Dedicated page for Packet Tracer - Oliver-Mustoe/Oliver-Mustoe-Tech-Journal GitHub Wiki
This page includes useful references for packet tracer:
Everything in {} should be replace by what it is asking for.
| Command: | Explanation: | Example: |
|---|---|---|
enable |
Go into privilege mode on router (Advanced user, should change router name from "router>" to "router#") | enable |
conf t |
Go to global config for the router (Configure router as a whole, should change router name from "router#" to "router(config)#") | conf t |
hostname {HOSTNAME} |
Setting hostname | hostname Oliver-DatacenterRouter |
interface {INTERFACE_NAME (usually gig or fast)} {NUMBER/NUMBER (usually 0/something)} |
Define a port to configure | interface GigabitEthernet 0/2 |
interface range {INTERFACE_NAME (usually gig or fast)} {NUMBER/NUMBER-NUMBER (usually 0/something)} |
Define a range of ports to configure at once | interface range FastEthernet 0/4-12 |
interface vlan {VLAN_NUMBER} |
Define VLAN to configure | interface vlan 100 |
no shutdown |
Turn the interface on | no shutdown |
ip address {IP_ADDRESS} {SUBNET_MASK} |
Set the IP of interface being configured | ip address 10.12.1.2 255.255.255.248 |
router ospf {INSTANCE_NUMBER (usually 1)} |
Get into the OSPF config on the router | router ospf 1 |
network {CONNECTED_NETWORK} {WILDCARD_SUBNET_MASK_OF_CONNECTED_NETWORK (Sub 255 from subnet mask)} area {AREA_NUMBER (often 0 in a flat network)} |
Advertise what networks are directly connected to the router being configured, in a certain area. | network 10.12.1.32 0.0.0.3 area 0 |
switchport access/trunk vlan {NUMBER} |
Define the VLAN for the defined ports | switchport access vlan 100 |
vlan {NUMBER} |
Create a vlan | vlan 10 |
ip routing |
Turn on routing on multi-layer switch | ip routing |
ip nate inside/outside |
Set the port as IP NAT inside or outside | ip nat inside |
ip nat inside source static {IP_OF_DEVICE} {NEW_PUBLIC_IP_OF_DEVICE} |
Create static rule | ip nat inside source static 10.0.0.2 50.0.0.1 |
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 {IP} |
Set the default route | ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 30.0.0.2 |
ip helper-address {IP_OF_DHCP} |
Setting the helper address to the DHCP server (like a relay agent) | ip helper-address 10.7.11.1 |
ip access-list {TYPE} {NAME} |
Create an access list with a certain type, standard or extended, and name | ip access-list standard STND-1 |
| For standard lists ONLY: | # | # |
permit/deny {IP_ADDRESS} {WILDCARD_MASK} |
Permit or deny a certain IP with a subnet mask (reversed for wildcard mask, sub 255 from each octet) | deny 192.168.11.0 0.0.0.255 |
permit any |
For deny lists, make sure that a hidden deny is nullified | permit any |
| # | # | # |
| For extended lists ONLY: | # | # |
permit/deny {protocol} {SOURCE_IP} {WILDCARD_MASK} {SOURCE_IP} {WILDCARD_MASK} eq {PORT} |
Permit or deny a certain source IP (can be "any") with subnet mask, the destination IP (can be "any") with subnet mask and a port | permit tcp any 192.168.20.200 0.0.0.0 eq 25 |
permit ip any any |
For deny lists, make sure that a hidden deny is nullified | permit ip any any |
| # | # | # |
ip access-group {NAME} in/out |
Apply the access-list to a interface either being inbound (is the router receiving the packets through this interface?) or outbound (is the router sending the packets through this interface?) | ip access-group MAIL-WEB out |
ip nat pool {NAME} {BEGINNING_OF_IP_RANGE} {END_OF_IP_RANGE} netmask {WILDCARD_MASK} |
Create Address pool for Public Ip addresses that clients can use | ip nat pool test 30.0.0.120 30.0.0.120 netmask 255.0.0.0 |
access-list {NUMBER} permit {INTERNAL_IP} {WILDCARD_MASK} |
Create an access-list that defines with internal IP's can use a certain Public IP pool | access-list 1 permit 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.255 |
ip nat inside source list {NUMBER (from made access list)} pool {NAME (name of pool)} overload |
Assign pool and access rule to interface with NAT statement, overload for large client usage |
ip nat inside source list 1 pool test overload |
show ip nat translations |
See the TCP ports used to track connections in the NAT Table | show ip nat translations |
I could have also used the following commands to configure the VLANs without GUI. For example VLAN 110:
enable
conf t
vlan 110
name Student
(config)interface range FastEthernet 0/x-y (let's you configure multiple ports at one time)
(config-if-range)switchport access vlan x (defines the vlan for all ports in the range)
For example of above, I could use the following commands, in order, to change the VLAN 100 range:
enable
conf t
interface range FastEthernet 0/4-12
switchport access vlan 100
Example breakdown (from top to bottom):
- Go into privilege mode on router (Advanced user, should change router name from "router>" to "router#")
- Go to global config for the router (Configure router as a whole, should change router name from "router#" to "router(config)#")
- Define a range of ports to configure at once (Should change router name)
- Define the VLAN for the range of ports
I got a multi-layer switch to act as a router. To do this, I used the following commands (THE LAST TWO MUST BE REPEATED PER VLAN):
enable
conf t
ip routing
interface vlan 100
ip address 10.25.100.1 255.255.255.0
Example breakdown (from top to bottom):
- Go into privilege mode on router (Advanced user, should change router name from "router>" to "router#")
- Go to global config for the router (Configure router as a whole, should change router name from "router#" to "router(config)#")
- I turn on routing
- I go into the VLAN interface (Should add "(config-if)")
- Set the IP and netmask for the VLAN (100) on the switch
Then I set the following configurations for the following pools: NOTE: serverPool is the default pool, also non-removable, and will be the pool used for VLAN 1 Management
Notes for DHCP configuration:
- Should be boxes to fill in (with labels indicating where IPs and stuff should go), should be fairly self explanatory
- Make sure to change the name, and click "Add" instead of "Save" for new pools
- DNS should be 0.0.0.0
- Starting IP is the first IP, recommended to start at 20, 50, or 100 in the last octet
- ENSURE SUBNET MASK FOR VLAN IS CORRECT
- Make sure to set default gateway for router address for THAT VLAN
- Pay attention to maximum users value!
To test my DHCP server, I added a workstation directly to EAST-Core-Switch on a open interface (configured for VLAN 1!) and using the command ipconfig /renew, from the command line, I was able to recieve a IP in the "serverPool" pool.
Then on the East-Core-Switch, so that my DHCP requests could cross a router, I told the router to forward DHCP broadcasts from user VLANs with the commmands (example for VLAN 100):
enable
conf t
interface vlan 100
ip helper-address 10.7.11.1
Command breakdown:
1 & 2. Entering global configuration
3. Selecting the VLAN needed
4. Setting the helper address to the DHCP server (like a relay agent)
Overall Lab 4-2 is good for looking at any lab before it.
On the router, I used the following command to check ip-helper address (PER VLAN):
sh ip int vlan 100
Notes from alternative 4.1
- Turn on router ports (may not be by default)
- How to change password (config mode)
-
- 1.
enable2.configure terminal3.enable secret <PASSWORD>4.end
- 1.
- Change banner (config mode)
-
banner motd $
-
-
- The “$” is how the command will know the motd is done
-
- The enable secret command uses the MD5 hashing function to encrypt the password, which is a very secure method of protection.
- "
exec-timeout [minutes] [seconds]” for timeout - Configure console line with "
line con <BEGINNING LINE> <LAST LINE>" - Configure console line with "
line vty <BEGINNING LINE> <LAST LINE>" - Password command is “
password <PASSWORD>”, follow that with “login” to enable login - Synchronous logging command is “
logging synchronous” - Set history with “
history size <AMOUNT>” - “
service password-encryption” command for global password configuration
Copy pastes from 6-1 to 6-3:
Lab 6-1
In this lab we setup a web server (10.0.0.2) to be accessible as the public IP (50.0.0.1) via NAT on Router 1.
R1 - COPY BLANK LINE
configure terminal
hostname R1
interface fastethernet 0/0
ip address 10.0.0.1 255.0.0.0
no shutdown
exit
interface serial 0/0/0
ip address 20.0.0.2 255.0.0.0
no shutdown
exit
ip route 30.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 20.0.0.1
interface fastEthernet 0/0
ip nat inside
exit
interface serial 0/0/0
ip nat outside
exit
ip nat inside source static 10.0.0.2 50.0.0.1
R0 - COPY BLANK LINE
configure terminal
hostname R0
interface fastethernet 0/0
ip address 30.0.0.1 255.0.0.0
no shutdown
exit
interface serial 0/0/0
ip address 20.0.0.1 255.0.0.0
clock rate 64000
bandwidth 64
no shutdown
exit
ip route 50.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 20.0.0.2
Finished Screenshot:
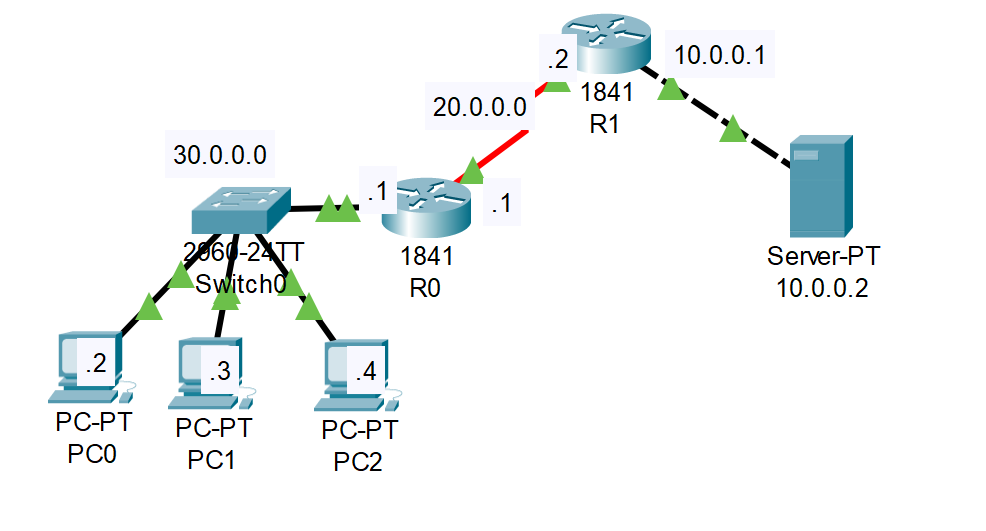
Lab 6-2
In this lab we used PAT to assign PC's on the 192.168.0.0/24 network to use the Public IP of 30.0.0.120.
R1 - COPY BLANK LINE
ip nat pool test 30.0.0.120 30.0.0.120 netmask 255.0.0.0
access-list 1 permit 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.255
ip nat inside source list 1 pool test overload
Finished screenshot:
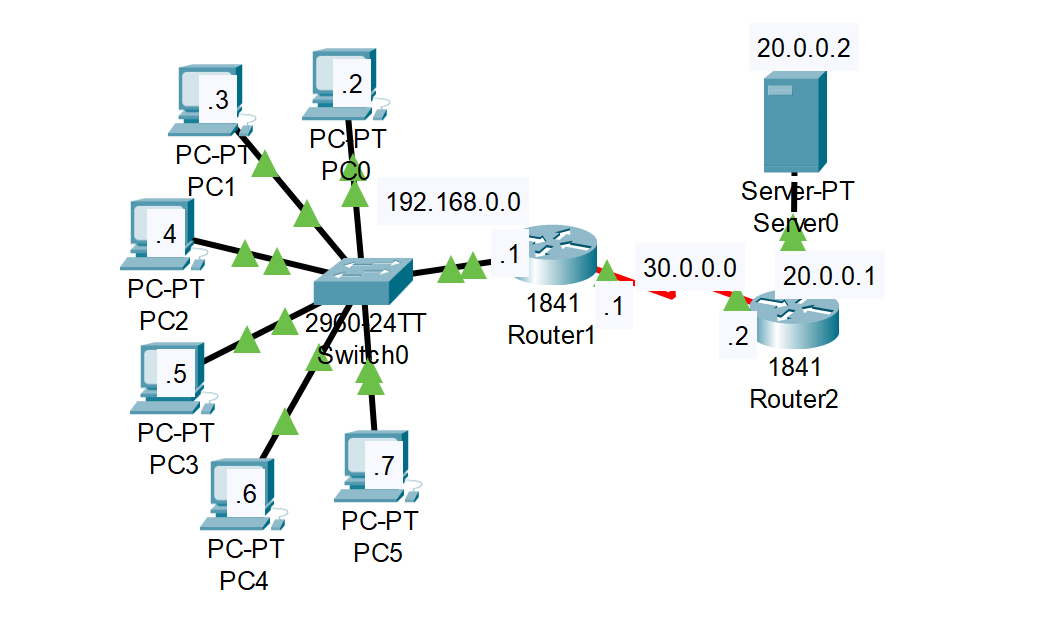
Example:
- https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/smb/switches/cisco-350-series-managed-switches/smb5557-configure-the-internet-protocol-ip-address-settings-on-a-swi.html
- https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/nfvis/switch_command/b-nfvis-switch-command-reference/ip_addressing_commands.pdf
- https://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=27650&seqNum=4
- https://community.cisco.com/t5/switching/2811-static-routing-setup/td-p/3080730
- https://www.cisco.com/E-Learning/bulk/public/tac/cim/cib/using_cisco_ios_software/cmdrefs/banner_motd.htm
- https://study-ccna.com/configuring-cisco-banner-motd-login-exec/
- https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/lan/catalyst3850/software/release/3se/security/configuration_guide/b_sec_3se_3850_cg/b_sec_3se_3850_cg_chapter_011.pdf
- https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/lan/catalyst2960cx_3650cx/software/release/15-2_7_e/configuration_guide/b_1527e_consolidated_3560cx_2960cx_cg/m_sec_passpr_cg.pdf
- https://www.netadmintools.com/how-to-configure-cisco-switches/#wbounce-modal
- https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/lan/cisco_ie3010/software/release/12-2_53_ez/configuration/guide/ie3010scg/swcli.html#wp1021783
- https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/smb/switches/cisco-250-series-smart-switches/smb5816-configure-idle-session-timeout-settings-on-a-switch-through.html
- https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/lan/catalyst3560/software/release/12-2_52_se/configuration/guide/3560scg/swlog.html?dtid=osscdc000283
- https://study-ccna.com/exec-timeout-command/#:~:text=By%20default%2C%20an%20IOS%20device,MINUTES%20SECONDS%20line%20mode%20command.&text=To%20disable%20the%20timeout%2C%20use,recommended%20in%20production%20environments!)