The default configuration of most of these files is suitable for first time users, until you become more familiar with FreeSWITCH it is advised that you leave them to their default settings.
freeswitch.xml is divided into multiple sections, and each section is used by a different component in FreeSWITCH. The sections are as follows:
- The configuration section has children for switch.conf and modules.conf which are used by the core, as well as a child for each module in use.
- The dialplan section defines which action to invoke when a call arrvies to the switch.
- The directory defines the users that can connect to the switch (user agents).
- The phrases section defines where FreeSWITCH can find the sound files, and if it can use any TTS engine
vars.xml
FreeSWITCH vars.xml contains some variables used throughout the system. This is the first place to start when configuring a new installation.
Notable variables defined in vars.xml include:
- default_password - YOU SHOULD CHANGE THIS default_password value if you don't want to be subject to any toll fraud in the future

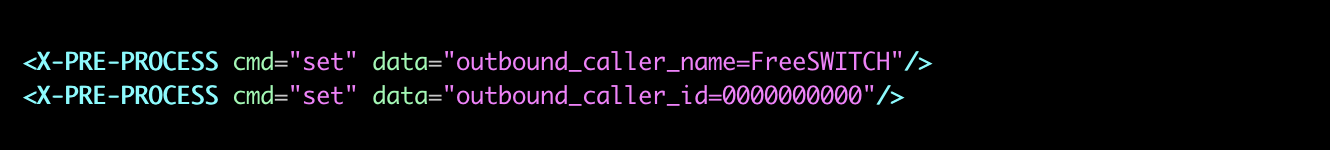
- outbound_caller_name - Name shown in phones when you make outbound calls.
- outbound_caller_numbe - Number shown in phones when you make outbound calls.
- domain - IP address or DNS name that entries in the user directory register. This is typically FreeSWITCH itself.

- external_rtp_ip and external_sip_ip - Public IP addresses of this FreeSWITCH system. Safest to use an IP address rather than DNS, in case a device can't resolve the domain.


Notice: Standard XML comments have no effect on Pre-Process commands. If you want to comment out a Pre-Process Command you can replace X-PRE-PROCESS with X-NO-PRE-PROCESS.