Syslog reference - Oliver-Mustoe/Oliver-Mustoe-Tech-Journal GitHub Wiki
Syslog reference
This page contains configurations/tips on working with the rsyslog.
Table of contents
- Configuring syslog service on logging server
- Configuring syslog service on logging client
- Custom log organization
Configuring syslog service on logging server
First, on the logging server, install "rsyslog" from your repository. Then, enable port 514 tcp/udp. For example on a Redhat server, the following commands would be used to install, setup firewall, and check the firewall:
sudo dnf install rsyslog
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=514/tcp
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=514/udp
firewall-cmd --reload
firewall-cmd --list-all
Then the following lines must be uncommented in /etc/rsyslog.conf:
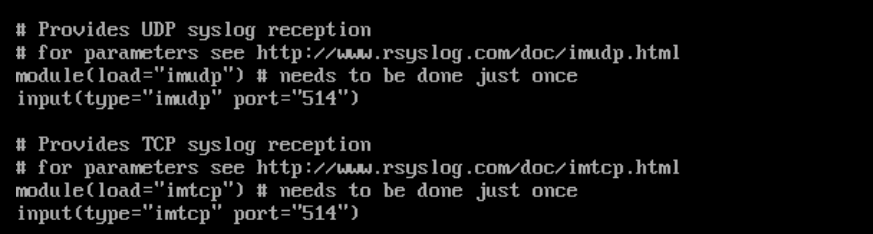
Afterwards, restart the rsyslog service with the following command:
sudo systemctl restart rsyslog
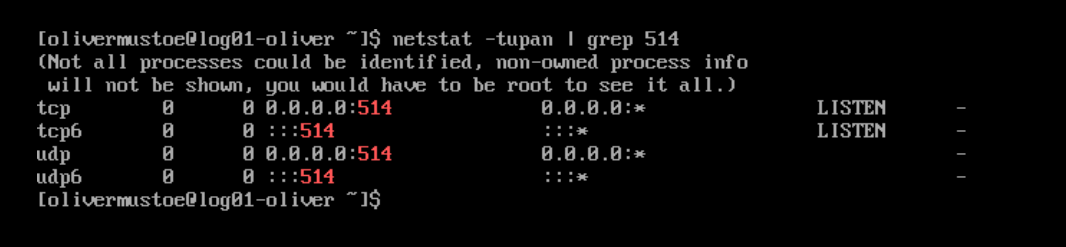
And then check if rsyslog is listening on the appropriate ports with the following command (image is desired output from a test server):
netstat -tupan | grep 514
Configuring syslog service on logging client
First, on the logging client, install rsyslog. For example, on a Redhat based client the following would be run:
sudo dnf install rsyslog
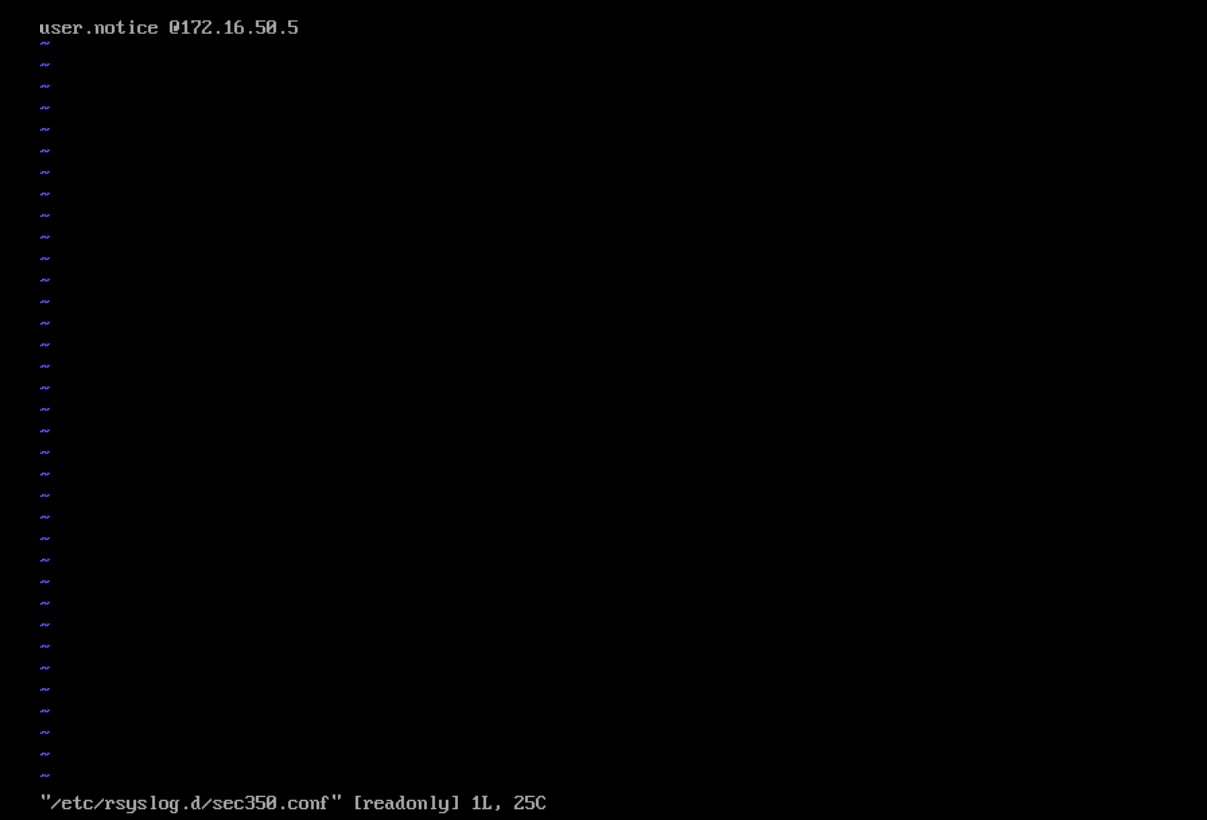
Then add the following line to a .conf file in /etc/rsyslog.d. For example, this tutorial will use a file called "sec350.conf". Replace {LOG_server_IP} with the IP of the logging server.
user.notice @{LOG_server_IP}
IN THE ABOVE LINE:
- user=syslog facility
- notice=syslog priority
- @=UDP (@@=TCP)
Example configuration (file should be edited with proper permissions!):

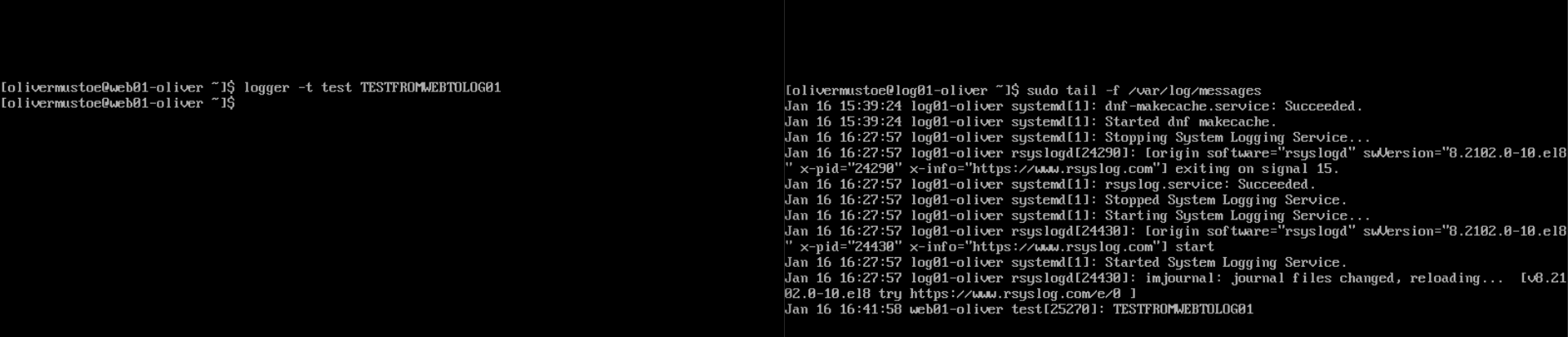
To test Syslog, run the command logger -t test SOMETHING from your logging client. This should appear in the logging server's /var/log/messages file. Below is a test showing the logging server "log01-oliver" receiving the test "TESTFROMWEB01TOLOG01" from "web01-oliver", a logging client:
Custom log organization
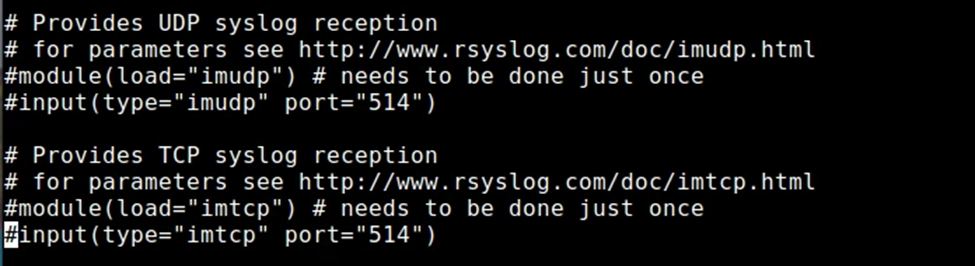
First, on the logging server, comment out the following lines inside "/etc/rsyslog.conf":
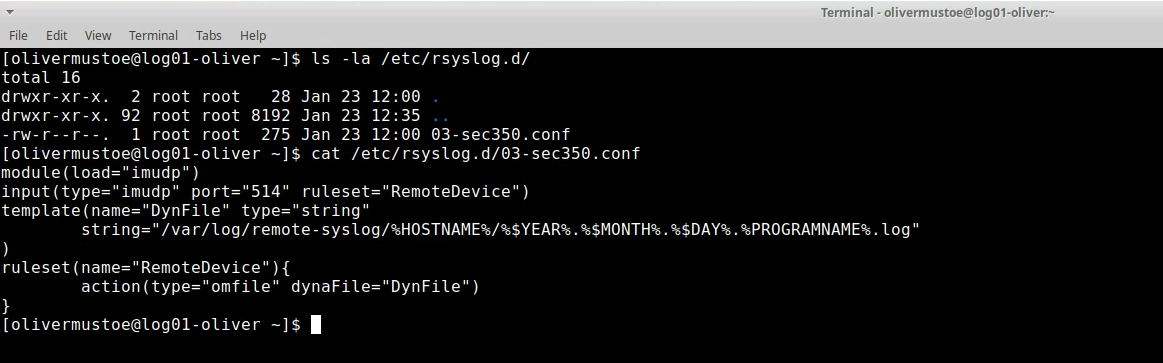
Then create a .conf file, such as “03-sec350.conf”, in /etc/rsyslog.d AS ROOT. Give it the following instructor provided content:
module(load="imudp")
input(type="imudp" port="514" ruleset="RemoteDevice")
template(name="DynFile" type="string"
string="/var/log/remote-syslog/%HOSTNAME%/%$YEAR%.%$MONTH%.%$DAY%.%PROGRAMNAME%.log"
)
ruleset(name="RemoteDevice"){
action(type="omfile" dynaFile="DynFile")
}
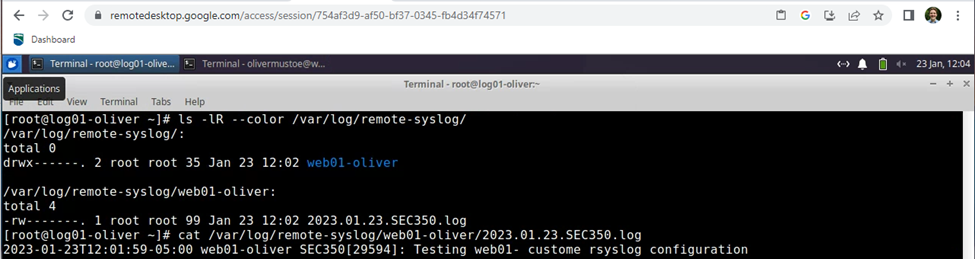
Then, restart syslog, and from the logging client, execute the test seen in the screenshot below:

Which will result in the message logged (shown in second command output) in a folder for the clients hostname (shown in first command output):
Sources:
- https://firewalld.org/documentation/howto/open-a-port-or-service.html
- https://firewalld.org/documentation/howto/reload-firewalld.html
- https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/7/html/security_guide/sec-viewing_current_status_and_settings_of_firewalld
Cant find something, check in the backup Syslog reference