2. Router Configuration & Best Practices - OmarFloresE/HomeNetSecUpgrade GitHub Wiki
Accessing Router Admin Panel
Once everything in your network is connected and operational, a crucial next step is to access and familiarize yourself with your Router Admin Panel. Far too often, people set up their home networks, access the internet, and then neglect the Admin Panel. However, this panel is akin to the control center of your home network; it’s where you can manage settings, enhance security, and optimize performance.
Why The Admin Panel Matters:
- Control: The Admin Panel allows you to control and customize network settings according to your needs.
- Security: It is the primary place to strengthen your network's security by changing default passwords, updating firmware, and adjusting firewall settings.
- Network Management: From monitoring connected devices to setting up guest networks, the Admin Panel is essential for efficient network management.
How to Access the Router Admin Panel:
Find Your Router's IP Address:
This is typically printed on the router itself, in the manual, or on the box. Common addresses you can input to your browser are 192.168.0.1, 192.168.1.1, or 10.0.0.1.
You can also open up your command prompt, type in "ipconfig" and copy the address from your default gateway into the browser.

Enter the IP Address in a Web Browser:
Open your preferred web browser and type the router's IP address into the address bar.

Login Using Default Credentials:
If you haven't changed them yet, use the default username and password. These are often found in the router's manual or online. Sometimes by default the username is admin and the password is admin until you change it.

Changing Default Values
Now that you're in your router's admin panel, you'll find a wide array of options and settings at your disposal. While it might seem overwhelming at first, there are a few key default values that you should prioritize changing to enhance the security of your home network.
Key Default Values to Change:
Admin Username and Password:
This is the first line of defense for accessing your router's settings. Change both the username and password from their defaults to something unique and strong. A strong password should include a mix of letters (both uppercase and lowercase), numbers, and special characters.

Wi-Fi Network Name (SSID) and Password:
Changing your network's name (SSID) can help disguise its make or model, making it less obvious for potential intruders to exploit known vulnerabilities. Set a strong, unique password for your Wi-Fi network, different from your router's admin password. Consider using a passphrase rather than a standard password for added security.

Additional Information:
- Dual Bands 2.4/5ghz signals: We'll go into more detail for this in the next section!
- WiFi Encryption: Make sure to enable the latest WiFi encryption standard, if WPA3 is not available WPA2-PSK[AES] will suffice!
- SSID Broadcast: By default, routers broadcast the network's name (SSID) so that it's visible to devices. While convenient, this can also be a security risk. For an added layer of security, consider disabling SSID broadcast. This makes your network invisible to casual scanning, although it's worth noting that it won't deter determined intruders.
Firmware Updates:
Always check for the latest firmware updates and install them. These updates often contain vital security improvements and bug fixes.

Dual Band Setup/Purpose
Modern routers often come with dual-band functionality, offering two separate Wi-Fi networks — the 2.4 GHz band and the 5 GHz band. Understanding and correctly setting up these bands can significantly enhance your home network's performance and reliability. Understanding the Bands:
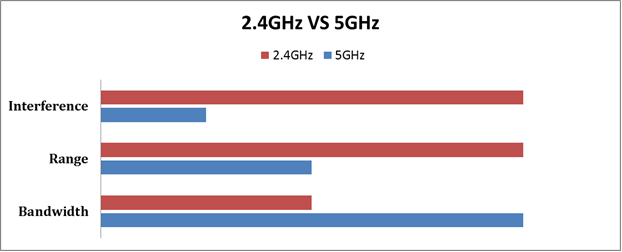
2.4 GHz Band:
- Range: Better range and can penetrate walls and solid objects more effectively.
- Speed: Generally slower than 5 GHz due to more interference (as many devices, like microwaves and Bluetooth devices, use this band).
- Best For: Devices that are far from the router or do not require high bandwidth, such as smart home devices.
5 GHz Band:
- Range: Shorter range but less likely to be obstructed by interference from other devices.
- Speed: Offers higher speeds, which is ideal for activities like streaming high-definition movies or online gaming with your friends!
- Best For: Devices that are closer to the router and require more bandwidth like your home desktop, or game console.
Optimizing Dual Band Usage:
- Device Allocation: Connect devices that require more bandwidth or are closer to the router to the 5 GHz band, while connecting others to the 2.4 GHz band such as your IoT devices (speakers, automated plugins, cast devices, and security cameras) that might be farther away from your router.
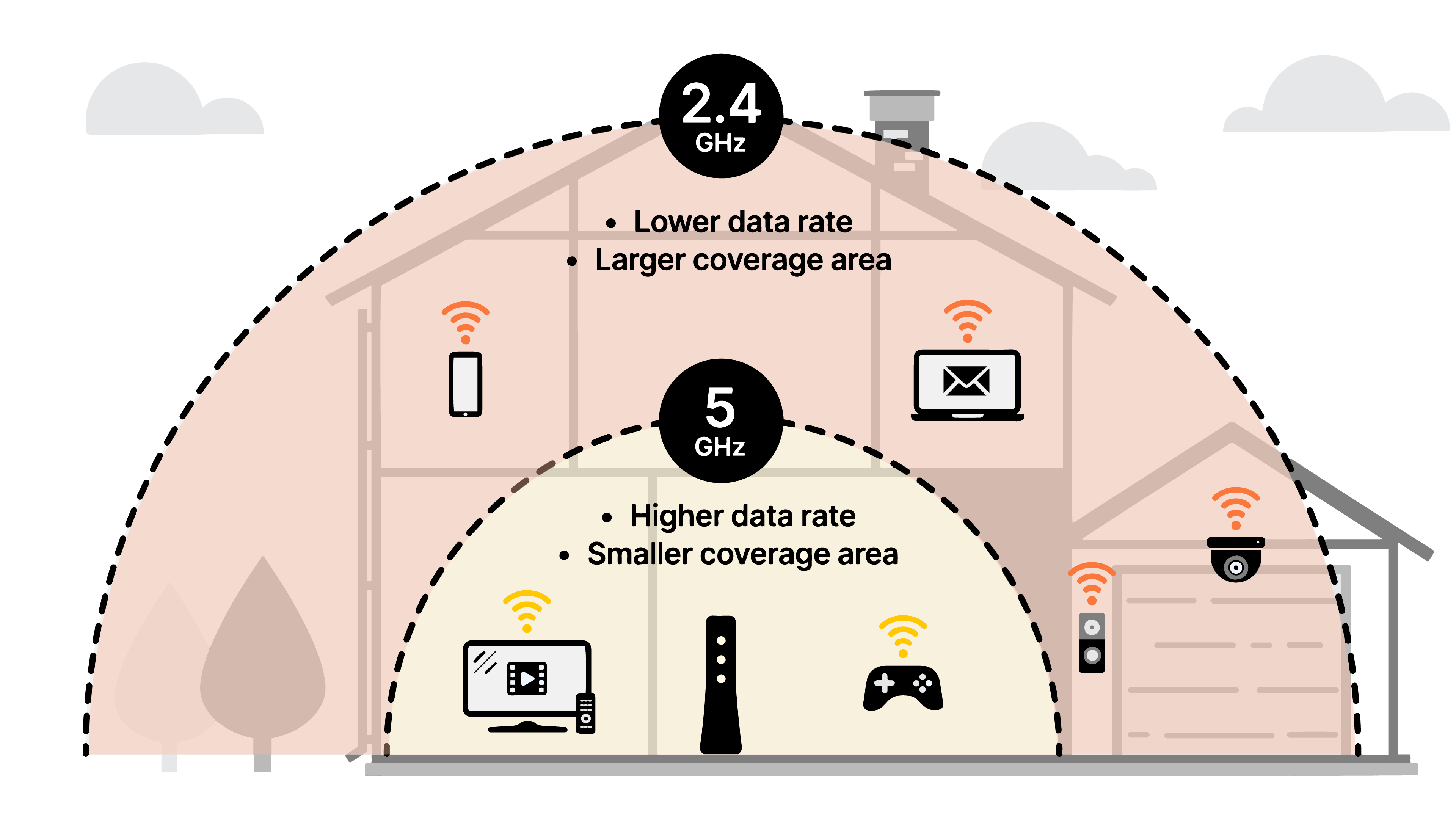
Remember, the dual-band setup allows for more flexibility and optimization in your home network. By understanding and configuring each band according to your needs, you can significantly improve your overall network experience.
Guest Networks
A guest network is a separate access point on your router that allows visitors to connect to the internet without granting them access to the primary network where your personal devices are connected. This feature is pivotal for both security and privacy.

Why Set Up a Guest Network?
- Security: It isolates your main devices from guest devices, reducing the risk of unauthorized access to your sensitive data. (Make sure to still use a strong password!)
- Convenience: Guests can easily connect to the internet without you having to share the primary network's password.
- Control: You can set limitations on bandwidth or restrict access to certain websites on the guest network, which is great for setting forth parental/user limitations.
Best Practices:
- Limitations and Restrictions: Consider whether you want to implement parental controls or block access to certain types of content on the guest network.
- Regularly Update Password: Change the guest network's password periodically for enhanced security.
- Monitor Usage: Keep an eye on the devices connected to the guest network and how much bandwidth they're using.

Setting up a guest network is an excellent way to keep your main network secure while still offering internet access to visitors. It's a feature that's often overlooked but can significantly enhance the overall security of your home network.
Disabling Features (Optional)
Routers come with a variety of features, some of which can create security vulnerabilities if not managed properly. Disabling certain features can enhance the security of your home network. Inside of your Router Admin Panel you might find the following options:
Identifying Features to Disable:
-
Universal Plug and Play (UPnP): UPnP makes it easier for devices to connect and communicate on the network but can also expose your network to external threats.
-
Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS): While WPS is designed to simplify the process of connecting devices to your Wi-Fi, it can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access.
-
Remote Management: This feature allows you to access your router’s settings remotely, but it can also provide a potential entry point for attackers.
Balance Between Security and Convenience
Disabling these features might reduce convenience in some cases. Weigh the security benefits against the ease of use!
Firewall Settings
The firewall in your router acts as a border guard, monitoring and controlling the incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. Properly configuring your router's firewall is key to protecting your home network from various external threats. Always make sure that your Firewall is activated. Some routers give you the option to enable/disable your router firewall.
Importance of Firewall Configuration:
- Security Layer: A firewall adds an essential layer of security that helps to block unauthorized access and potentially harmful traffic.
- Intrusion Prevention: It helps to prevent intruders from accessing your network and personal devices.
- Traffic Management: The firewall can also manage and monitor the flow of data to and from your network.
Steps to Configure Firewall Settings:
- Access Router Settings: Log into your router's admin panel.
- Locate Firewall Settings: Find the section dedicated to firewall settings. This is often under 'Security' or 'Advanced Settings'.
- Configure Basic Firewall Settings:
- Enable Firewall: Ensure that the firewall is turned on.
- Set Security Levels: Many routers offer different levels of security (e.g., low, medium, high). Choose the level that best suits your needs.
- Configure Rules: Depending on your router, you may be able to set specific rules for what traffic is allowed or blocked.
Advanced Firewall Features:
- Port Forwarding/Triggering: Use these features to control access to specific services and devices in your network.
- DMZ (Demilitarized Zone): This feature allows you to isolate a particular device from the rest of your network, typically used for gaming consoles or servers.
- Custom Rules: For advanced users, creating custom rules can provide more granular control over network traffic.
Best Practices:
- Regular Updates: Keep your router's firmware updated, as updates often include enhancements to firewall capabilities.
- Review Rules Periodically: Regularly review and update your firewall settings to ensure they continue to meet your security needs.
- Documentation: Keep a record of any changes you make, including the reasons and outcomes, for future reference.
Caution:
- Avoid Overblocking: Be cautious not to set the firewall rules too restrictively, as this can block legitimate traffic and disrupt normal network usage.
- Understand Implications: Make sure you're certain of what type of traffic you're altering and what results may come from that!
Properly setting up your router's firewall is a pivotal step in safeguarding your home network. While default settings provide basic protection, fine-tuning your firewall settings can significantly enhance your network's security posture!