API Versioning - NeoSOFT-Technologies/rest-dot-net-core GitHub Wiki
Description
While working on an existing application or creating a new one, we may create multiple APIs that may be consumed by many clients. At some point in time we eventually run into the point where a breaking change might be inevitable. Due to this, we may need to provide more functionality in the existing APIs. However, existing Web API can be consumed by many clients so instead of replacing the existing API we would provide a new version of our API so that consumers of the former model would be still served.
There are several ways to version a RESTful API. We are going to use URL based Versioning. In this type of versioning, we can define versions in a URL so that it is more readable.
NuGet Packages
- Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.Versioning
- Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.Versioning.ApiExplorer
Code Snippet
We need to write extension service class code for AddSwaggerVersionedApiExplorer as below,
public static void AddSwaggerVersionedApiExplorer(this IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddApiVersioning(options =>
{
options.DefaultApiVersion = new ApiVersion(1, 0);
options.AssumeDefaultVersionWhenUnspecified = true;
options.ReportApiVersions = true;
});
services.AddVersionedApiExplorer(options =>
{
options.GroupNameFormat = "'v'VVV";
options.SubstituteApiVersionInUrl = true;
});
}
Setting up the versioning is in Startup.cs file.
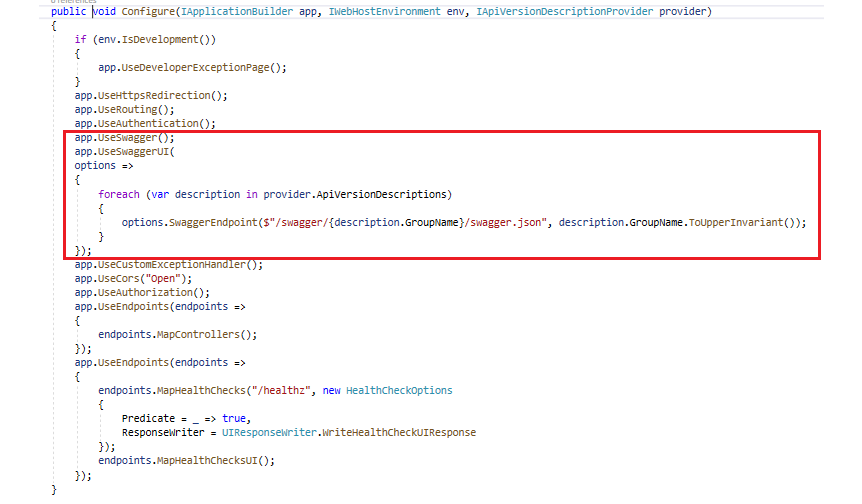
app.UseSwagger();
app.UseSwaggerUI(
options =>
{
foreach (var description in provider.ApiVersionDescriptions)
{
options.SwaggerEndpoint($"/swagger/{description.GroupName}/swagger.json", description.GroupName.ToUpperInvariant());
}
});
The next changes ensure that we have swagger doc pages created. For that let’s create a helper class that’ll get used later on.
public void Configure(SwaggerGenOptions options)
{
foreach (var description in _provider.ApiVersionDescriptions)
{
options.SwaggerDoc(description.GroupName, CreateInfoForApiVersion(description));
}
}
The next task is to tell Swagger how to differentiate one version of a controller apart from another. For that we must create a convention.
With a convention we inform Swagger about our architecture. This way we can control how Swagger generates the Swagger document, and therefore, the UI.
Create the following helper class:
public class SwaggerDefaultValues : IOperationFilter
{
public void Apply(OpenApiOperation operation, OperationFilterContext context)
{
var apiDescription = context.ApiDescription;
operation.Deprecated |= apiDescription.IsDeprecated();
if (operation.Parameters == null)
return;
foreach (var parameter in operation.Parameters)
{
var description = apiDescription.ParameterDescriptions.First(p => p.Name == parameter.Name);
if (parameter.Description == null)
{
parameter.Description = description.ModelMetadata?.Description;
}
if (parameter.Schema.Default == null && description.DefaultValue != null)
{
parameter.Schema.Default = new OpenApiString(description.DefaultValue.ToString());
}
parameter.Required |= description.IsRequired;
}
}
}
Then we need to tell Swashbuckle about it, navigate to startup.cs file and make changes as shown below,
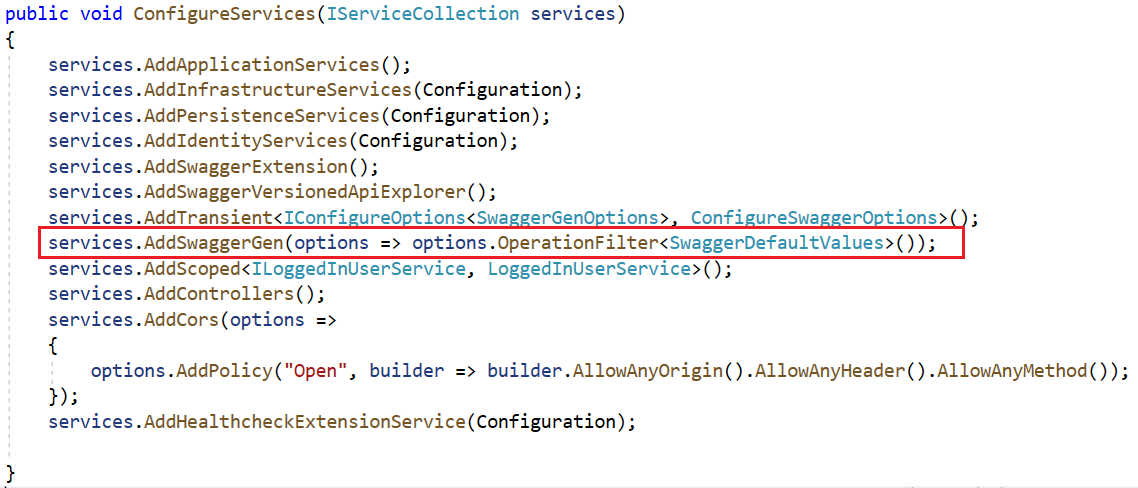
services.AddSwaggerGen(options => options.OperationFilter<SwaggerDefaultValues>());
To use URL based Versioning, add the ApiVersion attribute to the controller / action method. Along with this, we need to modify the Route attribute as well, so that the ASP.NET Core can route the requests.
namespace Api.Controllers
{
[ApiVersion("1")]
[Route("api/v{version:apiVersion}/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class CategoryController : ControllerBase
{
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult Get()
{
return new OkObjectResult("Categories from v1 controller");
}
}
}
Demo
Demo video to get the clear result view of above implemented module.
